
- Introduction to Cloud Computing Models
- Public Cloud Model
- Private Cloud Model
- Hybrid Cloud Model
- Community Cloud Model
- Choosing the Right Cloud Model for Your Business
- Benefits of Cloud Computing Models
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cloud Computing Models
Cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern technology, transforming how businesses operate, manage data, and deliver services. It offers scalable, on-demand resources, minimizing the need for extensive physical infrastructure.To fully leverage the cloud’s potential, it’s essential to understand the different cloud computing models through Cloud Computing Course. These models define how computing resources are delivered, who manages them, and how they are accessed. This blog will explain the various cloud computing models, their benefits, and practical examples of how they are used. Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, such as storage, processing, and software, over the internet (“the cloud”). Instead of relying on local servers or personal computers, users can access these services on-demand via the internet. There are several cloud computing models, each offering distinct features based on the level of control, flexibility, and management required. These models can be broadly categorized based on who owns and manages the infrastructure and how resources are shared among users. The four primary cloud computing models include public, private, hybrid, and community clouds.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
Public Cloud Model
In the public cloud model, cloud services and infrastructure are provided by third-party providers over the internet and are available to anyone who wants to use them. Public clouds are typically hosted in data centers, and resources like storage, servers, and applications are shared among multiple users, often referred to as a multi-tenant model. Available to the general public or a large group of organizations, Creating and Understanding Docker Images can enhance deployment and management efficiency. Generally lower because resources are shared. The cloud service provider is responsible for maintaining and managing the infrastructure. A startup or small business might choose a public cloud for scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use, enabling them to access powerful computing resources without the need for significant upfront investment.
Public clouds offer significant flexibility, allowing users to scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring that they only pay for what they use. They provide a wide range of services, including computing power, storage, networking, and machine learning tools, making them highly versatile. Security measures such as data encryption, identity management, and access control are implemented by the service provider to safeguard the shared infrastructure. Additionally, public clouds are often supported by robust disaster recovery and backup solutions, ensuring high availability. For businesses, this model eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure and reduces the burden of maintenance, enabling teams to focus on core activities.
Examples:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- Alibaba Cloud
- Salesforce
- Digital Ocean
Private Cloud Model
- The private cloud model is a cloud environment used exclusively by a single organization. It can either be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider.
- In a private cloud, the organization has greater control over the infrastructure, including customization, security, and compliance. Dedicated to a single organization.
- Offers more control over the infrastructure, security, and resources. More secure as the infrastructure is not shared with other organizations.
- A large enterprise with sensitive data or regulatory compliance requirements, such as a financial institution or healthcare provider, might opt for a private cloud to maintain higher control over security and ensure compliance.
- Private clouds allow for greater flexibility in configuring resources to meet the specific needs of the organization, including the use of Docker Redis for optimized data management.
- Organizations can implement advanced security protocols and customize access controls to protect sensitive data more effectively.
- The private cloud model also enables better performance and reliability, as resources are not shared with other tenants, reducing the risk of contention.
- For businesses with high regulatory requirements, a private cloud provides the ability to ensure compliance with industry standards such as HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI-DSS.
- While more costly than public clouds due to the need for dedicated resources, private clouds provide peace of mind in terms of data protection and operational control.
- AWS Outposts
- Microsoft Azure Stack
- Google Anthos
- The community cloud model is a shared infrastructure that is used by several organizations with common concerns, such as security, compliance, or performance needs.
- Community clouds can be managed by the organizations themselves or by a third-party provider. They are ideal for organizations that have similar business goals or regulatory requirements.
- Multiple organizations share the same cloud infrastructure. More cost-effective than a private cloud, as resources are shared among a community of users. Facilitates collaboration between organizations with similar needs.
- A group of hospitals or healthcare organizations that need to store and manage sensitive health data under HIPAA regulations could opt for a community cloud to share infrastructure and compliance costs while maintaining the required security and privacy standards.
- Community clouds enable organizations to share best practices, resources, and technologies, fostering collaboration and innovation, especially through Cloud Computing Course.
- They allow for a higher level of customization than public clouds while being more affordable than private clouds due to resource sharing.
- This model is especially beneficial for industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as finance, healthcare, or government, where compliance and security are paramount.
- By pooling resources, organizations can access advanced technologies and infrastructure that might be too costly on their own.
- Additionally, the shared environment enables better risk management, as the cost of maintaining and securing the infrastructure is distributed across the community.
- Scalability: Cloud computing allows businesses to scale up or down based on demand, making it easier to adjust resources as needed without investing in physical infrastructure.
