
- Introduction to Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Models
- Cloud Computing Architecture
- Cloud Deployment Models
- Cloud Services and Solutions
- Cloud Security and Compliance
- Cloud Migration Strategies
- Cloud Monitoring and Management
- Cloud Development and DevOps in the Cloud
- Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Use Cases and Real-World Applications
- Cloud Certification and Career Paths
- Why Cloud Computing?
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the Internet. It eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure and allows businesses to scale their operations flexibly based on demand. Cloud Computing Courses offers benefits such as cost savings, scalability, flexibility, reliability, and access to advanced technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence. It allows businesses to avoid the high costs of physical infrastructure and maintenance.
To Explore Cloud Computing in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cloud Computing Online Course To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Cloud Computing Models
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): provides virtualized computing resources such as virtual machines and storage. Examples include AWS EC2 and Google Compute Engine.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): This type of service offers hardware and software tools over the Internet, typically used for developing applications. Examples include Google App Engine and Microsoft Azure.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Delivers software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis. Example: Google Workspace, Microsoft Office 365.
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): Offers a comprehensive range of services, including computing power (EC2), storage (S3), databases (RDS), and more.
- Azure: Microsoft’s cloud platform that offers services like virtual machines, databases, and developer tools.
- GCP (Google Cloud Platform) Google’s cloud infrastructure, offering services such as computing, storage, and machine learning tools.
- Object storage (e.g., Amazon S3): Suitable for unstructured data like files and images.
- Block storage (e.g., Amazon EBS): Used for structured data and performance-intensive applications.
- File storage (e.g., Amazon EFS): Provides file-based storage for shared access.
- Cloud Security Fundamentals:Cloud security includes practices, technologies, and policies that protect data and applications in the cloud. This includes encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and vulnerability management.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM):IAM controls who can access cloud resources and what actions they can perform. It uses authentication methods such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC).
- Data Security and Encryption in the Cloud: Encryption ensures that sensitive data remains protected while stored (at rest) and during transmission (in transit). Cloud Computing Courses providers offer encryption tools and key management services.
- Cloud Compliance Standards (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.): Cloud services must comply with data protection laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), to ensure that sensitive data is handled properly.
- Cloud Monitoring Tools and Techniques: Cloud monitoring tools track the performance, health, and resource usage of cloud services. Examples include AWS Cloud Watch, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Operations Suite.
- Resource Allocation and Scaling: Cloud services offer automatic scaling based on demand, ensuring that resources are provisioned when needed and de-provisioned during low-demand periods. This is often achieved through auto-scaling groups.
- Performance Optimization: Cloud performance optimization ensures that cloud resources are utilized efficiently. This can include tuning virtual machines, optimizing storage usage, and leveraging caching mechanisms.
- Fault Tolerance and Disaster Recovery in the Cloud: Cloud platforms offer services like backup and disaster recovery (e.g., AWS Backup, Azure Site Recovery) to ensure data availability in case of failures, reduce downtime, and improve business continuity.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing moves computation closer to the data source (e.g., IoT devices), reducing latency and bandwidth usage by processing data locally before sending it to the cloud.
- Cloud AI and Machine Learning Services: Cloud platforms offer AI and ML services such as AWS Sage Maker, Azure Machine Learning, and Google AI to help businesses build and deploy intelligent applications.
- Blockchain and Cloud Integration: Cloud providers are integrating blockchain technologies, enabling secure and transparent data transactions within cloud applications.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies: Organizations are increasingly adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies to avoid vendor lock-in, improve resilience, and optimize performance by using multiple cloud providers.
- Cloud Certifications (AWS, Azure, GCP): Certifications like AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator, and Google Professional Cloud Architect validate a professional’s expertise in cloud technologies.
- Cloud Architect, Engineer, and Administrator Roles: Cloud architects design cloud infrastructure, engineers build and maintain cloud applications, and administrators manage cloud resources and services
- Job Opportunities and Career Growth in Cloud Computing: The demand for cloud professionals is growing rapidly. With the rise of cloud adoption, careers in cloud computing offer high growth potential and lucrative salaries across various industries.
Cloud Computing Architecture
Cloud architecture typically includes a three-tier system: the infrastructure layer (hardware), the platform layer (services and tools), and the application layer (the software that users interact with).Virtualization is the key technology behind cloud infrastructure. It allows multiple virtual servers to run on physical hardware, optimizing resource usage and allowing for scalable and flexible cloud environments, which is a fundamental concept in What is Utility Computing Cloud storage options include:
Cloud Network and Security Architecture
The cloud network architecture includes virtual networks, load balancers, and firewalls to control and secure data flow, which can be effectively managed with tools like Docker in Linux Software Development for streamlined containerization and deployment. Cloud security architecture ensures that data is protected at rest and in transit using encryption and authentication techniques.
