
- Introduction to Azure DNS
- Creating and Managing DNS Zones
- Configuring DNS Records in Azure
- Integrating Azure DNS with Other Azure Services
- Security and Access Control for Azure DNS
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting Azure DNS
- Conclusion
Introduction to Azure DNS
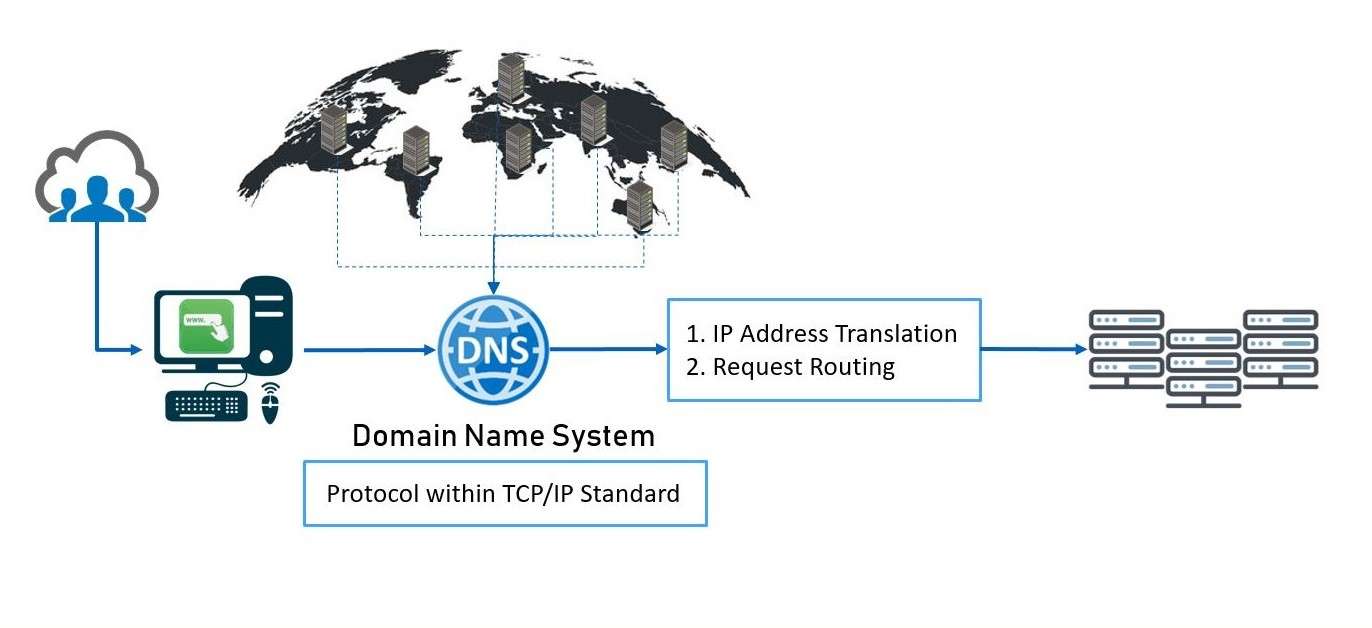
Azure DNS is a hosting service for DNS (Domain Name System) records within Microsoft Azure. It enables you to manage and resolve domain names in Azure, offering highly available and reliable DNS services for your applications. Azure DNS supports standard DNS functionalities and allows for seamless management of DNS zones and records in the cloud. Microsoft Azure Training uses the same global network of Microsoft datacenters that other Azure services rely on, ensuring performance and scalability. With Azure DNS, you can manage your DNS records through a user-friendly interface or programmatically via APIs, making it easy to integrate with your existing Azure infrastructure. Whether you’re hosting websites, web applications, or other resources on Azure, Azure DNS is a crucial part of the overall DNS management strategy, providing high availability, low latency, and robust security. Azure DNS also supports advanced features such as DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions), which helps protect your DNS records from certain types of attacks. Additionally, it integrates seamlessly with other Azure services, such as Azure Traffic Manager and Azure Front Door, to improve traffic routing and load balancing for your applications. Azure DNS offers robust monitoring and logging capabilities, allowing you to track DNS queries and performance metrics to optimize your infrastructure. It also provides automatic scaling to handle large volumes of DNS requests, ensuring consistent performance during traffic spikes. With built-in redundancy and automatic failover, Azure DNS guarantees reliable DNS resolution for your domain names.
Creating and Managing DNS Zones
A DNS zone is a container for records about a specific domain name, and Azure DNS allows you to create and manage DNS zones for your domain names easily. The following steps are involved in creating and managing Azure Active Directory
- Creating a DNS Zone: You can create a DNS zone in Azure using the Azure portal, CLI, or ARM templates. When creating a zone, you will specify the domain name (e.g., example.com) and link it to a resource group.
- Managing DNS Zones: After creating a zone, you can manage it by adding or removing records, configuring name servers, and setting up automated processes for DNS management. You can also configure custom DNS settings, such as TTL (Time-to-Live), for your records.
- Private DNS Zones: Azure also supports Private DNS zones, which allow you to manage DNS records for virtual networks and internal Azure resources. This is particularly useful for resolving private domain names within your Azure network, while keeping them isolated from the public internet.
