
- Introduction to Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
- Key Features of Azure VNet
- Benefits of Using Azure VNet
- How Azure VNet Works
- Setting Up an Azure Virtual Network
- Integrating Azure VNet with Other Azure Services
- Azure VNet vs. Traditional Networking
- Use Cases of Azure VNet
- Security and Compliance in Azure VNet
- Pricing and Cost Management
- Conclusion
Introduction to Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is the fundamental building block for private networking in Microsoft Azure Training . It enables many types of Azure resources, such as Azure Virtual Machines (VMs), to securely communicate with each other, the internet, and on-premises networks. VNet is akin to a traditional network that you’d operate in your own data center but brings with it the scalability, availability, and isolation of Azure’s infrastructure. With Azure VNet, organizations can establish secure and seamless hybrid cloud connectivity using VPN Gateway or ExpressRoute, ensuring reliable communication between cloud and on-premises environments. VNet allows the segmentation of networks using subnets, enabling better organization, security, and management of resources. It also supports network security mechanisms such as Network Security Groups (NSGs) and Azure Firewall, which help protect against unauthorized access and threats. Additionally, VNet integrates with Azure services like Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), Azure App Service Environments, and Azure Bastion, ensuring secure and efficient cloud networking. By leveraging VNet, businesses can build robust, flexible, and scalable cloud infrastructures.
Thrilled to Achieve Your AWS Certification?View The Microsoft Azure Course Available Now Through ACTE!
Key Features of Azure VNet
- Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is a fundamental building block for private networking in Azure, allowing organizations to create isolated and highly secure cloud environments. It provides complete control over IP address allocation, subnet configurations, and security policies, ensuring seamless integration with on-premises networks and other cloud environments.
- One of the key advantages of Azure VNet, as highlighted in the Microsoft Azure Course , is its ability to support subnet segmentation. This feature enables businesses to create logically separated networks, enhancing security and manageability. Additionally, private IP addressing within the VNet ensures secure internal communication by assigning unique IPs to resources, effectively preventing exposure to the public internet.
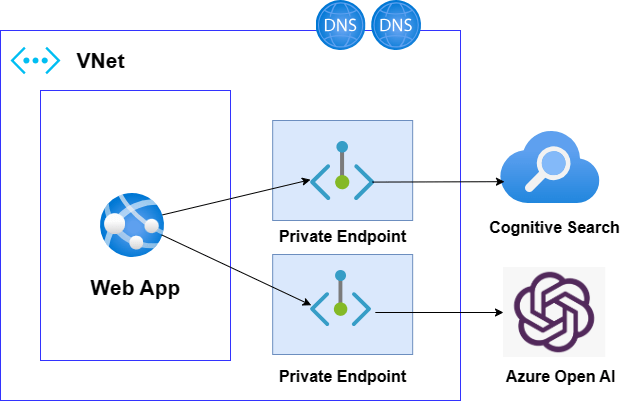
- For enhanced security, Network Security Groups (NSGs) act as virtual firewalls, allowing administrators to define rules that regulate inbound and outbound traffic at both the subnet and NIC levels. This helps in minimizing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive workloads.
- To establish secure, cross-premises connectivity, Azure VNet offers a VPN Gateway, which facilitates encrypted connections between Azure and on-premises networks. VNet Peering enables seamless communication between VNets, even across different regions, providing a scalable and efficient network topology.
- Additionally, Azure DNS ensures reliable name resolution for virtual machines and other resources within the network, improving accessibility and connectivity. With these features, Azure VNet delivers a robust, scalable, and secure networking solution for modern cloud environments.
Benefits of Using Azure VNet
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is a fundamental building block in Microsoft Azure in Cloud Computing Course networking architecture, enabling organizations to create private, isolated, and highly secure environments for their workloads. It provides full control over networking configurations, including IP address spaces, subnetting, routing, and network security groups, allowing businesses to design network topologies that align with their specific requirements. One of the key benefits of Azure VNet is its seamless integration with on-premises networks through VPN gateways and Azure ExpressRoute. This hybrid networking capability ensures a consistent and secure connection between on-premises data centers and cloud resources, facilitating smooth cloud adoption without compromising security or performance. Additionally, Azure VNet supports peering, which allows multiple VNets to communicate with low latency and high throughput, making it an ideal solution for enterprises with distributed workloads. Azure VNet also enhances security by incorporating Network Security Groups (NSGs) and Azure Firewall, enabling administrators to enforce strict access controls, segment traffic, and prevent unauthorized access. It supports service endpoints and private links to securely connect Azure resources without exposing them to the public internet. With built-in DDoS protection and traffic filtering capabilities, Azure VNet helps businesses maintain a robust security posture while optimizing network performance and scalability.
