- What is IaaS?
- Key Benefits of IaaS
- Core Components of IaaS
- Leading IaaS Providers (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Security Considerations in IaaS
- Challenges of IaaS Adoption
- The Future of IaaS
- Case Studies and Real-world Use of IaaS
- Conclusion
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. It allows organizations to scale IT infrastructure on demand without investing in physical hardware. IaaS offers flexibility, cost-efficiency, and high availability, making it essential for businesses of all sizes. Securing IaaS environments is crucial to prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, and service disruptions. This blog will explore IaaS security, its benefits, and the challenges of securing cloud infrastructure. We will also discuss best practices for IaaS security, including identity and access management (IAM), network security, data encryption, and compliance measures. Additionally, we will review cloud security tools and strategies that help organizations protect their cloud infrastructure from threats while ensuring operational efficiency. By implementing strong security practices, businesses can maximize the advantages of IaaS solutions while maintaining a secure and resilient cloud environment, as taught in the Cloud Computing Course.
What is IaaS?
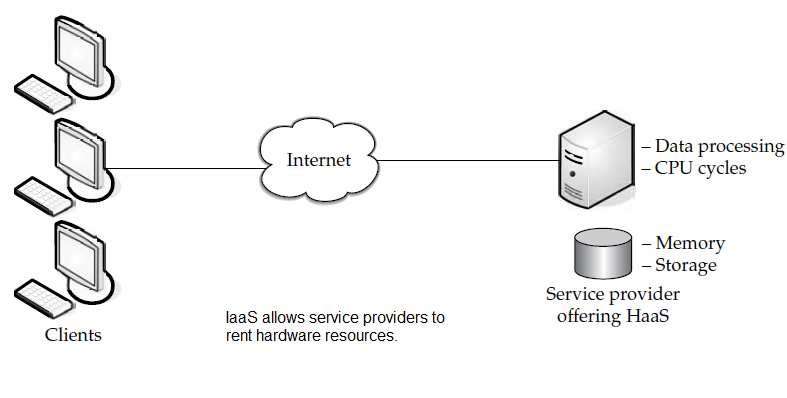
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides on-demand access to virtualized computing resources over the Internet. This model eliminates the need for organizations to invest in and maintain physical hardware, allowing them to rent essential infrastructure components such as virtual machines (VMs), storage, and networking. IaaS offers high scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency, making it an attractive option for businesses, developers, and enterprises looking to streamline their IT operations. By leveraging IaaS, organizations can allocate resources dynamically, ensuring optimized performance while reducing operational overhead. Additionally, IaaS enables businesses to deploy applications faster, enhance disaster recovery solutions, and improve overall IT agility. With built-in security features, automated management tools, and global accessibility, IaaS supports digital transformation efforts. By integrating IaaS with advanced technologies like AI, big data, and IoT, organizations can drive innovation and maintain a competitive edge.
To Explore Cloud Computing in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cloud Computing Online Course To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Key Benefits of IaaS
- Cost Savings: Eliminates capital expenses on physical hardware and reduces ongoing maintenance costs.
- Scalability: Dynamically adjusts computing resources to meet fluctuating workload demands.
- Flexibility: Supports a wide range of operating systems, development frameworks, and business applications, with the added benefit of seamless data transfer capabilities through AWS DataSync.
- Business Continuity: Ensures uptime with automated failover, backup solutions, and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Global Accessibility: Allows users to access cloud resources from any location, fostering remote collaboration.
- Security and Compliance: Offers built-in security controls, data encryption, and adherence to regulatory standards.
- Reduced Time to Market: Enables rapid provisioning of IT infrastructure, accelerating product and application deployment.