Cloud Deployment Models
Public Cloud infrastructure that is owned and operated by a third-party cloud provider and is available to the general public. Examples: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud.Private Cloud environment used exclusively by one organization provides greater control and security. It can be hosted internally or by a third-party provider.Hybrid Cloud is a combination of public and private cloud infrastructures that allows data and applications to be shared between them. This offers greater flexibility and optimization of existing infrastructure. Community Cloud has Several organizations with similar interests or requirements, such as security or compliance, need to use a shared cloud infrastructure.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
Cloud Services and Solutions
Cloud computing services allow businesses to rent virtual machines (VMs) and other computational resources for running applications. Examples include AWS EC2 and Azure Virtual Machines. Cloud storage services offer scalable storage solutions, such as Amazon S3 (object storage), Azure Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Storage. Cloud providers offer fully managed database as a service allowing organizations to use databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB without managing the underlying infrastructure. Cloud networking services allow the creation of virtual networks, load balancing, and setting up secure communication between different services and applications. Serverless computing abstracts server management, allowing developers to focus solely on writing code without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. An example is AWS Lambda.
Cloud Security and Compliance
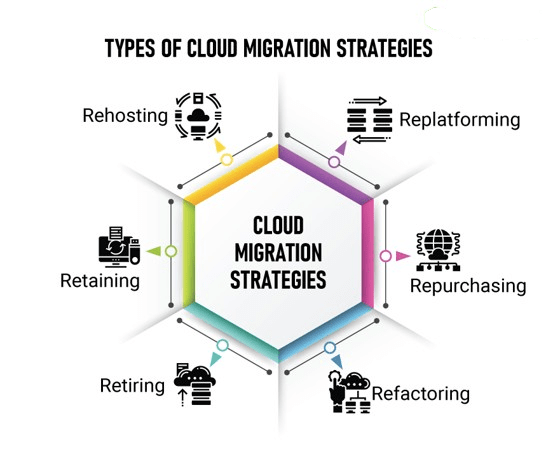
Cloud Migration Strategies
Cloud Adoption and Migration Planning involves assessing the current infrastructure, deciding on the best migration strategy, and moving workloads to the cloud. Strategies include “lift and shift,” re-platforming, and re-architecting. Tools like AWS Migration Hub, Azure Migrate, and Google Cloud Migrate for Compute Engine help businesses move data and applications to the cloud with minimal disruption, leveraging Key Cloud Computing Characteristics such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. Cloud cost optimization involves managing cloud resources efficiently, using tools like AWS Cost Explorer or Azure Cost Management to minimize unnecessary expenses. Real-world case studies demonstrate successful cloud migration strategies, focusing on cost savings, improved scalability, and performance optimization.
Cloud Monitoring and Management
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cloud Computing? Enroll in the Cloud Computing Masters Course Today!
Cloud Development and DevOps in the Cloud
Cloud application development involves using cloud services such as containers (Docker, Kubernetes), APIs, and microservices to build scalable, resilient applications. DevOps practices involve collaboration between development and operations teams to automate and streamline the deployment pipeline. Cloud environments provide the tools necessary for DevOps workflows, including version control, automated testing, and continuous integration, with Docker Swarm enabling efficient container orchestration and management. CI/CD pipelines automate the process of integrating code changes, testing them, and deploying them to production. This process is essential for maintaining code quality and accelerating software delivery. IaC allows for managing and provisioning cloud resources using code (e.g., Terraform, AWS Cloud Formation), automating infrastructure setup, and ensuring consistency.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing Use Cases and Real-World Applications
Cloud computing enables enterprises to scale their IT infrastructure quickly, enhance collaboration, and innovate with the latest technologies without heavy capital investment. Cloud solutions in healthcare enable remote monitoring and secure data sharing, while in finance, they ensure safe transactions and data storage. E-commerce platforms use the cloud to scale services and enhance customer experiences, while ensuring compliance and security through tools like Azure Policy. The cloud supports IoT applications by providing scalable storage, processing power, and real-time analytics for connected devices. Several industry leaders (e.g., Netflix, Spotify, and Uber) use cloud services to enhance their operations, demonstrating the benefits of scalability, cost reduction, and operational flexibility.
Cloud Certification and Career Paths
Preparing for Cloud Computing Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer To Ace Your Interview!
Why Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing has become a fundamental part of modern technology because it offers unmatched flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. By leveraging cloud services, businesses can access powerful computing resources without the need to invest in expensive hardware or manage complex IT infrastructures. This shift allows companies to scale up or down based on demand, improving operational efficiency and reducing costs, a key concept taught in Cloud Computing Courses. Additionally, cloud computing enables greater collaboration, as data and applications can be accessed from anywhere, at any time, fostering innovation and productivity. The security, disaster recovery capabilities, and rapid deployment of cloud platforms also ensure that businesses stay competitive and resilient in an increasingly digital world. With its ability to drive growth, enhance agility, and support global operations, cloud computing is a game-changer for organizations across all industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cloud Computing course equips students with the theoretical foundations and practical skills required to understand and apply cloud technologies effectively. By covering key areas such as cloud architecture, services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), cloud deployment models, and security considerations, the course prepares individuals for careers in cloud engineering, cloud architecture, and cloud services management. With the growing dependence on cloud infrastructures by businesses worldwide, the course provides valuable insights and hands-on experience, making it a crucial stepping stone for anyone interested in pursuing a career in the tech industry. The knowledge gained can be applied to real-world problems, ensuring that students are well-prepared to address challenges and innovations within the ever-evolving cloud space.





