
- Introduction to Cloud Computing
- History and Evolution of Cloud Computing
- Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Service Models
- Cloud Deployment Models
- Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Challenges and Risks in Cloud Computing
- Major Cloud Providers
- Cloud Security and Compliance
- Future Trends in Cloud Computing
- Use Cases of Cloud Computing in Different Industries
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has transformed the way organizations and individuals access and manage technology resources. It refers to the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and more over the Internet, commonly known as “the cloud.” Instead of investing in and maintaining physical hardware, users can access these resources on-demand from cloud service providers, paying only for what they use. This model offers numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, scalability, flexibility, and accessibility. Businesses can quickly scale resources up or down based on their needs, without the delays and costs associated with traditional IT infrastructure. Cloud Computing Course also reduces the burden of infrastructure management, allowing IT teams to focus more on strategic initiatives and innovation. Whether used by startups, large enterprises, or governments, cloud computing supports faster deployment, improved collaboration, and access to cutting-edge technology. As a result, it continues to be a driving force behind digital transformation across industries.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cloud Computing Certificate? View The Cloud Computing Online Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
History and Evolution of Cloud Computing
The concept of cloud computing is not entirely new; its roots can be traced back to the early days of computing. The idea of shared computing resources can be traced to the 1960s when computer scientist John McCarthy proposed that “computation may someday be organized as a public utility.” In the 1970s, time-sharing systems emerged, allowing multiple users to access computing resources remotely. However, the modern form of cloud computing began to take shape in the late 1990s and early 2000s, when internet and broadband access became more widespread. In 1999, Salesforce introduced one of the first SaaS (Software as a Service) models by offering online customer relationship management (CRM) software. The idea of renting out software rather than purchasing and installing it on individual machines was groundbreaking.
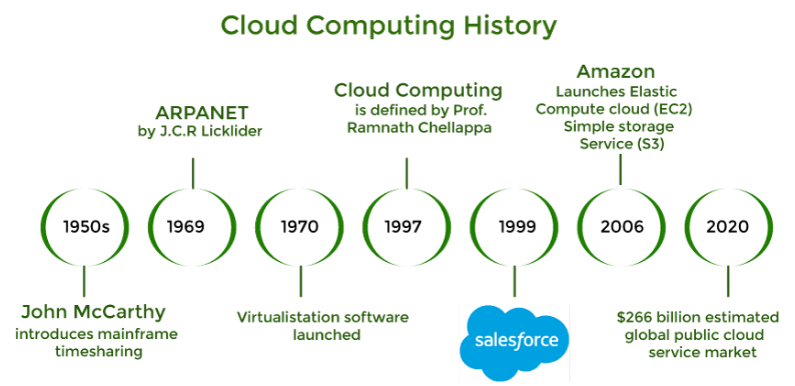
In 2006, Amazon launched Amazon Web Services (AWS), providing businesses with on-demand computing resources like storage and processing power. This marked the beginning of cloud computing as we know it today. Over the next few years, Google and Microsoft followed suit with their cloud offerings, Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure. Cloud computing evolved in response to businesses’ growing need to scale quickly, reduce costs, and increase flexibility. Today, it has grown to include everything from infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) to platform-as-a-service (PaaS) and software-as-a-service (SaaS), becoming a ubiquitous part of modern IT strategy.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- On-Demand Self-Service: Users can access computing resources as needed without requiring human intervention from the service provider. They can provision, manage, and scale resources through a web-based interface.
- Broad Network Access: Cloud services are accessible over the Internet from any device with network connectivity, allowing users to interact with services from virtually anywhere.
- Resource Pooling: Cloud providers use multi-tenant models to pool resources and distribute them dynamically to customers based on demand. This helps optimize efficiency and resource utilization a concept often discussed when explaining What is AWS Systems Manager.
- Rapid Elasticity: Cloud computing enables resources to be rapidly scaled up or down according to demand. This means businesses can easily handle surges in traffic or compute requirements without investing in permanent infrastructure.
- Measured Service: Cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go model, where users only pay for the resources they use. This helps optimize cost efficiency and prevents over-provisioning.
- Multi-Tenancy: Cloud computing allows multiple users (tenants) to share the same physical infrastructure while maintaining data privacy and security. This maximizes resource usage and reduces costs for the provider.
Cloud Computing Service Models
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. It allows businesses to rent servers, storage, networking, and other computing resources without investing in physical hardware. Users can scale up or down their resources as needed, making it ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads. Popular IaaS providers include Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform that enables developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS offerings include operating systems, middleware, development tools, and databases, all managed by the provider a feature that can be explored in relation to AWS Artifact. This allows developers to focus solely on building and deploying applications. Key PaaS providers include Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Services, and Heroku.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers fully functional applications over the Internet. The service provider hosts and maintains these applications, which are typically accessed through a web browser. SaaS eliminates the need for businesses to purchase and manage software installations, updates, and hardware. Popular SaaS solutions include Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Dropbox, and Salesforce.
To Explore Cloud Computing in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cloud Computing Online Course To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud computing can be deployed in various ways, depending on an organization’s specific needs, security requirements, and scalability goals. The most common cloud deployment models include public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and multi-cloud. Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. They can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider, but all infrastructure is used solely by that organization. This model offers enhanced control over security, compliance, and data privacy, making it ideal for industries with strict regulatory demands. Hybrid clouds blend public and private environments, allowing data and applications to move between them.
