
- Introduction
- Overview of CDNs
- The Need for CDNs
- How CDNs Operate
- Selecting the Best CDN
- Benefits of Using CDN
- CDNs in Various Industries
- CDN Use Cases
- Future of CDNs
- How CDNs Improve User Experience
- CDN Security Features
- Challenges with CDNs
- Conclusion
Introduction
Content delivery is a critical component of the digital world. Speed and reliability are crucial whether you’re downloading an application, viewing a webpage, or streaming a high-definition movie. In this context, a Content Delivery Network (CDN) ensures a smooth experience. A CDN is a system of geographically distributed servers that work together to deliver content such as web pages, images, videos, and other media files efficiently to end users. In Cloud Computing Course guide, we will explore the concept of CDNs, their importance, how they function, and how they impact various industries. We will also discuss how to select the best CDN for your needs and the numerous benefits they provide to businesses and end users.
Overview of CDNs
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a network of servers distributed across various locations to deliver content to users in the most efficient way. The goal is to minimize the time it takes for data to travel over the internet by serving content from the server nearest to the user. This reduces latency and improves load times, leading to a better user experience.
For example, when you visit a website hosted in New York while you are in Tokyo, a CDN can detect your location and serve content from a nearby server in Singapore, reducing the distance the data needs to travel and accelerating the response time.
CDNs provide more than just faster load times; they also ensure the scalability and reliability of content delivery, especially when handling global traffic and large-scale applications.The Need for CDNs
In today’s fast-paced, performance-driven digital world, CDNs are more essential than ever. The global demand for high-performance apps, smooth video streaming, and fast-loading websites requires systems capable of handling these demands. Without a CDN, users may experience buffering, outages, or delays, especially when accessing content from geographically distant servers. Here are some key reasons why CDNs are necessary for Top Cloud Databases:
- Decreased Latency: By caching content on servers closer to end users, CDNs minimize the time it takes for data to travel, resulting in faster load times.
- Better Performance: Even during periods of high traffic, CDNs ensure faster content delivery, preventing slowdowns.
- Global Reach: CDNs enable international businesses to deliver content to users worldwide without compromising speed or performance.
- Redundancy and Reliability: CDNs ensure high availability by routing traffic through alternate servers in the event of a failure.
- Scalability: As traffic volumes increase, CDNs can easily scale to meet demand, ensuring the consistent performance of websites and applications.
- Content Caching: Static content—such as images, videos, and files like CSS or JavaScript—is cached on CDN servers located around the world. These cached versions of content are stored closer to the users, ensuring fast access.
- Request Routing: When a user requests content, the CDN identifies the user’s location and routes the request to the server nearest to Microsoft Azure Portal. This reduces the time it takes for data to travel, providing quicker delivery.
- Delivery: The CDN serves the requested content from the local edge server. If the content is unavailable on that server, it is retrieved from the origin server or another edge server.
- Dynamic Content Handling: CDNs are also capable of caching dynamic content, although this is typically refreshed more frequently to ensure users receive the most up-to-date information.
- Faster Load Times: By caching content closer to the user, CDNs significantly reduce the time it takes for websites and apps to load.
- Improved Reliability and Availability: With multiple servers in different locations, CDNs ensure content remains available even if one server goes down, reducing the risk of downtime.
- Cost Savings: CDNs help lower hosting and bandwidth costs by reducing the load on your origin server, which also prevents costly bandwidth overages.
- Scalability: As traffic increases, CDNs can scale to meet demand, ensuring that your site or Applications of Cloud Computing, regardless of user load.
- Better SEO: Search engines favor websites with faster load times. By using a CDN, your website’s performance can improve, resulting in better search engine rankings.
- Enhanced Security: CDNs offer features such as web application firewalls (WAF), DDoS protection, and data encryption to safeguard your content and user data.
- Video Streaming: Services like YouTube and Netflix use CDNs to stream video content globally, ensuring smooth playback without buffering.
- E-Commerce: Online retailers like AWS Workspaces use CDNs to deliver product images and data quickly, even during high-traffic events like Black Friday.
- Software Updates: Software companies use CDNs to distribute updates and patches to users around the world without delays.
- Gaming: Game developers such as Epic Games utilize CDNs to distribute downloadable content (DLC) and patches quickly to users in different regions.
- DDoS Protection: Many CDNs offer protection against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks by distributing traffic across multiple servers and identifying suspicious activity.
- SSL Encryption: SSL/TLS encryption ensures that data transmitted between the user and the server is secure and cannot be intercepted by malicious actors.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): A WAF can block malicious requests and prevent common Amazon Web Services Workmail, such as SQL injections or cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Bot Mitigation: CDNs can help detect and block bots that attempt to scrape content or perform automated attacks on your site.
- Cost Management: As traffic grows, the costs of using a CDN can rise significantly. Careful monitoring of usage is needed to avoid unexpected charges.