- Cost Efficiency: Many cloud models, particularly public and hybrid clouds, offer pay-as-you-go pricing, meaning organizations only pay for the resources they use.
- Flexibility: Cloud computing offers businesses the flexibility to choose the best cloud model that fits their specific needs, whether it’s the cost-effectiveness of a public cloud or the security of a private cloud.
- Security: Private and community clouds provide higher levels of security for sensitive data, along with An In-Depth Exploration of Content Delivery Networks to optimize data distribution and performance. While public clouds are generally secure, they may not be suitable for highly regulated industries.
- Reliability and Uptime: Cloud providers offer Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with uptime guarantees. Cloud computing infrastructure is often more reliable than on-premises infrastructure.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud computing offers robust disaster recovery solutions, often with built-in redundancy and data backup options. In the event of a system failure or natural disaster, cloud services ensure that data can be quickly recovered, minimizing downtime and loss of business continuity.
- Automatic Updates and Maintenance: Cloud providers handle software updates, maintenance, and patches automatically, reducing the burden on IT teams. This ensures that businesses are always running the latest versions of software with the latest security fixes, without additional manual effort.
- Global Accessibility: Cloud services can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and global collaboration. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for businesses with a distributed workforce or those with international operations.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cloud Computing Certificate? View The Cloud Computing Online Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Hybrid Cloud Model
The hybrid cloud model combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. Organizations use the hybrid cloud to take advantage of the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public cloud services while retaining control and security with private cloud infrastructure for certain applications or data. Combines the best of both worlds public and private clouds. Organizations can move workloads between private and public clouds based on demand, optimizing costs. Public clouds handle peaks in demand while private clouds can manage sensitive or critical data, with a deeper Understanding GCP Analytics to optimize cloud resources and performance. A business might store sensitive data in a private cloud while running non-sensitive applications on the public cloud to reduce costs and increase flexibility.
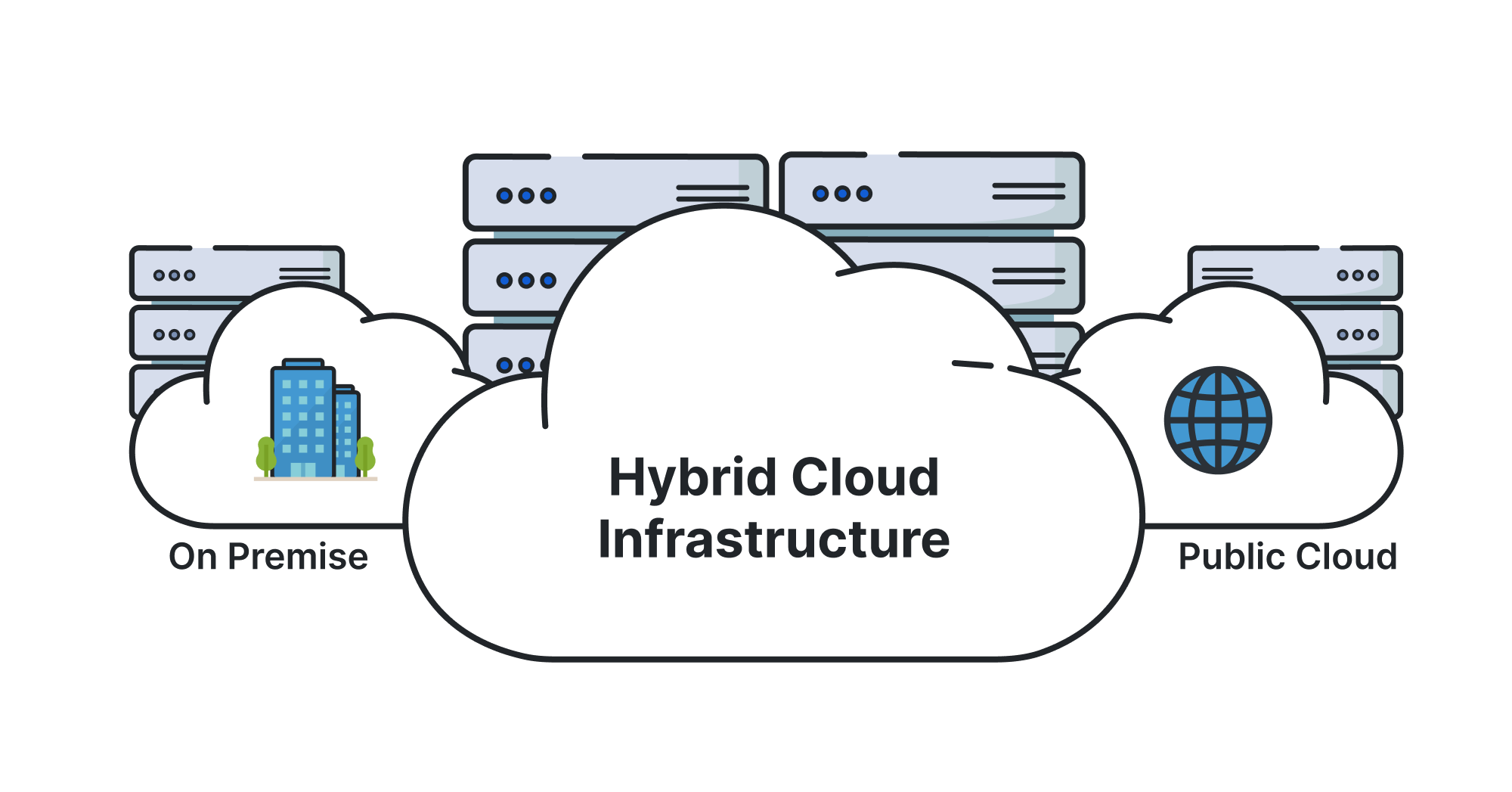
A retail company could use a hybrid cloud to manage inventory data on private servers while using public cloud services for customer-facing applications like their website. The hybrid cloud model provides organizations with the flexibility to scale resources up or down depending on changing business needs, without compromising security or performance. It allows businesses to avoid vendor lock-in by utilizing multiple cloud providers, ensuring they get the best services for each specific workload. Hybrid clouds also facilitate disaster recovery and business continuity by enabling data replication between on-premises and cloud environments. Integration between the public and private clouds can be achieved using APIs, VPNs, or other tools, ensuring seamless data flow and management. This model is ideal for organizations looking to optimize their IT infrastructure and improve agility, especially in industries with fluctuating demands.
