
- Introduction to Mobile Cloud Computing
- Benefits of Mobile Cloud Computing
- Mobile Cloud Architecture
- Challenges in Mobile Cloud Computing
- Mobile Cloud Storage Solution
- Key Features of Mobile Cloud Storage
- Future Trends in Mobile Cloud Computing
- Conclusion
Introduction to Mobile Cloud Computing
Mobile Cloud Computing (MCC) is a transformative technology that integrates cloud computing and mobile computing to enhance the capabilities of mobile devices by leveraging cloud-based resources. The primary objective of MCC is to provide users with high-performance computing and storage without the constraints of mobile hardware limitations. As mobile applications become more complex and data-intensive, MCC ensures seamless access to computational power and storage via cloud servers, reducing the burden on mobile devices, a concept thoroughly explored in the Cloud Computing Course. MCC enables mobile users to run applications on cloud infrastructure instead of on local device hardware, improving efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Applications such as mobile gaming, healthcare monitoring, real-time data analytics, and enterprise solutions leverage MCC to offer an enhanced user experience. The integration of MCC with emerging technologies like 5G, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) is further driving its adoption.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
Benefits of Mobile Cloud Computing
- Reduced Processing Load – Offloading computational tasks to cloud servers reduces the workload on mobile devices, leading to better performance and a smoother user experience.
- Scalability – Cloud services provide scalable resources, allowing applications to handle fluctuating demands without compromising performance.
- Extended Battery Life – By outsourcing processing tasks to the cloud, MCC minimizes energy consumption on mobile devices, extending battery life.
- Data Synchronization – Users can access synchronized data across multiple devices in real-time, ensuring a seamless experience, powered by various Cloud Technologies.
- Cost-Effectiveness – MCC reduces the need for high-end mobile hardware by leveraging cloud-based storage and computing power.
- Enhanced Security – Centralized cloud storage solutions incorporate encryption, authentication, and data backup mechanisms to ensure robust security.
- Faster Development & Deployment – Developers can build and deploy applications rapidly using cloud-based platforms, reducing time-to-market.
- Real-time Access to Applications – Cloud-hosted applications can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, improving accessibility and flexibility.
Mobile Cloud Architecture
The architecture of Mobile Cloud Computing consists of three primary layers: Mobile Devices, Cloud Services, and Network Infrastructure. Each layer plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless connectivity and performance.
Mobile Devices (Client Layer):
These include smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices that interact with cloud-based applications and services. Mobile devices function as thin clients that offload computational tasks to the cloud while providing an intuitive user interface. This design allows users to access powerful applications without requiring substantial local processing power. The client layer primarily facilitates interaction between the end-user and the cloud, leveraging the cloud’s resources for tasks such as data storage, processing, and analytics. Mobile devices typically run applications optimized for touch interfaces, enabling a seamless experience across different platforms, with the added security benefits of DevSecOps integration. Additionally, these devices often utilize wireless networks (such as Wi-Fi, 4G, or 5G) to maintain constant communication with the cloud, ensuring real-time access to services and data updates. The integration of sensors, GPS, and cameras in mobile devices further enhances their capability to interact with cloud services in ways that extend beyond traditional computing devices.
Cloud Services (Backend Infrastructure):
The cloud layer consists of various cloud-based resources such as virtual machines, storage, databases, and application servers. This layer provides on-demand computing power and storage to mobile applications. Cloud services are categorized into three main models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized hardware resources such as servers, storage, and networking.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a cloud-based development platform for building and deploying applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers cloud-based applications that users can access via mobile devices.
