
- Introduction
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
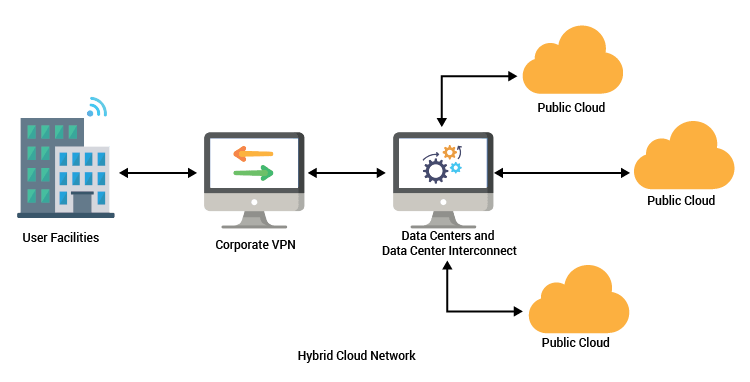
- Hybrid Cloud
- Community Cloud
- Choosing the Right Cloud Deployment Model
- The Future of Cloud Deployment Models
- Conclusion
Cloud deployment models define how computing resources are managed and accessed. The Public Cloud offers scalability and cost-effectiveness by hosting services on shared infrastructure. The Private Cloud provides greater control and security for a single organization. The Hybrid Cloud combines public and private environments for flexibility and optimized workloads. The Cloud Computing Course is shared among organizations with common interests, ensuring collaboration and compliance. Choosing the Right Cloud Deployment Model depends on factors like security, budget, and business needs. The Future of Cloud Deployment Models includes advancements in edge computing, AI-driven cloud management, and enhanced security measures. In conclusion, selecting the right cloud model ensures efficiency, security, and scalability for businesses.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
Introduction
Cloud computing has transformed IT management by offering scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions. Choosing the right cloud deployment model is crucial, as it impacts security, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Mastering AWS Cloudformation are four primary models: Public Cloud, which provides cost savings and scalability through shared resources; Private Cloud, offering enhanced security and control for sensitive data; Hybrid Cloud, combining public and private environments for flexibility; and Community Cloud, serving organizations with shared compliance needs. Each model has unique benefits, and selecting the right one ensures optimal performance, security, and efficiency for your business. This article explores these models to help you make an informed choice.
Public Cloud
- Scalability & Flexibility: Public cloud services offer on-demand scalability, allowing businesses to expand or reduce resources as needed. This flexibility helps manage varying workloads without upfront infrastructure investment. It is ideal for startups and enterprises with fluctuating demands.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Since resources are shared among multiple users, the public cloud operates on a pay-as-you-go model. Guide to Cloud Security eliminates the need for costly hardware and maintenance, making it a budget-friendly solution. Companies only pay for what they use, optimizing expenses.
- Easy Deployment & Management: Public cloud platforms provide user-friendly interfaces and automated tools for quick deployment. IT teams can manage applications remotely without worrying about physical hardware. This makes it convenient for businesses to launch and scale their services efficiently.
- Security & Compliance: Leading public cloud providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and compliance certifications. Although security concerns exist due to shared infrastructure, providers continuously enhance protection. Businesses can leverage built-in security features for safe operations.
- Wide Accessibility & Global Reach: Public cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and global collaboration. Data centers in multiple locations ensure low latency and high availability. This makes it suitable for businesses operating in different regions.
- Balanced Flexibility & Security: A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud environments, allowing businesses to balance scalability and security. Sensitive data can be stored in a private cloud, while less critical operations run on a public cloud. This approach enhances data protection without sacrificing agility.
- Cost Optimization & Resource Efficiency: Organizations can optimize costs by using public cloud resources for dynamic workloads while keeping critical operations in a private cloud. This reduces infrastructure expenses while ensuring optimal performance. It also allows businesses to scale resources without overprovisioning.
- Improved Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity: A hybrid cloud enables seamless backup and disaster recovery solutions by distributing data across multiple environments. Amazon Lightsail Uncovered Simplified Cloud Hosting of failure, workloads can be shifted between clouds, ensuring minimal downtime. This approach enhances resilience and reliability for businesses.
- Enhanced Performance & Scalability: Hybrid cloud models provide the ability to scale applications dynamically based on demand. Businesses can leverage the public cloud for high-traffic periods while maintaining stable performance through the private cloud. This ensures efficiency and better resource utilization.
- Seamless Integration & Workload Distribution: Companies can integrate on-premise infrastructure with cloud services, allowing smooth workload transitions. This flexibility supports cloud bursting, where excess traffic is handled by the public cloud. It is ideal for enterprises with fluctuating computing demands.
