
- Introduction to Virtualization
- Types of Virtualization
- Hypervisors in Virtualization
- Virtualization vs Containerization
- Virtualization Challenges
- Benefits of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Use Cases of Virtualization in Cloud
- Conclusion
Introduction to Virtualization
Virtualization is the technology that allows multiple virtual instances of computing resources (such as servers, storage devices, or networks) to run on a single physical machine. By abstracting the physical hardware, virtualization enables more efficient use of resources, isolation, and the ability to run multiple operating systems (OS) on the same machine. In virtualization, a layer of software called a hypervisor sits between the hardware and the operating systems. Enrolling in a Cloud Computing Course can provide you with a deeper understanding of virtualization technologies and how they are leveraged in cloud environments. The hypervisor manages the virtual machines (VMs), which are isolated from one another and can run different OS instances. This approach allows organizations to maximize their hardware utilization, reduce operational costs, and improve flexibility and scalability in computing environments. Virtualization is a cornerstone of cloud computing, enabling the dynamic allocation of resources, high availability, and efficient resource management. It is a key technology for data centers, cloud services, and enterprise IT infrastructure.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cloud Computing Certificate? View The Cloud Computing Online Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
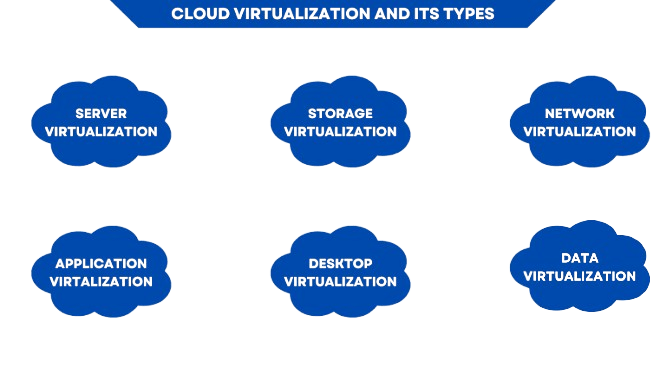
Types of Virtualization
Hardware Virtualization (also known as Server Virtualization):Hardware virtualization involves creating multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server. Each VM runs its own operating system and applications, and the hypervisor manages the allocation of physical resources (CPU, memory, storage) to these virtual instances.
- Example: VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine).
- Use case: Running multiple applications or operating systems on a single physical machine, improving resource utilization and simplifying management. Network Virtualization
- Example: VMware NSX, Cisco ACI.
- Use case: Creating isolated virtual networks for different applications or departments within an organization, improving network efficiency.
Network virtualization combines the physical network resources into a single virtualized network, which can be managed and configured as a whole. It allows for more flexible, scalable, and efficient use of network resources, as well as isolation of different virtual networks.
-
Storage Virtualization:
- Example: VMware vSAN, IBM SAN Volume Controller.
- Use case: Consolidating storage from different devices into a single virtual storage pool, improving storage efficiency and simplifying management. Desktop Virtualization:
- Example: VMware Horizon, Citrix XenDesktop.
- Use case: Providing remote desktop access to employees while maintaining centralized control over desktop configurations and software. Application Virtualization:
- Example: Microsoft App-V, Citrix XenApp.
- Use case: Running legacy applications or applications with specific OS requirements on modern systems without requiring the full installation of the application on each device.
Storage virtualization abstracts the storage resources from the physical hardware and presents them as a single virtualized pool. Understanding VMware vSphere Best Practices can help you optimize storage management, ensuring efficient resource allocation and improved performance in virtualized environments. This allows for simplified storage management and better resource utilization.
Desktop virtualization allows multiple virtual desktops to run on a single physical machine or server. This enables centralized management of desktops and provides users with remote access to their desktops, regardless of their location.
Application virtualization allows applications to run in a virtualized environment, isolating them from the underlying operating system. This enables the deployment and management of applications without worrying about compatibility issues.