These services are available to the general public or large industry groups, offering cost-efficiency and scalability by sharing computing resources across multiple users a capability that can be integrated with Amazon AWS Directory Service. Private clouds, on the other hand, are dedicated exclusively to a single organization. This approach offers greater flexibility and allows organizations to optimize existing infrastructure by keeping sensitive workloads on private clouds and leveraging public clouds for less critical tasks. Lastly, multi-cloud strategies involve using services from multiple cloud providers. This helps prevent vendor lock-in, enhances resilience, and allows organizations to tailor solutions to specific requirements while distributing risk and improving uptime.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing eliminates the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure. Instead, users pay for the resources they use on a subscription or pay-per-use basis.
- Scalability: Cloud services allow businesses to scale resources up or down according to demand, ensuring they only pay for their use.
- Flexibility and Mobility: Cloud services are accessible from any internet-enabled device, allowing users to work from anywhere and collaborate in real time.
- Disaster Recovery: Many cloud providers offer built-in backup and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring that data is safe and can be restored quickly in an emergency.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud providers handle software updates, patches, and maintenance, ensuring that users can always access the latest features and security fixes.
- Security: Leading cloud providers offer advanced security measures, including encryption, authentication, and compliance with various industry standards, to protect user data.
Challenges and Risks in Cloud Computing
Despite its numerous benefits, cloud computing does come with several challenges and risks:
- Data Security and Privacy: Storing sensitive data on third-party servers raises concerns about security breaches, data theft, and compliance with privacy regulations.
- Downtime and Reliability: Although cloud providers offer high availability, service interruptions or outages are always risky, which can affect business operations.
- Vendor Lock-in: Switching cloud providers can be difficult due to proprietary technologies, data transfer limitations, and integration challenges, leading to potential vendor lock-in a topic often addressed in Cloud Computing Course.
- Compliance: Organizations operating in regulated industries must ensure that their cloud provider complies with industry-specific regulations (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR).
- Cost Management: While cloud computing can reduce upfront costs, improper resource management or scaling can lead to unexpected expenses.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance for IoT (Internet of Things) devices and real-time applications.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Cloud platforms increasingly offer AI and ML services, enabling businesses to analyze large datasets and gain insights without managing complex infrastructure—a trend that complements the capabilities of the ELK Stack Powerful Logging.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing abstracts infrastructure management, allowing developers to focus purely on code. It offers automatic scaling and cost efficiency, making it ideal for specific use cases.
- Quantum Computing: While still in its early stages, quantum computing promises to solve complex problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers. Cloud providers are beginning to experiment with quantum computing services.
- Healthcare: Cloud-based systems enable electronic health records (EHR) management, telemedicine, and medical data storage, improving accessibility and collaboration.
- Finance: Cloud computing helps financial institutions streamline operations, improve customer experiences, and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Retail: Cloud-based e-commerce platforms and inventory management systems help retailers scale their businesses and enhance customer experiences.
- Education: Cloud Computing Course enables online learning platforms, collaboration tools, and data storage, making education more accessible to people around the world.
Looking to Master Cloud Computing? Discover the Cloud Computing Masters Course Available at ACTE Now!
Major Cloud Providers
Several major cloud service providers lead the industry, offering a wide range of services to meet the diverse needs of businesses and developers. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the largest and most widely adopted cloud platform globally. It provides a vast array of services, including computing power, storage, networking, databases, machine learning, and more. AWS is recognized for its scalability, high reliability, and extensive global infrastructure, making it a preferred choice for organizations of all sizes. Microsoft Azure is another prominent cloud platform, offering comprehensive services such as virtual machines, databases, analytics, and networking. It is especially favored by enterprises that already use Microsoft products, as Azure integrates seamlessly with tools like Office 365, Active Directory, and Windows Server, enhancing productivity and compatibility across environments. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is known for its strengths in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics. It offers infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) solutions. GCP is often chosen by organizations seeking advanced data processing capabilities and innovative AI-driven tools for business intelligence and automation a choice that aligns with best practices in a Guide to Cloud Security.
Cloud Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are critical concerns in cloud computing, as organizations increasingly rely on cloud services to store and manage sensitive data. To safeguard information, cloud providers implement a range of robust security measures. These typically include data encryption both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access, access control mechanisms to restrict who can view or modify data, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of protection for user accounts. In addition to technical safeguards, leading cloud providers also focus on compliance with industry regulations. They often obtain certifications and adhere to standards such as HIPAA for healthcare, PCI-DSS for finance, and FedRAMP for government data. These certifications help ensure that cloud services meet specific regulatory and legal requirements, giving customers confidence in the provider’s ability to protect sensitive information. By combining advanced security features with compliance assurance, cloud providers support organizations in maintaining data privacy, integrity, and regulatory readiness in today’s complex digital environment.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
Go Through These Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
Use Cases of Cloud Computing in Different Industries
Conclusion
Cloud computing has transformed the IT landscape by providing businesses and individuals with scalable, cost-efficient, and flexible solutions. With its wide range of service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and deployment options (public, private, hybrid, multi-cloud), cloud computing offers significant benefits, including cost savings, scalability, and flexibility. However, challenges such as security, compliance, and vendor lock-in must be carefully managed. Major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud continue to lead the market, while trends like edge computing, AI, and quantum computing shape the future of cloud computing. As cloud adoption grows, its impact will be felt across industries and geographies, driving innovation and digital transformation.