Interested in Obtaining Your Microsoft Azure Certificate? View The Microsoft Azure Online Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
How Azure VNet Works
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is a fundamental component of Azure’s cloud networking infrastructure, providing a secure and isolated environment for deploying and managing resources. It operates similarly to traditional on-premises networks but with enhanced scalability, flexibility, and integration with Azure services. Organizations use VNets to create a logically isolated network, enabling secure communication between Azure resources, on-premises environments, and the Internet.
- Define IP Address Space: Users specify a private IP address range using CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) notation. This ensures that resources within the VNet can communicate securely while avoiding IP conflicts.
- Create Subnets: The allocated IP space is divided into multiple subnets, allowing for better resource segmentation, improved security, and efficient traffic management.
- Deploy Resources: Azure resources such as Virtual Machines (VMs), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and databases can be deployed within the subnets, enabling seamless communication within the network.
- Configure Routing: Route tables define how traffic flows between subnets and external networks, ensuring proper connectivity and optimized performance.
- Apply Security: Network Security Groups (NSGs) and Azure Firewall provide security by controlling inbound and outbound traffic and protecting applications from unauthorized access and threats.
- Additionally, Introduction to amazon gateway highlights AWS connectivity solutions like Transit Gateway and API Gateway for secure, scalable communication.
Setting Up an Azure Virtual Network
To create a Virtual Network (VNet) in Azure, start by logging into the Azure Portal and navigating to the Virtual Network section. Click “Create” to begin the setup process. You will need to provide details such as the resource group, name, region, and IP address space. It’s essential to choose an address range that does not overlap with any existing networks to avoid conflicts when establishing connections. Defining Subnets and Security Settings Once the VNet is created, define subnets within the address space to segment the network logically. Subnets help organize resources and improve security by isolating workloads. For enhanced protection, configure Network Security Groups (NSGs) to control inbound and outbound traffic at both the subnet and network interface levels. NSGs allow you to define rules that permit or deny traffic based on factors such as source IP, destination IP, and protocol type. Deploying Resources and Establishing Connectivity After setting up the VNet, you can deploy Virtual Machines (VMs) and other resources within the network. Additionally, VNets can be peered to enable seamless communication between different Azure VNets, or connected to on-premises environments using VPN Gateway or Azure Expressroute . These connectivity options ensure secure and efficient communication across cloud and hybrid environments.
Azure VNet vs. Traditional Networking
- Scalability: One of the key benefits of Azure VNet is its ability to instantly scale resources and networks without the constraints of physical hardware. Organizations can dynamically adjust their network capacity based on demand, ensuring optimal performance without over-provisioning. This elasticity is particularly beneficial for enterprises experiencing fluctuating workloads or rapid growth.
- Global Reach: Azure VNet enables businesses to seamlessly connect networks across different regions and continents using Azure’s global infrastructure. With features like VNet peering and ExpressRoute, organizations can establish high-performance, private, and secure connections between on-premises data centers and Azure resources. This global connectivity ensures minimal latency and enhanced user experiences for applications serving a worldwide audience.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Unlike traditional networking solutions that require substantial investment in physical infrastructure, Azure VNet follows a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to optimize costs. By eliminating upfront hardware expenses and reducing ongoing maintenance costs, companies can allocate their budgets more efficiently while maintaining high network reliability.
- Advanced Security: Security is a top priority in Azure VNet, with built-in security features like network security groups (NSGs), Azure firewall , and DDoS protection. Microsoft also provides compliance certifications, ensuring organizations meet industry-specific regulatory requirements. By leveraging encryption, access control, and threat detection, businesses can safeguard sensitive data and prevent cyber threats.
- Hosting Web Applications: Azure VNet allows businesses to host web applications securely while integrating with services like Azure Load Balancer and Application Gateway. By distributing traffic efficiently, it ensures high availability and optimal performance for users worldwide.
- Hybrid Cloud Solutions: For enterprises with existing on-premises infrastructure, Azure VNet serves as a bridge between on-prem and cloud environments. Using VPN Gateway or Azure ExpressRoute, businesses can extend their networks securely, facilitating seamless hybrid cloud operations.
- Disaster Recovery: By deploying VNets across multiple Azure regions, organizations can implement robust disaster recovery strategies. If a primary data center fails, traffic can be rerouted to backup locations, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
- Development and Testing: Azure VNet helps developers create isolated environments for software development, testing, and staging. These environments replicate production settings, enabling teams to test applications thoroughly before deployment.
