
- Introduction to SaaS
- SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS
- Key Benefits of SaaS
- Popular SaaS Applications (Salesforce, Dropbox)
- Security Risks in SaaS
- Future of SaaS in Cloud Computing
- SaaS and Business Digital Transformation
- SaaS and Data Analytics
- SaaS and Remote Workforce Management
- SaaS and E-Commerce Growth
- Conclusion
Introduction to SaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a based service that delivers applications over the Internet, eliminating the need for local installation, maintenance, and hardware management. SaaS allows users to access software applications on a subscription basis, with the software hosted and maintained Guide to Cloud Computing by third-party service providers. This delivery model offers scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, making it popular among businesses and individual users alike. SaaS is typically accessed through a web browser, enabling users to work from any location with an internet connection. It can be used for a variety of purposes, including email services, customer relationship management (CRM), project management, and collaboration tools. Examples of popular SaaS solutions include Google Workspace, Salesforce, and Dropbox.
SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS
The terms SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS refer to different levels of service models. Here’s a breakdown of the differences:
SaaS (Software as a Service)
- Definition: SaaS provides ready-to-use applications over the Internet that are managed and maintained by the service provider.
- Users: End-users who require software for specific tasks (e.g., CRM, email, collaboration tools).
- Examples: Salesforce, Google Workspace, Dropbox.
- Responsibility: The provider manages everything, include Real World Applications of Cloud Computing hardware, software, and security, while the user focuses on using the application.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- Definition: PaaS offers a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure.
- Users: Developers who need a platform for creating applications.
- Examples: Microsoft Azure, Google App Engine, Heroku.
- Responsibility: The provider manages infrastructure and platform services, while users manage the application code and data.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- Definition: IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers basic infrastructure services like storage, networking, and computing power.
- Users: Organizations need scalable infrastructure for running applications and storing data.
- Examples: AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine.
- Responsibility: The provider handles infrastructure, while the user manages the operating systems, applications, and data.
Key Difference: SaaS delivers fully functional software, PaaS provides a platform for developing apps, and IaaS provides raw infrastructure resources. SaaS is the most end-user-focused, while PaaS and IaaS are more developers- and IT infrastructure-focused, respectively.
To Explore DevOps in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cloud Computing Online Course To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
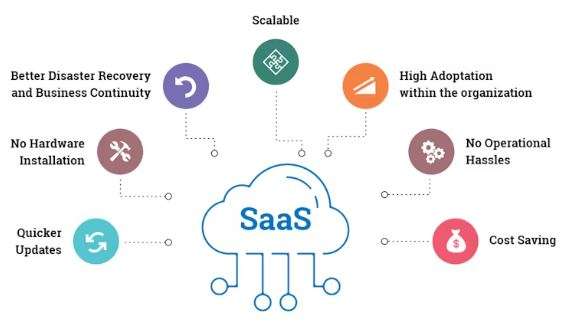
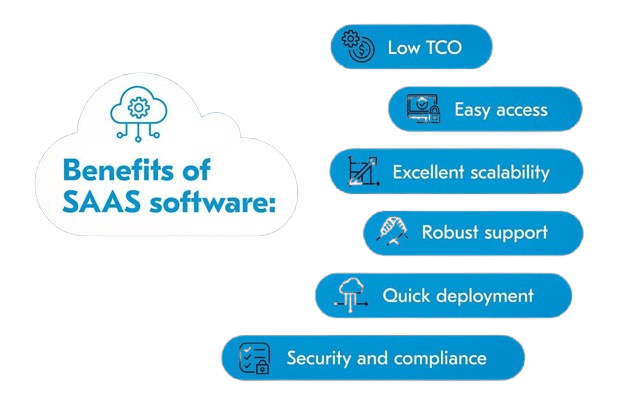
Key Benefits of SaaS
- Cost-Effective: SaaS eliminates the need for businesses to purchase, maintain, or upgrade hardware and software. Instead, users pay a subscription fee, which can be more predictable and affordable.
- Scalability: SaaS solutions are highly scalable,Cloud Computing Course allowing businesses to easily increase or decrease usage as needed without worrying about physical infrastructure.
- Accessibility: Since SaaS applications are accessed via the internet, users can access them from any device with a web browser and internet connection, enabling remote work and global collaboration.
- Automatic Updates: Providers handle updates, patches, and maintenance, ensuring that the software is always up-to-date without requiring manual intervention from users.
- Security and Backup: SaaS providers typically offer robust security measures and backup solutions, which might be more advanced than what an organization could implement on its own.
- Reduced IT Burden: SaaS reduces the need for in-house IT teams to manage software installations, configurations, and ongoing maintenance, freeing them to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Popular SaaS Applications
Salesforce Salesforce is a widely used customer relationship management (CRM) platform that offers cloud-based tools for sales, marketing, and customer support. Helps businesses manage customer data, track sales performance, automate marketing tasks, and integrate with other systems.
Dropbox Dropbox is a cloud-based file storage and collaboration platform that allows users to store, share, and synchronize files across devices. Easy access to files from any device, collaboration tools for teams, and robust sharing options.
Google Workspace : Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) is a suite of productivity tools that includes Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, Sheets, and Cloud Computing training more, designed for collaboration and communication. Seamless collaboration across teams, real-time document editing, and easy integration with other Google services.