- Consider Security and Compliance: If you handle sensitive data or are subject to strict regulations (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR), a private cloud or hybrid cloud may be the best option to maintain control over data security.
- Evaluate Flexibility and Scalability Needs: If your organization experiences fluctuating workloads or requires rapid scalability, a public or hybrid cloud model may provide the agility needed.
- Cost Constraints: Public clouds tend to be more cost-effective, especially for startups or smaller organizations, as they don’t require significant upfront investment in infrastructure.
- Collaboration: If your organization works with other entities in a specific industry or regulatory framework, a community cloud may provide a cost-effective and secure environment for shared resources.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cloud Computing Certificate? View The Cloud Computing Online Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a dedicated cloud computing environment exclusively used by a single organization, offering enhanced security, control, and customization. Unlike public clouds, private clouds operate on either on-premises data centers or third-party-hosted infrastructures, ensuring that resources are not shared with other entities. This model provides businesses with complete authority over their IT infrastructure, allowing them to implement strict security protocols, regulatory compliance measures, and custom configurations to suit specific needs. Private clouds deliver superior performance since computing resources are not affected by external users, resulting in lower latency and greater reliability. Industries dealing with sensitive data, such as healthcare, finance, and government agencies, benefit significantly from private clouds due to their robust security features and compliance adherence. Although the initial investment and maintenance costs are higher compared to Cloud Computing Platforms and Services, organizations gain long-term cost efficiency by avoiding recurring subscription fees and tailoring infrastructure according to their workload demands. Private clouds also support seamless integration with existing IT systems, enabling businesses to modernize their operations without completely overhauling their technology stack. With increased flexibility, scalability, and operational efficiency, private clouds are an ideal choice for enterprises seeking full control over their cloud environment while ensuring data privacy, reliability, and high performance.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cloud Computing? Enroll in the Cloud Computing Masters Course Today!
Hybrid Cloud
Community Cloud
A Community Cloud is a shared cloud infrastructure designed for multiple organizations with common goals, requirements, or regulatory concerns. It allows businesses within the same industry, such as healthcare, finance, education, or government sectors, to collaborate while maintaining better security and compliance than a public cloud. Since the infrastructure is jointly owned or managed, costs are distributed among the participating organizations, making it more affordable than a private cloud while offering greater control. One of the key advantages is its ability to ensure industry-specific compliance, as the cloud is tailored to meet regulatory standards and security policies relevant to the sector. Additionally, Cloud Computing Course enable efficient collaboration by allowing organizations to share data, applications, and resources, reducing duplication of efforts and fostering innovation. Despite being a shared model, it provides scalability and customization, ensuring that each organization can adjust resources based on its unique needs. This approach optimizes operational efficiency, enhances data privacy, and offers a cost-effective solution for businesses with similar security, compliance, and performance requirements.
Choosing the Right Cloud Deployment Model
Go Through These Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
The Future of Cloud Deployment Models
The future of cloud deployment models is evolving with advancements in artificial intelligence, edge computing, and hybrid multi-cloud strategies. As businesses demand greater flexibility, hybrid and multi-cloud adoption will increase, allowing organizations to seamlessly integrate public, private, and on-premise infrastructure for optimized performance. Edge computing will play a crucial role by processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making, especially in IoT and AI-driven applications. Hybrid Cloud Hypervisors for Scalability and compliance enhancements will remain a priority, with stricter data privacy regulations pushing cloud providers to develop more robust security frameworks and industry-specific compliance solutions. Serverless computing and automation will further transform cloud deployment by reducing infrastructure management complexities and enabling businesses to focus on innovation. Additionally, advancements in quantum computing and AI-driven cloud management will enhance efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. As cloud technology continues to mature, deployment models will become more adaptable, ensuring businesses can meet the growing demands of digital transformation while maintaining security, performance, and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Cloud deployment models play a crucial role in shaping how organizations manage and utilize cloud resources, ensuring efficiency, security, and scalability. Businesses must carefully evaluate their requirements when choosing between a public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, or community cloud, as each model offers distinct advantages and trade-offs. Public clouds provide cost-effective, scalable solutions with minimal maintenance but may raise security concerns due to shared infrastructure. Private clouds offer enhanced control and data privacy, making them ideal for industries with strict regulatory requirements, though they require significant investment. Hybrid clouds blend the flexibility of public clouds with the security of private clouds, allowing businesses to optimize workloads dynamically. Cloud Computing Course , on the other hand, enable collaboration among organizations with similar needs, ensuring compliance and cost-sharing benefits. Selecting the right deployment model depends on factors such as data sensitivity, compliance mandates, cost considerations, and performance expectations. By understanding these models, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their cloud strategy and IT infrastructure goals.





