ExpressRoute is an Azure service that lets you create private connections between Microsoft datacenters and infrastructure that’s on your premises or in a colocation facility.
- What is Azure ExpressRoute?
- Main benefits of express route
- Characteristics of ExpressRoute
- Microsoft ExpressRoute Scenarios
- Requirements for Using Azure ExpressRoute
- ExpressRoute Pricing and Billing
- Azure ExpressRoute and CoreSite
- Uses for Azure ExpressRoute
- Benefits of Azure ExpressRoute
- Conclusion
What is Azure ExpressRoute?
Express Route allows a private connection between the local network and the Microsoft cloud. Organisations/users using Express Route can connect to multiple Microsoft cloud services (cloud products such as Microsoft Dynamics 365, Microsoft Azure and Office 365)
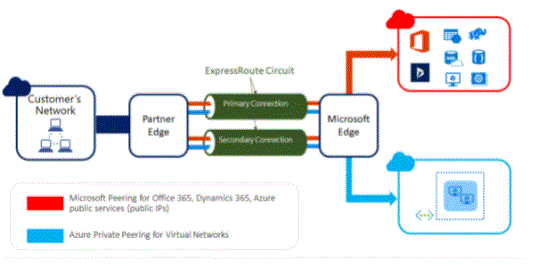
Connection to Microsoft services may be via a point-to-point Ethernet connection through the Universal Network or through a network connectivity provider to the data centre. Public Internet cannot be used to establish a connection to the Express Route.
- Express Route allows organisations to connect to Microsoft cloud services anywhere in the world
- Express routing provides layer 3 connection between Azure cloud and local network
- Increases express route reliability due to built-in redundancy
- Express Route improves security and privacy by avoiding sensitive traffic travelling over the public Internet
- supports skype for business
Main benefits of express route:
Characteristics of ExpressRoute:
Microsoft uses BGP to establish routing between local networks, Microsoft public addresses, and Azure:
Extravagance
Each Express Route connection includes two Microsoft Enterprise Edge and two-router connections between the connectivity provider and the local network perimeter. Microsoft ensures that there is a BGP connection between the connectivity and the edge of the on-premises network, which is allocated for each MSEE router. For verification of the SLA, a redundant Layer 3 must be configured.
Microsoft Cloud Services Connectivity
Express Route enables anyone to access the following cloud services: Microsoft Office 365 Services, Microsoft Azure Services, and Microsoft Dynamics 365
Connectivity to all regions of the world
Through the use of Azure Express Route, organisations can connect to Microsoft in one place and access all of Microsoft Cloud’s services around the world. Global connectivity with the Premium Express Route add-on. You are able to extend the connectivity beyond geo-political boundaries allowing high quality express route add-on facility.
Express Route Connectivity Model
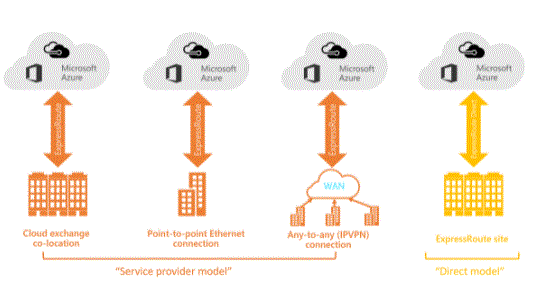
Users can create a connection between an on-premises network and Microsoft Cloud via point-to-point Ethernet, cloud-based co-location and Universal Connection (IPVPN) connections. Connectivity companies may offer one or more connectivity models.
point-to-point ethernet connection
Ethernet links are used in point to point connections. On-premises and Azure can be connected using point-to-point Ethernet providers. Relationships can be either layer 2 or managed layer three connections.
Universal Network (IPVPN)
Extended networks can be integrated into the Microsoft cloud using IPSec VPN providers. The above providers connect data centres and branch offices. To look like any other branch, Microsoft Cloud can be connected to a WAN whose providers primarily provide managed layer three connectivity. Connectivity providers use ExpressRoute circuits that allow connections between local infrastructure and Microsoft. For all connectivity models, ExpressRoute capabilities and features are the same.