Slack : Slack is a cloud-based messaging and collaboration platform used by teams for communication, project management, and file sharing. Enhances team collaboration, integrates with other business tools, and supports real-time messaging, video calls, and file sharing.
Zoom: Zoom is a cloud-based video conferencing platform that supports virtual meetings, webinars, and team collaboration. High-quality video and audio, screen sharing, virtual backgrounds, and integrations with other business applications.
Security Risks in SaaS
While SaaS offers many benefits, it also presents specific security risks that organizations must consider: Since SaaS applications store sensitive data in the cloud, a breach of the service provider’s system could expose private information. It’s critical to assess the provider’s security measures, such as encryption and access controls. Organizations in regulated industries (e.g., healthcare, finance) must ensure that the SaaS provider complies with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Non-compliance could lead to legal and financial penalties. Cloud Computing Course Switching between SaaS providers can be difficult and costly due to differences in data formats, integration complexities, and long-term contracts. It’s important to assess data portability options and exit strategies. Employees with access to sensitive data or applications could potentially exploit their privileges, causing data breaches or system disruptions. Although most SaaS providers back up data, there is always a risk of data loss due to unforeseen incidents like technical failures or cyberattacks. Organizations should assess backup options and disaster recovery plans. Cloud based services depend on the provider’s infrastructure. Service outages or downtime, often caused by maintenance or attacks, can disrupt access to critical applications.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
Future of SaaS in Cloud Computing
The future of SaaS in looks promising, as the demand for cloud-based solutions continues to grow. Key trends shaping the future of SaaS include:
- Industry-Specific SaaS Solutions: As businesses continue to seek specialized solutions, the demand for industry-specific SaaS applications will rise. SaaS providers will develop tailored solutions for industries like healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments: Organizations are moving toward multi-cloud and hybrid environments, where SaaS applications are integrated with both public and private cloud solutions. This allows for greater flexibility, reliability, and data sovereignty.
- Edge Computing Integration: With the rise of IoT Cloud Computing Architecture and real-time applications, SaaS solutions will increasingly integrate with edge computing to enable faster data processing at the network’s edge, reducing latency and improving application performance.
- Advanced Security Features: As security concerns grow, SaaS providers will continue to enhance their security measures, incorporating end-to-end encryption, identity management, and zero-trust frameworks to ensure data protection.
- Low-Code/No-Code SaaS Platforms: The demand for low-code and no-code platforms will increase, allowing users with little to no programming experience to build and customize their own applications. This democratizes app development and expands SaaS adoption among non-technical users.
SaaS and Business Digital Transformation
SaaS plays a crucial role in digital transformation, helping businesses automate processes, enhance customer experiences, and improve operational efficiency. Companies are leveraging SaaS to transition from traditional IT infrastructure to more agile, cloud-based solutions. This shift allows businesses to:
- Optimize Workflows – Automating tasks through AI-powered SaaS solutions saves time and reduces errors.
- Enhance Collaboration – Cloud Computing Companies in India remote teams can seamlessly collaborate.
- Improve Customer Engagement – SaaS CRM tools help businesses better understand and serve customers.
- Drive Innovation –Companies can quickly test new business models without heavy IT investments.
SaaS and Data Analytics
Modern SaaS applications integrate robust data analytics capabilities that empower businesses with insights for decision-making. Benefits include:
- Real-Time Analytics – SaaS tools provide up-to-date insights, enabling quick business decisions.
- Predictive Analytics – AI-driven SaaS tools can forecast market trends and customer behaviors.
- Data Integration – SaaS solutions can aggregate data from multiple sources for a unified view.
- Business Intelligence – Advanced reporting features help businesses monitor performance and ROI.
Looking to Master Cloud Computing? Discover the [REAL-TIME] Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers Available at ACTE Now!
SaaS and Remote Workforce Management
SaaS solutions play a crucial role in enabling and managing remote workforces. Key advantages include cloud-based collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams and Asana, which allow teams to work together in real time from different locations. SaaS platforms also provide performance monitoring capabilities, helping businesses track employee productivity and engagement through analytics. Additionally, Cloud Computing Is Essential secure access control mechanisms ensure that remote employees can access only authorized resources, reducing security risks while maintaining operational efficiency.
SaaS and E-Commerce Growth
SaaS solutions are accelerating the growth of e-commerce by providing businesses with scalable online platforms. Tools like Shopify enable quick and hassle-free store setup, allowing businesses to go online without extensive technical knowledge. Payment integration features ensure seamless transactions by supporting multiple gateways, improving customer convenience. Additionally, automated inventory management helps businesses track stock levels in real-time and streamline order fulfillment, reducing manual workload and improving overall efficiency.
Conclusion
SaaS is a cornerstone of modern, providing businesses with accessible, cost-effective, and scalable software solutions. While there are challenges such as security risks and vendor lock-in, the benefits of SaaS in enhancing productivity, collaboration, and IT efficiency make it an attractive option for many organizations. As technology evolves, SaaS will continue to integrate cutting-edge advancements like AI, machine learning, and edge computing, transforming how businesses operate and interact with their software tools.