Learn how to manage and deploy cloud services by joining this Azure Training today.
- DNS Zone Delegation: Azure allows you to delegate DNS management to different Azure resources or external DNS providers. You can configure NS (Name Server) records within your DNS zone to delegate authority to another DNS service, which can be useful when managing multiple zones across different platforms or when splitting responsibilities between different teams.
- Automated DNS Management: Azure provides tools like Azure CLI, ARM templates, and Azure PowerShell that allow you to automate DNS zone management. This is particularly beneficial for large-scale environments where you may need to programmatically create, update, or remove records in DNS zones as part of a DevOps workflow or deployment process.
- Zone Import and Export: Azure DNS supports importing and exporting DNS zones from and to BIND format. Azure Data Box Secure Data Transfer Solution feature is helpful when migrating from an existing DNS provider to Azure DNS or when you need to back up your DNS configurations. You can use this feature to move DNS records efficiently between environments or across different DNS systems.
- Simplifying Hybrid Cloud Management: Outposts are designed to simplify the management of hybrid environments. By extending AWS’s infrastructure and offering support for cloud-native services, organizations can focus on building applications rather than managing complex hybrid architectures.
- Integrated Networking: Outposts are designed to provide low-latency connectivity with AWS’s global infrastructure. You can easily connect your on-premises Outposts with AWS services over AWS Direct Connect or AWS VPN, ensuring secure and fast communication between your on-premises and cloud environments.
- Azure Virtual Machines: When you deploy Azure Virtual Machines (VMs), you can automatically update DNS records to reflect changes in their public or private IP addresses. This is useful for dynamic applications hosted on VMs.
- Azure Load Balancer: Azure DNS can be integrated with the Azure Load Balancer to route traffic to VMs or services behind the load balancer. You can configure the DNS to point to the load balancer’s IP, ensuring that traffic is properly distributed across your backend servers.
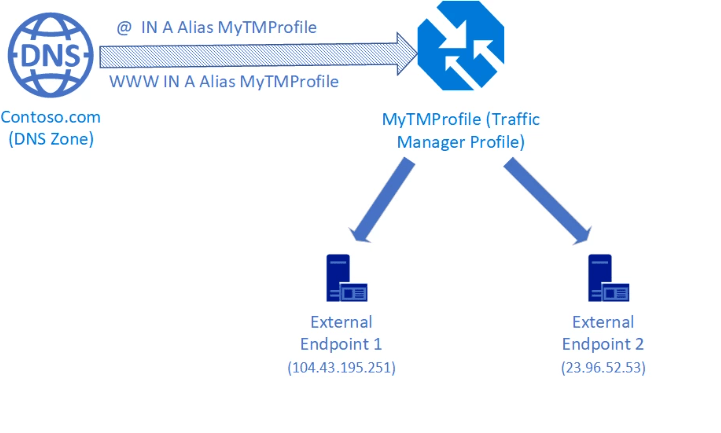
- Azure Traffic Manager: Azure Traffic Manager is a global traffic distribution service that works with Azure DNS to manage traffic routing across multiple endpoints. DNS records in Azure DNS can be configured to point to Traffic Manager profiles for efficient traffic management and optimization.
- Azure App Services: Azure DNS can be used with Azure App Services to configure custom domain names for your applications. You can easily map your custom domain to your Azure-hosted applications, ensuring users can access them with branded URLs.
- Azure CDN (Content Delivery Network): When using Azure Availability Sets vs Zones deliver content globally, you can configure DNS records in Azure DNS to route requests to the nearest CDN endpoint, improving performance and reducing latency.
- Azure Key Vault: For added security, Azure DNS can integrate with Azure Key Vault to store and manage DNS credentials and API keys required for secure access to DNS records.
- Azure Monitor: Azure Monitor can track DNS queries, failures, and the overall health of your DNS setup. By using Metrics and Logs, you can view performance data, set alerts for unusual activities, and perform deep dives into issues.
- DNS Query Logs: Azure Traffic Manager a Complete Guide provides query logging capabilities that allow you to monitor DNS requests and responses. This helps in troubleshooting issues such as DNS resolution failures, misconfigured records, or performance bottlenecks.
- Azure Network Watcher: Azure Network Watcher provides tools like Connection Monitor to track the status of your network connections, including DNS resolution. It allows you to diagnose issues related to DNS and connectivity between different Azure resources.
- Custom Alerts: You can set up custom alerts in Azure Monitor to notify you if certain DNS thresholds are exceeded, such as an unusually high number of DNS query failures or timeouts.
- Troubleshooting DNS Issues: Common DNS issues include misconfigured DNS records, DNS propagation delays, or network-related problems. Using tools like nslookup or dig, you can diagnose and resolve DNS resolution issues. Additionally, Azure provides a DNS Troubleshooter to assist in identifying and fixing DNS-related problems.
Unlock your potential in Azure with this Azure Training .