Express route circuit
A logical connection between Microsoft cloud services and local infrastructure through a connection provider referred to as an ExpressRoute circuit. Express Route Circuits can be ordered in bulk and can be purchased in all regions. The connection between ExpressRoute circuits and your data centres is through connectivity providers. In particular, expressroute circuits are never mapped to physical entities. Instead, they are identified using a standard GUID, known as a service key (S-key). The S-Key is the only information shared between the user, the connectivity provider, and Microsoft. It is not for security reasons that the s-key is secret. Between the ExpressRoute circuit and the service key, a one-to-one mapping exists.
Peering Express Route
The ExpressRoute circuit consists of Azure Public, Azure Private and Microsoft Associated Routing/Peering domains. For high availability, each peering is configured identically on a pair of routers (in active-active or load-sharing configurations). To represent IP addressing schemes, Azure services are classified as Public Azure and Private Azure.
Azure Private Authentication
The Private Trust Domain connects Azure Computer Services, i.e. Virtual Machines (IaaS) and Cloud Services (PaaS) that are deployed within a virtual network. In Microsoft Azure, the connection is considered a reliable extension of the core network. A configuration can be done to establish bidirectional connectivity between the core network and the Azure virtual network. The above registration allows virtual machines and cloud services to be added directly to the private IP address.
- Some services must be offered in public IP addresses, for example, Azure Storage, SQL databases, and websites. Connectivity to services hosted on public IP addresses, including virtual IP addresses of cloud services, can be done privately through public trust routing domains. A connection can be established to a public trust domain for the user DMZ and connected to all Azure services on the public IP address from the user WAN without communicating via the Internet.
- Often, connectivity to Microsoft Azure services is initiated from the user’s WAN. The above routing does not allow connectivity to the domain user network. Users can sign in to all Azure services once publication registration is enabled. The user is not allowed to select the services for which the routes are published.
Microsoft ExpressRoute Scenarios:
Since Office 365 is built to be accessed reliably and securely over the Internet, it is recommended that ExpressRoute be used in special scenarios.
Microsoft Trust allows connectivity to Microsoft online services, i.e. Office 365, Dynamics 365 and Azure PaaS services. Microsoft Trust Routing enables two-way connectivity between domain WANs and Microsoft cloud services. However, the connection must be through public IP addresses that are owned by the user or the connectivity provider. All defined rules must be respected.
Azure Public Peering (deprecated for new circuits)
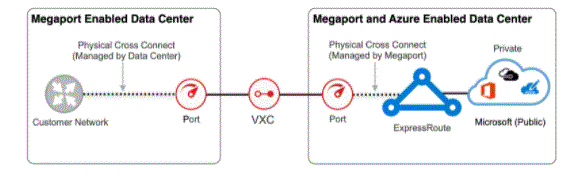
- Microsoft Azure ExpressRoute is a connector that a connectivity provider uses to extend your on-premises network to Microsoft Azure and the Microsoft 365 cloud over a private connection.
Azure ExpressRoute supports any-to-anyone (IP VPN) networks and point-to-point Ethernet networks. If you are using a colocation facility, you can take advantage of virtual cross-connection through a connectivity provider.
- ExpressRoute delivers connections that are usually faster and more secure by connection, never going to the public Internet. Once all the requirements for running ExpressRoute have been met, your connections will work as follows.
- express route_connection_overview
- Source: Microsoft
- To use Microsoft cloud services through ExpressRoute, you need to ensure that the following prerequisites are in place:
- You need an active Microsoft Azure account. You have set up ExpressRoute circuits, which are resources within your Azure subscription through your Azure account. Microsoft 365 cloud services also require an Azure subscription.
- You need an active Microsoft 365 subscription for Microsoft 365 services in the cloud.
- connectivity provider requirements
- You need an ExpressRoute connectivity provider to connect to Microsoft Cloud.
- If your provider is not an ExpressRoute connectivity partner, you need a cloud Exchange provider to connect to Microsoft Cloud.
- Azure ExpressRoute comes with a number of network requirements that your organisation must meet before using this tool.
- You need to establish redundant BGP sessions between Microsoft’s router and the peering router on each ExpressRoute circuit. This requirement also applies if you run only one physical connection to Cloud Exchange.
- You must have at least two express route circuits in different peering locations to establish adequate redundancy levels.
- You or your provider must set up and manage BGP sessions for the routing domain.
- You need to translate any private IP addresses you are using within your on-premises network into public IP addresses.
Requirements for Using Azure ExpressRoute:
How Express Route Connections Work
Azure Account Requirements
Network requirements
- You pay a monthly fee, while all inbound and outbound data transfer is free.