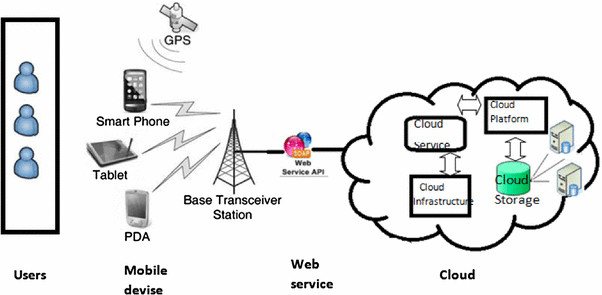
Network Infrastructure (Communication Layer):
This layer ensures secure and efficient communication between mobile devices and cloud services. It consists of wireless networks, mobile internet (4G/5G), and content delivery networks (CDNs) to optimize data transfer and minimize latency. These networks enable continuous, high-speed data exchange, which is essential for real-time applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and collaborative tools. The infrastructure is designed to handle large volumes of data while maintaining security protocols, such as encryption and authentication, to protect user privacy. Network reliability and coverage are critical to prevent disruptions, especially in remote or densely populated areas, ensuring users have a smooth and uninterrupted experience. Additionally, edge computing technologies can be integrated into this layer to further reduce latency by processing data closer to the user, enhancing overall performance and responsiveness. The seamless integration of these layers enables users to run high-performance applications without overloading their mobile devices, making MCC a preferred solution for modern mobile computing needs.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
Challenges in Mobile Cloud Computing
Despite its numerous advantages, MCC faces several challenges that impact its widespread adoption. Some of the most significant challenges include:
- Network Latency – Dependence on internet connectivity can result in delays, affecting application performance, especially in regions with poor network coverage.
- Security Risks – Data transmitted between mobile devices and cloud servers is vulnerable to cyber threats such as hacking, data breaches, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
- Energy Consumption – Continuous data transmission between mobile devices and cloud servers can lead to high energy consumption, draining device batteries quickly.
- Data Privacy Concerns – Storing sensitive user data on cloud servers raises privacy concerns, necessitating stringent encryption and access control measures.
- Service Reliability – Mobile cloud applications rely on third-party cloud providers, making them susceptible to downtime, outages, and service disruptions, which can be exacerbated by threats such as Cyber Extortion.
- Integration Complexity – Ensuring compatibility between various mobile operating systems, cloud platforms, and network protocols can be complex and time-consuming.
- Bandwidth Constraints – Cloud-based applications require a stable and high-speed internet connection, which may not always be available in remote or rural areas.
- Regulatory Compliance – Adhering to data protection laws and industry regulations (such as GDPR, HIPAA) poses challenges for businesses leveraging MCC.
- Scalability Issues – While cloud services are generally scalable, ensuring that mobile cloud applications can efficiently handle a large number of users or rapid growth in data volume can be challenging. This requires continuous optimization of resources and infrastructure.
- Cost Management – The cost of mobile cloud services can accumulate over time, especially with frequent data transfers, large storage needs, or enterprise-level usage. Managing these costs effectively while ensuring a good user experience can be a significant challenge for both businesses and individual users.
Addressing these challenges requires continuous advancements in cloud security, network optimization, and energy-efficient mobile computing technologies.
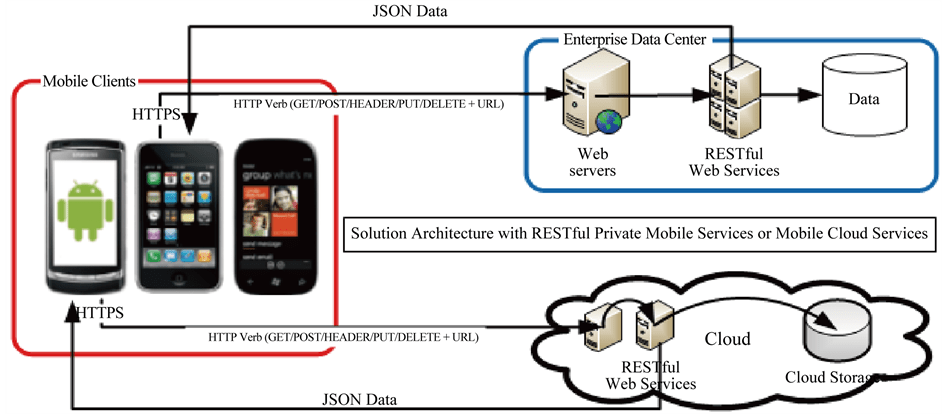
Mobile Cloud Storage Solutions
Mobile cloud storage solutions enable users to store, access, and manage their data remotely via cloud-based platforms. These solutions provide scalability, security, and seamless synchronization across multiple devices. Offers cloud storage, real-time collaboration, and file sharing capabilities integrated with Google Workspace. Provides cloud storage, automatic backups, and seamless file synchronization across devices, as covered in the Cloud Computing Course. Apple’s cloud storage solution that allows users to store photos, documents, and app data securely. Microsoft’s cloud storage service that integrates with Windows and Microsoft 365 applications. A scalable cloud storage service designed for developers and enterprises needing high-performance storage. A secure cloud storage platform with robust data protection and collaboration features.