- Cache Invalidation: Sometimes, outdated content can remain in the cache for too long, causing users to receive outdated information. Effective cache management is essential to prevent this.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Integrating a CDN into legacy infrastructures or applications may require substantial effort, particularly when dynamic content is involved.
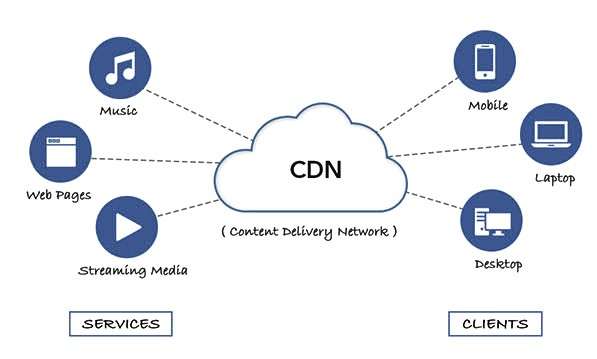
How CDNs Operate
The fundamental operation of a CDN revolves around the distribution of content across a network of strategically placed edge servers. These edge servers serve content to users based on their geographic proximity, ensuring fast delivery and minimizing latency. Here’s a closer look at how CDNs work:
Gain in-depth knowledge of Cloud Computing by joining this Cloud Computing Online Course now.
Selecting the Best CDN
Choosing the right CDN is critical to optimizing the performance of your website or application. Here are several factors to consider when selecting a CDN provider:
Ensure the CDN provider has servers strategically located across the globe, so users in various regions can access content quickly. Look for a provider with a strong track record of fast content delivery and low latency. Review performance benchmarks and user reviews. CDNs offer various security features, such as SSL encryption, DDoS protection, and secure token authentication. Choose a CDN with robust security to protect your data. The CDN should seamlessly integrate with your current infrastructure. Look for easy-to-use APIs, plugins, and CMS integrations. While CDNs excel at caching static content, Cloud Computing Course also important to choose a provider that supports dynamic content caching for applications that require real-time data. CDN pricing varies, with providers typically charging based on data usage, requests, or bandwidth. Compare different pricing structures to ensure you get the best value for your needs.
Benefits of Using CDN
Using a CDN offers numerous advantages for businesses, content providers, and end users. Here are the key benefits:
Start your journey in Cloud Computing by enrolling in this Cloud Computing Online Course .
CDNs in Various Industries
CDNs are employed across a wide range of industries to ensure optimal performance, security, and user experience. Here are a few key sectors that benefit from CDNs:
E-commerce websites rely on CDNs to deliver product images, videos, reviews, and real-time updates to customers worldwide. This reduces load times and enhances the shopping experience. Streaming services like Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify depend on CDNs to deliver buffer-free, high-definition video and audio content to users globally. CDNs help online gaming companies reduce latency and lag, ensuring a smooth and responsive gaming experience for players around the world. Online learning platforms use CDNs to efficiently distribute course materials, videos, and interactive content to students in various regions. CDNs are used by healthcare providers to securely deliver large medical files, telemedicine services, and patient data, ensuring fast, reliable, and secure transfers.
CDN Use Cases
CDNs are applied in various real-world scenarios to improve performance and scalability. Here are some common use cases:
Future of CDNs
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the role of CDNs is expected to grow. With advancements in edge computing and the increasing importance of real-time data processing, CDNs will continue to be essential in delivering high-performance, low-latency content across the globe. Additionally, the rise of 5G technology will further enhance the effectiveness of CDNs by enabling faster and more reliable content delivery.
As businesses expand their digital footprint, the demand for robust and scalable CDNs will only increase, making them a vital tool for ensuring a seamless online experience.
Aspiring to lead in Cloud Computing? Enroll in ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course and start your path to success!
How CDNs Improve User Experience
One of the primary reasons businesses rely on CDNs is their ability to enhance user experience. By reducing latency and ensuring fast content delivery, CDNs make websites and applications more responsive. Users can access content quickly, regardless of their geographic location. Furthermore, CDNs also help optimize content delivery for different devices, including smartphones and tablets, ensuring that users on all platforms enjoy a consistent experience.
CDN Security Features
Security is a major consideration when choosing a CDN. Modern CDNs come with various security features that help protect websites and applications. Some common CDN security features include:
Preparing for Cloud Computing interviews? Visit our blog for the best Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers!
Challenges with CDNs
While CDNs offer numerous advantages, they are not without challenges. Some of the key challenges include:
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have revolutionized how content is distributed and delivered to end users. By improving performance, scalability, security, and reliability, CDNs provide significant benefits to businesses and users alike. Whether you are a software provider, media platform, or e-commerce company, leveraging the power of a CDN can significantly enhance your Cloud Computing Course. As online traffic continues to grow, CDNs will remain a critical component for businesses looking to provide a smooth, fast, and secure user experience. By selecting the right CDN and optimizing content delivery, you can stay competitive in the fast-paced digital world and meet the needs of your global audience.