- metering data.
- You pay a monthly fee and all incoming data transfer is free. You are charged per GB of outbound data transfer, while rates vary by region.
- Express Route Premium Add-on
- ExpressRoute Premium is an add-on that expands routes for Azure public and private peering from 4,000 to 10,000, providing global connectivity for services and increasing the number of VNet links per ExpressRoute circuit.
ExpressRoute Pricing and Billing:
Azure ExpressRoute offers three billing models designed to meet the needs of different organisations and use case scenarios.
Unlimited Data.
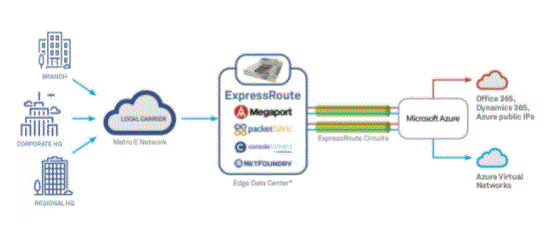
Azure ExpressRoute and CoreSite:
With Microsoft Azure ExpressRoute, you can establish a direct connection to the Microsoft cloud at CoreSite’s ExpressRoute locations in Los Angeles, Silicon Valley, Denver, Chicago, Boston, New York, and Northern Virginia. ExpressRoute connections are available through CoreSite Open Cloud Exchange™ in connection speeds of 50 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 200 Mbps, 500 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 2 Gbps, 5 Gbps, 10 Gbps, and 100 Gbps. The integration of Microsoft Azure ExpressRoute and CoreSite Open Cloud Exchange provides access to best-in-class, end-to-end, fully redundant connection architectures backed by superior performance, improved reliability and industry-leading availability SLAs.
Uses for Azure ExpressRoute:
optimal performance– Network connectivity that bypasses the public Internet and provides 44% lower latency
Less cost– All data transferred over ExpressRoute private connections benefits from low data withdrawal rates
Enhanced security– Private, secure connectivity to almost all Microsoft services
Reliability– Up to 60% less variability with private connectivity
Azure ExpressRoute and Azure Stack– Microsoft Azure Stack enables enterprises to bring the power of Azure’s Cloud Compute to on-premises environments, creating a fully integrated hybrid cloud solution. Customers who use CoreSite data centres to deploy Azure Stack have direct access to Microsoft Azure ExpressRoute via CoreSite Open Cloud Exchange, which enables close, low-latency connectivity between Azure and Azure Stack compute resources. enabled.
- ExpressRoute is a Microsoft Azure service that lets you create private connections between Microsoft Azure data centre locations and the infrastructure on your premises or at a colocation facility. Express Route connections do not go over the public Internet and offer higher security, reliability and speed with lower latency than normal connections on the Internet.
- ExpressRoute supports most Microsoft Azure services, Office 365 and Dynamics 365.
- ExpressRoute CoreSite is available through the Open Cloud Exchange to CoreSite customers in Los Angeles, Silicon Valley, Denver, Chicago, Boston, New York, and Northern Virginia.
- Express Route supports 50 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 200 Mbps, 500 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 2 Gbps, 5 Gbps, 10 Gbps and 100 Gbps bandwidth options.
- Express Route Local is available in 100 Gbps bandwidth at CoreSight’s Denver, Silicon Valley and Northern Virginia campuses.
- You do not pay for data transfer separately for your Express Route Local Circuit. In other words, the price of Express Route Local includes data transfer charges. ExpressRoute Local is a more economical solution if you have a large amount of data to transfer.
- Azure Stack is a fully integrated system that enables enterprises to build, deploy and operate Azure hybrid cloud applications on-premises. Customers who deploy Azure Stack within CoreSite data centres will have direct access to Microsoft Azure ExpressRoute via CoreSite Open Cloud Exchange.
Benefits of Azure ExpressRoute:
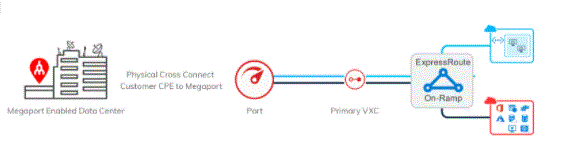
Conclusion:
Azure ExpressRoute provides your organisation with a number of benefits related to expanding your on-premises network with Azure and Microsoft 365 cloud infrastructure. It enables you to connect to cloud services locally and globally while getting scalable and redundant service.