Known for offering a generous amount of free storage and end-to-end encryption, Mega provides a secure platform for storing and sharing large files. A privacy-focused cloud storage solution that ensures end-to-end encryption, offering secure file storage and sharing for both personal and business use. A cloud storage service that combines user-friendly features with strong encryption options, allowing users to store files securely and access them from any device. A highly secure cloud storage platform with end-to-end encryption, aimed at individuals and businesses that prioritize privacy and data protection. It offers strong file sharing and collaboration features as well.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Cloud Computing Master’s Degree? Enroll For Cloud Computing Masters Course Today!
Key Features of Mobile Cloud Storage:
- Automatic Backup & Sync – Ensures that files are regularly backed up and accessible across all devices.
- Encryption & Security – Cloud storage providers use encryption and access control mechanisms to protect user data.
- Cross-Platform Access – Users can access files from multiple devices, including smartphones, tablets, and desktops.
- File Versioning & Recovery – Allows users to retrieve previous versions of files and recover deleted data.
- Offline Access – Enables users to download and access files even without an internet connection, with the support of Docker Swarm for efficient container orchestration.
- Collaboration Tools– Cloud storage services often include features like real-time editing, file sharing, and commenting, making it easier for teams to collaborate on documents and projects.
- Scalability – Many cloud storage solutions offer flexible plans that allow users to increase or decrease storage capacity as their needs change, making it suitable for both individuals and businesses.
- Automatic File Synchronization – Cloud services ensure that any changes made to files are automatically synced across all devices, providing seamless access and updated versions without manual intervention.
- Access Control & Permissions – Users can set permissions to control who can view, edit, or share their files, helping to manage privacy and security within shared folders or documents.
- Cost Efficiency – With pay-as-you-go models or tiered storage plans, users only pay for the amount of storage they need, offering more affordable solutions compared to traditional storage methods.
The widespread adoption of mobile cloud storage solutions has revolutionized data management, enabling users to securely store and access their files anytime, anywhere.
Future Trends in Mobile Cloud Computing
The rapid evolution of cloud and mobile technologies is shaping the future of MCC. The rollout of 5G networks will significantly enhance the performance of mobile cloud applications by reducing latency and increasing data transfer speeds. Processing data closer to the user (at the edge of the network) will reduce latency and improve real-time processing capabilities. AI-driven cloud services will enable smarter mobile applications, including voice recognition, image processing, and predictive analytics. Blockchain-based cloud solutions will enhance data security and privacy by providing decentralized and tamper-proof storage, with the integration of AWS State Machine to automate and manage workflows securely. The adoption of server less architectures will enable developers to build and deploy applications without managing server infrastructure. As IoT devices increase, MCC will play a vital role in processing and analyzing vast amounts of IoT-generated data. Cloud-based AR/VR applications will become more prevalent, enabling immersive experiences on mobile devices. The potential integration of quantum computing with MCC will revolutionize data processing capabilities. The combination of 5G networks and cloud computing will make cloud gaming more accessible by offering ultra-low latency and seamless experiences on mobile devices. The rise of cloud-native development will enable faster, more scalable mobile applications that are continuously updated and optimized for performance, resilience, and flexibility. The future of MCC is promising, with continuous innovations driving new possibilities for mobile applications and services. As cloud computing, AI, and network technologies advance, MCC will remain at the forefront of digital transformation.
Preparing for Cloud Computing Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Mobile Cloud Computing is a game-changing technology that bridges the gap between mobile computing and cloud services, enabling high-performance applications and seamless data access. With its numerous benefits, including scalability, security, and cost-efficiency, MCC is widely adopted across industries. However, challenges such as network latency, security risks, and energy consumption must be addressed for widespread implementation, as explored in the Cloud Computing Course. As emerging technologies like 5G, AI, and edge computing continue to evolve, MCC will play a crucial role in shaping the future of mobile applications, offering limitless possibilities for innovation.





