
- Introduction to Google Cloud Engineer
- Prerequisites and Required Skills
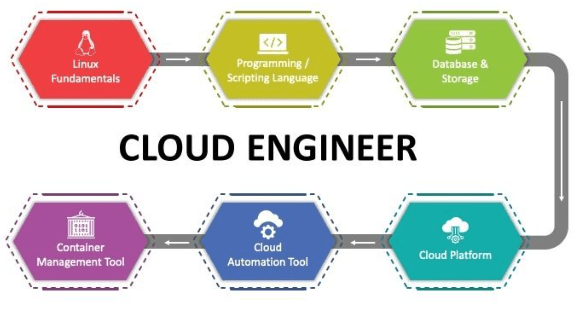
- Learning Path for Cloud Engineers
- Cloud Computing Certifications to Pursue
- Hands-on Experience and Real-world Projects
- Understanding Cloud Security Principles
- Cloud Storage and Networking Fundamentals
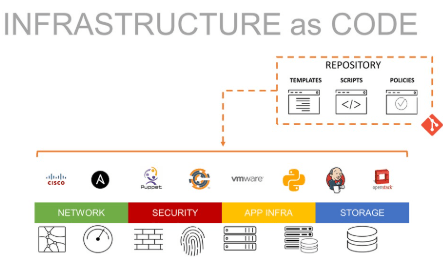
- Mastering Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Job Opportunities and Career Growth
- Salary Trends for Cloud Engineers
- Best Learning Resources for Cloud Engineering
- Conclusion
Introduction to Google Cloud Engineer
Cloud engineering is a rapidly growing field that designs, implements, and manages cloud-based Infrastructure as Code and applications. Cloud engineers are responsible for the entire lifecycle of Cloud Computing Course , from the architecture and design phase to deployment and ongoing management. As businesses increasingly shift their operations to the cloud, cloud engineers are critical in ensuring that systems are scalable, secure, and efficient. Cloud computing offers flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, pivotal for modern businesses to maintain competitiveness. As a result, the demand for skilled cloud engineers has grown substantially. In this context, cloud engineers work across platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), each offering unique features and services for building cloud-based systems.
Prerequisites and Required Skills
Cloud engineers require technical skills, industry knowledge, and hands-on experience. The following prerequisites and skills are essential for aspiring cloud engineers:
Basic IT Knowledge:
- A solid understanding of computer networks, operating systems (Linux, Windows), and database management systems is foundational.
- Knowledge of networking protocols (e.g., TCP/IP, HTTP, DNS) and virtualization technologies is also crucial.
Cloud Platforms:
- Proficiency with cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud is essential. Understanding the key services of each platform, such as computing, storage, networking, and databases, forms the backbone of Cloud Computing Skills for Career Growth.
Programming/Scripting Skills:
- Cloud engineers must be able to write code for automation and deployment tasks. Standard programming and scripting languages include Python, Shell scripting, PowerShell, and JavaScript.
- Understanding tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, and Ansible for infrastructure management is also essential.
- It is critical to have a strong understanding of cloud security principles, including identity and access management (IAM), encryption, compliance, and secure software development practices.
- Familiarity with DevOps principles and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines is a huge asset. Tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and Azure DevOps are widely used in cloud environments.
- Cloud engineers should know how to configure and manage various cloud storage options (e.g., S3, Blob Storage, Databases such as Applications of Cloud Computing!, Azure SQL Database).
- It is essential to quickly identify and resolve issues in cloud environments. This includes monitoring, logging, and using diagnostic tools provided by cloud platforms.
- Step 1: Build a Strong Foundation
- Step 2: Get Familiar with Cloud Platforms
- Step 3: Learn DevOps Tools
- Step 4: Understand Cloud Security
- Step 5: Gain Practical Hands-On Experience
- Step 6: Keep Learning and Stay Updated
- Shared Responsibility Model: Understand the division of responsibility between cloud providers and customers for securing data and infrastructure.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Implement IAM best practices, such as least privilege access, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access control (RBAC).
- Data Encryption: Ensure data is encrypted in transit and at rest to Cloud Architect Pay by Experience Industry sensitive information.
- Compliance: Be aware of industry regulations and standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, ensuring that your cloud solutions comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Cloud-native tools (e.g., AWS CloudTrail, Azure Security Center) monitor, log continuously, and audit cloud resources for unusual activity.
- Cloud Storage: Learn how cloud storage works, including different types of storage (block, object, file storage), and how to choose the right storage solution for various use cases (e.g., AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage).
- Networking: Understand how virtual networks, subnets, firewalls, and load balancers work in the cloud, and learn how to configure and secure networking in a cloud environment (e.g., Amazon Web Services VPC, Azure Virtual Network).
- Cloud Engineer: General role focused on cloud infrastructure deployment and management.
- Cloud Architect: Focuses on designing cloud-based solutions and large-scale cloud architectures.
- Cloud Security Engineer: Specializes in securing cloud-based environments.
- DevOps Engineer: Combines software development with cloud management and automation.
- Site Reliability Engineer (SRE): Ensures the reliability and uptime of cloud systems.
- Entry-Level: $70,000 – $90,000 annually.
- Mid-Level: $90,000 – $120,000 annually.
- Senior-Level: $120,000 – $180,000 annually.
Cloud Security:
DevOps and CI/CD:
Database and Storage Management:
Problem-Solving and Troubleshooting:
Master Cloud Computing skills by enrolling in this Cloud Computing Online Course today.