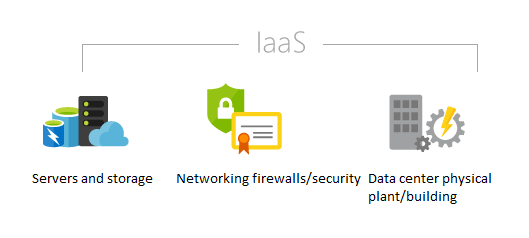
Core Components of IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides a range of essential cloud-based resources that enable businesses to build, scale, and manage their IT infrastructure efficiently. One of the core components of IaaS is compute resources, which include virtual machines (VMs), containers, and cloud-based CPU/GPU resources. These resources support various workloads, from web applications to machine learning models, allowing organizations to scale processing power as needed. Storage services play a crucial role in handling data across different performance levels. IaaS providers offer object storage, block storage, and file storage solutions, catering to various data management needs. Object storage is ideal for large-scale unstructured data, while block storage enhances database performance, and file storage simplifies file-sharing operations. To ensure secure and reliable connectivity, IaaS platforms offer advanced networking services such as virtual networks, firewalls, load balancers, VPNs, and content delivery networks (CDNs), while also considering factors like MAC Addresses Functions, Risks, and Operation for network identification and security. These features optimize traffic flow, enhance security, and enable seamless global data transfer while protecting against cyber threats. Security remains a top priority in cloud computing, and security & identity management features are essential for safeguarding cloud environments. IaaS providers implement Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies, encryption methods, and compliance controls to ensure data confidentiality and access restrictions. These security measures help organizations meet regulatory requirements while mitigating potential risks. Efficient cloud operations require monitoring & management tools that provide real-time insights into resource utilization. IaaS solutions include dashboards, logging tools, and automated scaling mechanisms that enable businesses to track performance, detect issues early, and optimize resource allocation. Lastly, backup & disaster recovery solutions ensure high availability and business continuity. Cloud-based data replication, failover mechanisms, and snapshot backups help organizations prevent data loss, quickly recover from failures, and maintain operational resilience in the face of unexpected disruptions.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cloud Computing Certificate? View The Cloud Computing Online Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Leading IaaS Providers (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS provides a comprehensive range of IaaS solutions, including EC2 instances for computing, S3 for scalable storage, and VPC for secure networking. It is known for its high reliability, scalability, and extensive global infrastructure. Businesses benefit from on-demand resources, automated scaling, and integrated security features. AWS supports hybrid cloud strategies, making it a versatile choice for enterprises of all sizes.
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft Azure offers virtual machines, Azure Blob storage, and advanced networking to support diverse cloud workloads. It seamlessly integrates with Microsoft products like Windows Server, Active Directory, and Office 365. Azure’s hybrid cloud capabilities allow businesses to connect on-premises data centers with the cloud. It provides robust security, AI-driven analytics, and enterprise-grade compliance for regulated industries.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP specializes in high-performance computing, AI-driven cloud services, and Kubernetes-based container management. It is widely chosen for data-intensive applications, big data analytics, and machine learning workloads. Google’s cloud infrastructure ensures low-latency global networking, powerful data processing, and scalable storage solutions, all of which are explored in the Cloud Computing Course. GCP also emphasizes sustainability, using energy-efficient data centers for cloud operations.
Security Considerations in IaaS
Security in IaaS is a shared responsibility between the cloud provider and the customer. While providers handle the physical and infrastructure-level security, customers must focus on securing their applications, data, and configurations. Key security considerations include: Identity and Access Management (IAM). Implement strict role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to minimize unauthorized access. Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest to prevent breaches and leaks. Use firewalls, VPNs, and security groups to protect virtual networks from unauthorized access.Ensure adherence to industry-specific regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, and ISO 27001. Conduct vulnerability assessments, patch management, and continuous monitoring for threat detection. Implement automated backup policies and redundancy plans to ensure data protection. Additionally, organizations should focus on endpoint security to protect devices accessing cloud resources. Using security information and event management (SIEM) tools, businesses can gain real-time visibility into threats and anomalies. AI-powered threat detection enhances response mechanisms, enabling quicker mitigation of cyber risks. Implementing zero-trust security frameworks further strengthens defenses by verifying every access request. Security awareness training for employees is equally important, as human errors often lead to breaches. Establishing incident response plans ensures quick action during security incidents, minimizing downtime and data loss. As cloud environments evolve, businesses must adopt a proactive security approach, leveraging advanced technologies and best practices to safeguard their IaaS infrastructure effectively.