Hypervisors in Virtualization
A hypervisor is a software layer that enables multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical machine, optimizing resource utilization, scalability, and flexibility. It allows different operating systems to share the same hardware while remaining isolated from each other, ensuring enhanced security and performance. Depending on the deployment environment, hypervisors can either run directly on physical hardware or operate on top of an existing operating system. In enterprise environments, hypervisors are widely used for server virtualization, enabling businesses to maximize hardware efficiency, reduce costs, and improve scalability. They help manage workloads efficiently by dynamically allocating resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance, fault tolerance, and security. Understanding The AWS Engineer Job Roles, Salaries & the Career Path can provide insight into how cloud engineers leverage such technologies to drive performance and scalability in AWS environments. Many organizations leverage hypervisors to create virtualized data centers, supporting cloud computing, disaster recovery solutions, and hybrid cloud architectures. For individual users, hypervisors provide a way to run multiple operating systems on a single machine, making them ideal for software development, testing, cybersecurity research, and running legacy applications in isolated environments. They facilitate seamless switching between different operating systems, enhancing productivity, flexibility, and system compatibility. By enabling virtualization, hypervisors enhance IT infrastructure, simplify management, reduce downtime, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall operational efficiency, making them a crucial technology in both enterprise and personal computing.
To Earn Your Cyber Security Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
Virtualization vs Containerization
Although both virtualization and containerization aim to isolate and manage workloads on a single physical machine, they differ in their implementation and use cases.
-
Virtualization:
- Hypervisor-based: Virtualization relies on a hypervisor, which runs on top of physical hardware to create multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM runs a full operating system and applications, which can include a dedicated kernel.
- Resource Overhead: VMs are more resource-intensive because each VM includes the full OS and associated services, requiring more CPU, memory, and storage.
- Use Cases: Suitable for running multiple operating systems or complex applications that require full OS isolation. Containerization:
- OS-level Isolation: Containerization isolates applications at the OS level, sharing the host OS’s kernel while running each application in its own container. A Cloud Computing Course can help you understand how containerization works and how it can be effectively used in cloud environments for improved scalability and management. This makes containers lighter and faster than VMs.
- Lower Overhead: Containers are more lightweight compared to VMs, as they only include the application and its dependencies, without the need for a full OS.
- Use Cases: Ideal for microservices, cloud-native applications, and scalable workloads that require fast provisioning and minimal overhead. Key Difference:
- Virtualization offers complete OS-level isolation with higher overhead and flexibility, while containerization provides faster, more lightweight isolation suitable for modern, scalable applications.
Virtualization Challenges
Virtualization offers numerous benefits, but it also comes with challenges that must be addressed for optimal performance and security. Resource contention is a common issue when multiple virtual machines (VMs) share the same physical hardware, leading to competition for resources such as CPU, memory, and storage. Without proper resource allocation and management, performance degradation can occur, impacting the efficiency of applications running in virtualized environments. Another challenge is overhead, as virtualization, while reducing overall hardware requirements, still introduces additional processing demands. Running multiple VMs requires system resources to manage and maintain the virtual environment, which can lead to performance bottlenecks, especially in resource-intensive workloads. Managing virtual machines at scale is another complexity, particularly in large cloud environments where administrators must monitor performance, allocate resources efficiently, and ensure correct VM configurations. Learning How to Become an Azure Developer can equip you with the skills needed to manage and optimize virtual machines effectively within Azure’s cloud environment. Without effective management tools, maintaining a virtualized infrastructure can become overwhelming. Licensing costs are another consideration, as virtualization, despite reducing hardware expenses, can introduce additional software licensing fees. Each VM often requires its own software license, increasing operational costs and impacting budget considerations for businesses deploying large-scale virtualization solutions. Lastly, security risks remain a significant challenge. While VMs are isolated, vulnerabilities in the hypervisor or misconfigurations can expose virtualized environments to potential threats. To mitigate security risks, organizations must implement strong patch management, access controls, and additional security layers to protect against breaches and unauthorized access. Addressing these challenges effectively ensures a stable, efficient, and secure virtualization infrastructure, making it essential to implement best practices in resource management, security, and cost control.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cloud Computing? Enroll in the Cloud Computing Masters Course Today!