Examples:
Community Cloud Model
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cloud Computing? Enroll in the Cloud Computing Masters Course Today!
Choosing the Right Cloud Model for Your Business
Choosing the right cloud model for your organization depends on several factors, such as the type of data you handle, the size of your business, your budget, and your security requirements. Public Cloud is ideal for startups or businesses that need scalability and cost-effectiveness without handling sensitive data. Private Cloud suits larger enterprises with strict security and compliance needs. Hybrid Cloud offers flexibility for businesses to move workloads between public and private clouds, ideal for fluctuating demands or complex data. Community Cloud is great for businesses in regulated industries or those with shared objectives, like government, healthcare, or education. Multi-Cloud avoids vendor lock-in, providing redundancy across multiple providers and enhancing resilience, performance, and access to the best services, including the use of Docker on Ubuntu for efficient container management. Edge Cloud is designed for low-latency processing and real-time analysis close to data sources, making it perfect for IoT, manufacturing, or autonomous vehicles needing quick decision-making. Each cloud model has its unique benefits, allowing businesses to choose the right mix based on their specific needs. Many organizations combine multiple models for optimal efficiency and performance. The choice of cloud model depends on factors such as security, cost, performance, and regulatory compliance. Cloud models can also evolve over time as businesses grow and their needs change. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each model can help organizations make informed decisions about their cloud strategy.
Benefits of Cloud Computing Models
Each cloud computing model comes with its own set of benefits depending on the organization’s specific needs and goals. Here are some of the general benefits:
Preparing for a Cloud Computing Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer
Conclusion
Cloud computing models are central to the digital transformation journey, providing businesses with the tools they need to remain agile, cost-effective, and secure. The key is to understand the different cloud models public, private, hybrid, and community clouds and select the one that aligns with your business needs. By leveraging the appropriate cloud model, organizations can enhance their operations, improve collaboration, and scale efficiently as they move forward into the future of technology. Each cloud model offers unique benefits, and the choice largely depends on factors like control, scalability, and security needs, which can be better understood through Cloud Computing Course. As the cloud landscape continues to evolve, companies can explore hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to optimize their operations further. Additionally, organizations should regularly evaluate their cloud infrastructure to ensure it continues to meet evolving business requirements and compliance standards. Cloud models also enable businesses to take advantage of cutting-edge technologies like AI, machine learning, and big data analytics, which can drive innovation and competitive advantage. By making informed decisions about their cloud adoption strategy, companies can future-proof their operations and stay ahead in a rapidly changing digital landscape.