- Big Data and Analytics: With VNet, enterprises can connect securely to Azure’s data services, such as Azure data lake and Synapse Analytics, for large-scale data processing. This ensures efficient analytics workflows while maintaining data security.
- Gateway Type (Basic, Standard, High Performance, etc.)
- Bandwidth Capacity (Higher bandwidth increases costs)
- Connection Time (Pricing is typically per hour of usage)
- Inbound data (data coming into Azure) is typically free.
- Outbound data (data leaving Azure) incurs charges, especially for large-scale applications with significant external traffic.
- Monitor usage Utilize Azure Cost Management tools to track and analyze network expenses.
- Optimize routing Reduce unnecessary inter-region data transfer to minimize costs.
- Estimate costs beforehand Use the Azure Pricing Calculator to predict expenditures before deployment.
Integrating Azure VNet with Other Azure Services
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is a fundamental component of Microsoft Azure, providing a secure and isolated environment for cloud resources. It enables businesses to build sophisticated network architectures while ensuring seamless connectivity and integration with various Microsoft Azure Training. One of the key integrations is with Azure Load Balancer, which efficiently distributes incoming network traffic across multiple virtual machines (VMs), improving application performance and reliability. This ensures high availability and fault tolerance by preventing server overloads. For web applications, Azure Application Gateway provides advanced traffic management features, including SSL termination, URL-based routing, and Web Application Firewall (WAF) protection. It helps enhance security while optimizing traffic flow for improved performance. Security is further strengthened with Azure Bastion, which allows secure remote access to VMs without exposing them to public IP addresses. This reduces attack surface vulnerabilities and ensures a more secure environment for administrators managing cloud resources. For organizations requiring dedicated, high-speed connections between on-premises infrastructure and Azure, Azure ExpressRoute offers private, reliable, and low-latency connectivity. It bypasses the public internet, ensuring better performance and security for mission-critical workloads.
Use Cases of Azure VNet
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is a fundamental building block in Microsoft Azure, providing secure and scalable networking capabilities. It enables organizations to create isolated network environments, establish private communication between resources, and connect to on-premises data centers seamlessly. Below are some key use cases where Azure VNet proves highly effective:
Thinking About Earning a Master’s Degree in Microsoft Azure?Enroll For Azure Masters Program by Microsoft Today!
Security and Compliance in Azure VNet
Security is a cornerstone of Azure Virtual Network (VNet), with multiple layers of protection designed to safeguard data, applications, and network resources. Azure VNet ensures a secure environment by providing various security tools and configurations that help mitigate cyber threats, unauthorized access, and data breaches. One of the primary security mechanisms within Azure VNet is Network Security Groups (NSGs), which allow administrators to define and enforce fine-grained inbound and outbound traffic rules. These rules help restrict or allow access based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols, ensuring that only authorized communication occurs within the network. Additionally, Application Security Groups (ASGs) enable logical segmentation of workloads, simplifying security policies for large-scale environments. For advanced threat protection, Azure Firewall offers stateful inspection, filtering both inbound and outbound traffic while allowing administrators to create rules that block malicious activities. Azure DDoS Protection further strengthens network resilience by detecting and mitigating distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks in real-time, ensuring high availability of applications even under attack. All data within Azure VNet is encrypted both in transit and at rest, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. Moreover, integration with Azure Active Directory (AAD) enhances identity and access management (IAM), enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and conditional access policies to prevent unauthorized access.
Pricing and Cost Management
-
VNet Peering Costs
VNet Peering allows seamless communication between VNets in Azure. However, data transferred between peered VNets incurs charges based on the data volume and the regions involved. Peering across different regions (Global VNet Peering) is costlier compared to peering within the same region.
VPN Gateway CostsAzure VPN Gateway enables secure hybrid connectivity between on-premises networks and Microsoft Azure Portal . Pricing is influenced by:
-
Data Transfer Costs
Azure follows a standard pricing model for data transfer:
Getting Ready for a Cloud Computing Job Interview?Check Out Our Blog on Microsoft Azure Interview Questions & Answer
Cost Management TipsTo optimize VNet costs, consider the following strategies:
Conclusion
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is a powerful tool for building secure, scalable, and flexible cloud-based networks. With its rich set of features and seamless integration with Azure services, VNet offers businesses the ability to create sophisticated networking solutions that meet diverse operational needs. By leveraging Microsoft Azure Training VNet, organizations can enhance their cloud strategy, ensure robust security, and achieve greater operational efficiency, all while benefiting from the scalability and reliability of Microsoft Azure’s infrastructure.