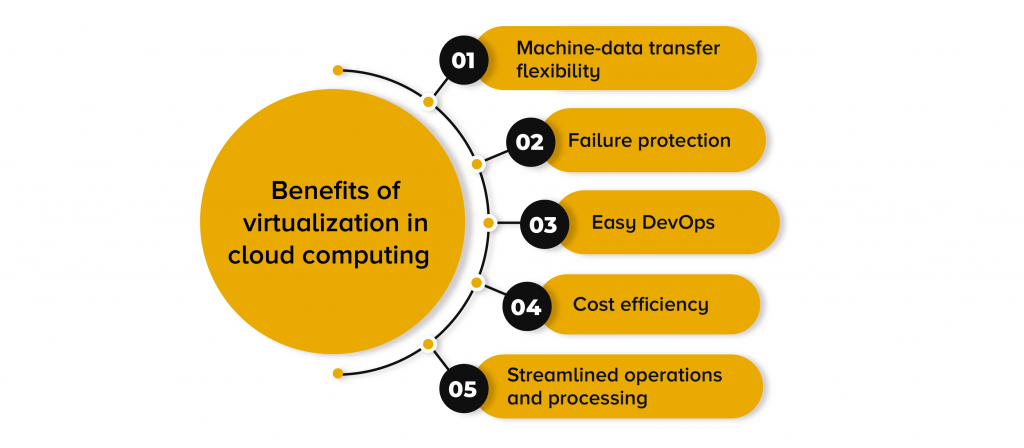
Benefits of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Resource Optimization: Virtualization allows for the efficient use of physical hardware by enabling multiple virtual machines (VMs) to share the same physical resources. This maximizes hardware utilization and reduces the need for additional physical machines.
- Scalability: Virtualization makes it easy to scale up or down by creating or removing virtual machines quickly. This is a key benefit in cloud environments where businesses can adjust resources based on demand without having to invest in additional physical infrastructure.
- Isolation and Security: VMs are isolated from one another, meaning that if one VM experiences an issue, it does not affect other VMs running on the same host. Understanding What Is Microsoft Azure in Cloud Computing can help you leverage Azure’s virtual machine capabilities to enhance security, scalability, and reliability in your cloud infrastructure. This isolation improves security and stability in multi-tenant environments.
- Disaster Recovery: Virtualization simplifies disaster recovery by enabling the easy replication of virtual machines across different physical servers or data centers. Virtualized environments can also be backed up and restored more quickly compared to traditional physical infrastructures.
- Cost Reduction: Virtualization reduces the need for physical hardware, which results in lower hardware procurement, maintenance, and power costs. Cloud providers leverage virtualization to offer scalable, pay-as-you-go services, which also lower the cost of IT infrastructure.
- Faster Provisioning: Virtual machines can be quickly provisioned and decommissioned, allowing for faster deployment of applications and resources. This makes virtualized environments ideal for dynamic, cloud-based workloads.
Use Cases of Virtualization in Cloud
Virtualization is a powerful technology that enables the creation of multi-tenant environments, allowing multiple users or customers to share the same physical infrastructure while maintaining data isolation and security. This is a fundamental aspect of cloud computing platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, where resources are efficiently allocated to different tenants without compromising performance or privacy. One significant application of virtualization is in Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), which allows organizations to deploy virtual desktops that users can access remotely. When comparing options for VDI, understanding the differences between Citrix Xenserver Vs Vmware vSphere can help organizations choose the right platform based on their specific needs and requirements. This eliminates the need for maintaining individual physical workstations, making it easier to manage, update, and secure desktop environments across an organization. Additionally, virtualization plays a crucial role in disaster recovery and high availability.
Since virtual machines (VMs) can be easily backed up, replicated, and migrated across data centers, businesses can ensure continuity in the event of hardware failures or cyber incidents, minimizing downtime and data loss. Another key area where virtualization excels is cloud hosting and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). By virtualizing servers and applications, cloud providers can offer scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient solutions to businesses and individuals. In software development and testing, virtualization allows developers to create isolated environments for testing software, patches, and configurations without impacting production systems, ensuring reliability before deployment. Moreover, virtualization simplifies legacy system migration, enabling organizations to run older applications as virtual machines in modern cloud environments. This ensures compatibility with current hardware and software infrastructures, extending the lifespan of legacy systems while benefiting from cloud scalability and security.
Preparing for Cloud Computing Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Virtualization is a foundational technology in cloud computing, enabling efficient resource utilization, scalability, and flexibility across diverse IT environments. By allowing multiple virtual machines to run on shared physical infrastructure, it enhances cost-effectiveness, security, and operational efficiency. Whether through multi-tenant environments, virtual desktops, disaster recovery, cloud hosting, or development and testing, virtualization plays a critical role in modern computing. A Cloud Computing Course can provide the knowledge and skills needed to effectively implement and manage virtualization technologies in cloud environments. It also simplifies legacy system migration, ensuring businesses can transition seamlessly to cloud-based solutions without compatibility concerns. As cloud computing continues to evolve, virtualization will remain an essential driver of innovation, helping organizations optimize their IT infrastructure while improving performance, security, and business continuity.