Challenges of IaaS Adoption
- Cost Management: While IaaS reduces capital expenses, improper resource allocation may lead to increased operational costs.
- Integration Challenges: Migrating legacy systems to cloud environments can be complex and time-consuming.
- Performance Variability: Network latency and shared resources may impact application performance, and using tools like Azure Advisor can help optimize resources and improve overall performance.
- Dependency on Cloud Providers: Vendor lock-in can limit flexibility and increase switching costs.
- Security Risks: Misconfigurations and inadequate security policies can make cloud resources vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Compliance Complexity: Organizations in regulated industries must navigate complex compliance requirements when using IaaS.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Masters Course.
The Future of IaaS
The future of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is set for continuous growth, driven by emerging technologies and evolving business needs. Edge computing is gaining traction as cloud providers deploy IaaS at edge locations to minimize latency and enable real-time data processing. AI and automation will further enhance IaaS by streamlining workload management, security, and performance optimization through machine learning-driven solutions. While IaaS already offers virtualized resources, the rise of serverless computing will simplify cloud operations by eliminating the need for manual infrastructure management. Organizations are also increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to improve flexibility, ensure redundancy, and reduce vendor lock-in, with Azure DNS Management playing a key role in efficiently handling domain name resolution across multiple cloud environments. Additionally, green cloud computing is becoming a priority, with providers investing in energy-efficient data centers and carbon-neutral cloud infrastructure to minimize environmental impact. As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, IaaS will remain a fundamental driver of innovation. It enables enterprises to scale efficiently, optimize costs, and improve operational agility while ensuring security and high performance. With advancements in cloud security, AI-driven automation, and sustainable computing, IaaS is set to revolutionize IT infrastructure and support the next generation of cloud-powered solutions.
Case Studies and Real-World Use of IaaS
- Netflix: Uses AWS IaaS to support its scalable, high-performance streaming services, allowing seamless content delivery to millions of users globally.
- Airbnb: Leverages cloud infrastructure to manage a vast database of listings, bookings, and user interactions while ensuring reliability.
- NASA: Uses cloud computing for data storage, large-scale simulations, and deep space research projects, with the added benefit of leveraging Docker Containers on AWS for efficient containerization and scalability.
- Dropbox: Migrated from a traditional data center model to IaaS, improving storage scalability and reducing operational overhead.
- Pinterest: Utilizes GCP IaaS to process billions of image searches and recommendations daily.
- Siemens: Implements Azure IaaS for industrial automation, predictive maintenance, and AI-driven insights.
- Toyota: Uses cloud infrastructure to enhance its connected vehicle ecosystem, optimizing data analytics and real-time communication.
Preparing for a Cloud Computing Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer
Conclusion
A crucial aspect of securing Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is implementing proactive security measures to safeguard cloud environments. Organizations must adopt a comprehensive security strategy that includes identity and access management, data encryption, network protection, and compliance adherence. By addressing these key areas, businesses can mitigate risks and protect their cloud-based assets from evolving cyber threats.IaaS security is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, vulnerability assessments, and timely updates. Integrating automation, AI-driven threat detection, and incident response mechanisms ensures rapid identification and resolution of security issues. Organizations should also implement a zero-trust security model to minimize unauthorized access and enhance overall system resilience, as emphasized in the Cloud Computing Course. Furthermore, employee training and security awareness programs play a vital role in strengthening an organization’s security posture. As cloud environments evolve, businesses must stay updated with the latest security trends and best practices. By adopting a proactive approach to IaaS security, organizations can maximize the benefits of cloud computing while maintaining a secure, scalable, and high-performing infrastructure. Ultimately, securing IaaS environments requires a combination of technology, strategy, and vigilance. With the right security measures in place, businesses can build a resilient cloud infrastructure capable of withstanding modern cybersecurity challenges.