Configuring DNS Records in Azure
After creating a DNS zone in Azure, the next step is to configure DNS records for your domain. Azure DNS supports several types of DNS records that help route traffic to the right destinations. Common types of DNS records include, An A record maps a domain to an IPv4 address. For example, an A record could point your domain (e.g., www.example.com) to the public IP address of a web server hosted on Azure. A CNAME (Canonical Name) record maps an alias to another domain name, making How to Understand Azure API Management useful for setting up subdomains that point to external services or other subdomains.MX (Mail Exchange) records are used to route emails for a domain to the appropriate mail servers. This is crucial for email delivery.TXT records allow you to associate text with a domain, which is useful for verification purposes, such as with Google Search Console, Microsoft 365, or SPF (Sender Policy Framework) for email security. SRV records define services (such as Skype for Business or Office 365) available at specific ports, enabling easier configuration for applications. NS (Name Server) records define the authoritative name servers for a domain. These are crucial when delegating DNS management to Azure DNS from another DNS provider.
AAAA records are used to map a domain to an IPv6 address, which is important for supporting IPv6-capable devices and applications. PTR (Pointer) records are used for reverse DNS lookups, which map an IP address to a domain name. This is commonly used in email servers to verify the authenticity of incoming messages and improve spam filtering. CAA (Certification Authority Authorization) records allow you to specify which certificate authorities (CAs) are permitted to issue SSL/TLS certificates for your domain, adding an extra layer of security for SSL/TLS management. DNSSEC can be used with Azure DNS to add digital signatures to DNS records, enhancing the security by protecting against DNS spoofing and ensuring that responses are not tampered with. Similar to CNAME records, ALIAS records are used to point a domain to a resource like a load balancer or a CDN, but unlike CNAME, they can be used at the zone apex (root domain), making it suitable for cases where CNAME is not allowed. While not natively supported as a specific DNS record type, URL redirect services can be configured within Azure DNS using HTTP redirection techniques, enabling traffic routing and redirection to different URLs or domains as required.
Integrating Azure DNS with Other Azure Services
Azure DNS integrates seamlessly with a wide range of Azure services to enhance functionality and automate processes. Key integrations include:
Azure DNS integrates smoothly with various Azure services, enhancing functionality and automating DNS record management. It ensures efficient traffic routing, improved performance, and strong security by working with services like Virtual Machines, Load Balancer, Traffic Manager, and App Services. These integrations simplify application management, optimize user experience, and protect critical credentials within a scalable cloud infrastructure.
Looking to master Azure? Sign up for ACTE’s Azure Training and begin your journey today!
Security and Access Control for Azure DNS
Azure DNS offers several features to secure and control access to your DNS records. Azure uses RBAC to manage permissions at various levels. Microsoft Azure Training can assign roles such as DNS Contributor, DNS Reader, and others to users or service principals to ensure only authorized personnel can modify DNS configurations. Azure DNS integrates with Azure Active Directory (AAD) for managing user identities and permissions. This allows for centralized identity management, ensuring that only users with the right access can make changes to DNS settings.
You can track changes to your DNS records using Azure Activity Logs. These logs provide detailed information about who made changes to DNS settings, when the changes were made, and the nature of the changes.DNSSEC adds an additional layer of security to DNS by allowing you to digitally sign your DNS records. This helps prevent DNS spoofing and ensures that DNS responses are authentic and have not been tampered with during transmission.Azure supports Private DNS Zones, allowing organizations to isolate their internal DNS traffic from the public internet. This is particularly important for maintaining secure communication between internal services and avoiding potential external threats.
Boost your chances in Azure interviews by checking out our blog on Azure Interview Questions And Answers !
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Azure DNS
Monitoring and troubleshooting your DNS infrastructure is critical to maintaining high availability and performance. Azure provides a range of tools to help you monitor and troubleshoot DNS configurations:
By leveraging Azure DNS, you can effectively manage and scale your DNS infrastructure, integrate it with other Azure services, ensure security, and troubleshoot potential issues efficiently. The combination of Azure’s powerful features with DNS management tools makes it an essential component for businesses looking to manage their domain name resolution needs in the cloud.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Azure DNS is a powerful and scalable service that provides efficient and secure DNS management within the Azure ecosystem. By utilizing Azure DNS, businesses can ensure high availability, low latency, and seamless integration with other Azure services, making it a crucial component of any cloud-based infrastructure. The service offers a comprehensive solution for creating and managing DNS zones, configuring various types of DNS records, and integrating with other Azure resources like Virtual Machines, Traffic Manager, and CDN.Furthermore, Azure DNS prioritizes security with robust features such as role-based access control, Azure Active Directory integration, DNSSEC, and Private DNS zones, allowing organizations to maintain a secure and well-controlled DNS environment. The integration with Azure Monitor and other monitoring tools also provides powerful capabilities for diagnosing, troubleshooting, and optimizing DNS performance, ensuring that organizations can respond to issues proactively.Overall, Azure DNS simplifies the complexities of DNS management in theMicrosoft Azure Training, making it easier for businesses to scale, secure, and monitor their domain name infrastructure. Whether you are managing public or private DNS zones, integrating with other Azure services, or ensuring the integrity of your DNS configurations, Azure DNS offers a reliable and flexible solution.