Learning Path for Cloud Engineers
If you’re looking to pursue a career in Google Cloud Engineer , here’s a structured learning path:
Start with understanding the basics of Networking (e.g., subnets, IP addressing, VPNs, routing) and Operating Systems (e.g., managing virtual machines, cloud operating systems). Learn scripting languages like Python or Bash to automate tasks.
Begin exploring major cloud platforms, such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. Most platforms offer free tiers that allow you to experiment with real services. Learn the core services (computing, storage, networking) and how to interact with these services using the platform’s console and CLI (command line interface).
Familiarize yourself with DevOps practices and tools such as Docker (containerization), Kubernetes (container orchestration), Terraform, and Top Cloud Certifications (for Infrastructure as Code). Learn CI/CD tools to automate the deployment pipeline.
Explore the shared responsibility model of cloud security. Understand how identity and access management (IAM) works, learn about encryption (data at rest, data in transit), and apply best practices for securing cloud environments.
Once you have foundational knowledge, build your projects in the cloud, such as hosting a web application or setting up a simple cloud infrastructure. You can take on real-world tasks like setting up an EC2 instance in Amazon Web Services , creating virtual machines in Azure, or configuring databases and load balancers.
Cloud technologies are continuously evolving, so it’s crucial to stay current with the latest trends, new services, and best practices.
Cloud Computing Certifications to Pursue
Certifications are a great way to demonstrate your skills and validate your expertise in cloud engineering. Some of the top certifications include, AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate/Professional Recognized as one of the top certifications for cloud engineers, this certification validates your ability to design scalable, reliable, and cost-effective solutions on Amazon Web Services. Microsoft Certified Azure Solutions Architect Expert is ideal for engineers who specialize in designing and implementing Azure solutions. It covers various aspects of the Cloud Computing Course. Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect focuses on designing, planning, and managing GCP solutions, which is beneficial for engineers working in Google Cloud environments. Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) has become a key skill in cloud engineering, and this certification helps validate your expertise in deploying and managing Kubernetes clusters. CompTIA Cloud+ excellent entry-level certification covers essential cloud concepts and basic cloud services, ideal for those new to cloud computing.
Enhance your knowledge in Cloud Computing. Join this Cloud Computing Online Course now.
Hands-on Experience and Real-world Projects
Gaining hands-on experience is crucial to your success as a Google Cloud Engineer. It’s not enough to pass exams and learn from theory; real-world expertise allows you to apply your skills to solve problems and build solutions. Some practical steps include, Set Up Your Cloud Environment Experiment with Essential Cloud Computing Tools and Beyond free tiers to create virtual machines, deploy applications, set up networking, and work with storage services. Contribute to Open-Source Project Many cloud-based open-source projects need contributors to help with cloud infrastructure. Contributing will help you gain real-world experience and expand your professional network. Build a Personal Cloud Portfolio Document your projects, such as building a scalable web application, creating a CI/CD pipeline, or managing a multi-cloud environment. This portfolio can demonstrate your practical skills to potential employers. Internships and Apprenticeships If possible, pursue internships to gain exposure to cloud-based projects in a professional environment.
Understanding Cloud Security Principles
Cloud security is a critical area of focus for cloud engineers, as it involves safeguarding data, applications, and services from various threats. The key cloud security principles include:
Want to lead in Cloud Computing? Enroll in ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course and start your journey today!
Cloud Storage and Networking Fundamentals
Mastering Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is a key skill for cloud engineers, allowing for automated infrastructure provisioning and management. Popular IaC tools include, Terraform declarative IaC tool that works across multiple cloud platforms. AWS CloudFormation native IaC tool allows you to define cloud resources using templates. Ansible Primarily used for configuration management but can also be used for provisioning cloud infrastructure. Learning IaC enables The Issues in Cloud Computing to automate the entire lifecycle of Infrastructure as Code deployment, leading to more efficient, reproducible, and error-free cloud environments.
Job Opportunities and Career Growth
The demand for cloud engineers is at an all-time high. Some of the job roles you can pursue include:
As businesses adopt cloud technologies, the need for skilled cloud engineers will only increase. Cloud engineers can advance their careers by gaining more experience, earning higher-level certifications, and specializing in cloud security, DevOps, or cloud architecture.
Preparing for a job interview? Explore our blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers!
Salary Trends for Cloud Engineers
The salary for cloud engineers can vary depending on experience, location, and skillset. However, the Google Cloud Engineer field generally offers competitive salaries.
Salaries are higher in areas with a strong tech industry presence, such as Silicon Valley, New York, or London. Cloud engineers with advanced certifications or expertise in niche areas (e.g., cloud security) can command even higher salaries.
Best Learning Resources for Cloud Engineering
AWS Training and Certification Official training resources and certification paths for Amazon Web Services. Microsoft Learn Free learning paths for Azure-related cloud engineering skills. Google Cloud Training Google Cloud offers extensive courses and certifications. Linux Academy (now A Cloud Guru) Provides hands-on labs and learning modules for cloud technologies. Udemy/Coursera Numerous courses on cloud platforms and cloud engineering fundamentals.
Conclusion
Cloud engineering is a dynamic and rewarding career that offers many opportunities for growth and advancement. By gaining the right skills, certifications, and hands-on experience, aspiring cloud engineers can build a successful career in this rapidly evolving field. Cloud Computing Course future is bright, and professionals who stay updated on the latest technologies, security practices, and tools will continue to be in high demand.





