
- Introduction to Blockchain Architecture
- Core Components of Blockchain Architecture
- Types of Blockchain Architecture
- Data Structure and Blocks Explained
- Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain Architecture
- Smart Contracts and Their Role in Blockchain Architecture
- Security Aspects of Blockchain Architecture
- Conclusion
Introduction to Blockchain Architecture
Explain the blockchain architecture is a revolutionary technology that forms the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum but has far-reaching implications beyond digital currencies. At its heart, architecture of blockchain technology defines how the technology works, from data storage to transaction validation.
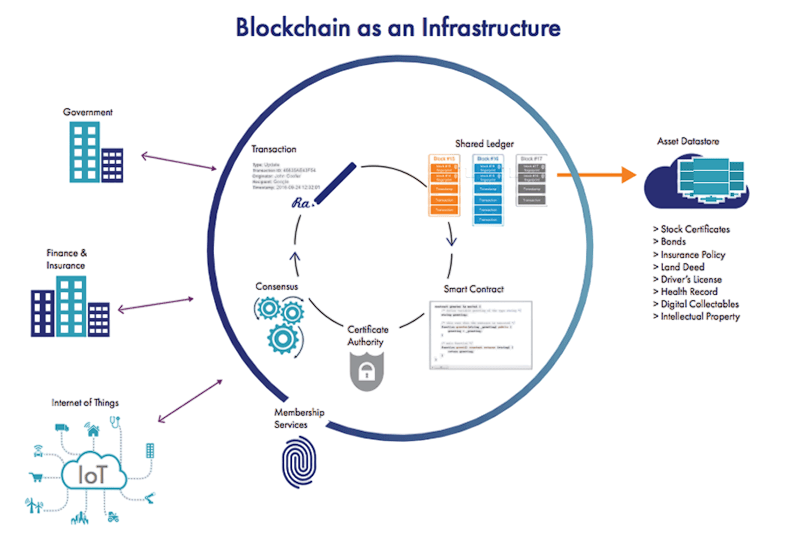
Understanding blockchain technical architecture is crucial for developers, enterprises, and anyone interested in how decentralized systems operate securely and transparently. This article breaks down the structural layers of blockchain, the types of architectures in use, and why these architectural decisions matter.
Do You Want to Learn More About Blockchain? Get Info From Our Blockchain Training Course Today!
Core Components of Blockchain Architecture
Explain the Blockchain architecture Components consists of several key components that work in unison: A blockchain is essentially a distributed ledger where all participating nodes have a synchronized copy of the ledger. This ensures transparency and resilience, as the network is not dependent on any single central authority. Data is grouped into blocks. Each block contains multiple transactions, a timestamp, a nonce (in Proof of Work systems), and a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a chain. Nodes are individual computers participating in the blockchain network. They validate and propagate transactions and maintain the ledger’s state. Nodes can be full nodes (holding the entire blockchain) or light nodes (holding only parts). This protocol ensures that all nodes agree on the blockchain’s current state. It prevents double-spending and maintains integrity despite the network’s decentralized nature. Hash functions and asymmetric encryption secure transactions and blocks. Public-private key cryptography allows users to sign transactions securely.
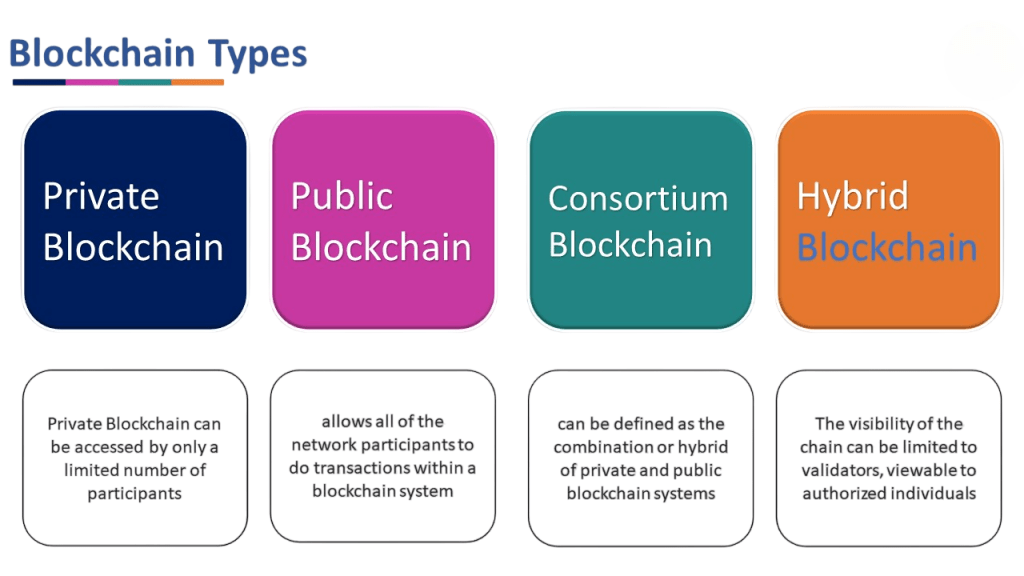
Types of Blockchain Architecture
- Types of Blockchain is Open networks where anyone can join, read, or write transactions. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum. They prioritize decentralization and censorship resistance but can face scalability challenges.
- Controlled by a single organization. Access is permissioned, and only authorized participants can validate transactions. These are used primarily in enterprises needing privacy and control.
- A hybrid model governed by a group of organizations. It combines some decentralization with permissioning, ideal for industries where multiple trusted parties collaborate, such as banking or the supply chain.
- Each block references the previous block through its hash, forming an immutable chain. This linkage means that altering one block would require recalculating all subsequent blocks, providing security against tampering.
- Transactions within blocks are organized in a Merkle tree, a binary hash tree that efficiently verifies large datasets. It allows quick validation that a transaction exists within a block without downloading the entire block.
- Deployment: Stored on the blockchain, smart contracts execute automatically when triggered by transactions.
- Languages: Solidity (Ethereum), Chaincode (Hyperledger Fabric), and others.
- Use Cases: Automated payments, supply chain automation, voting systems, decentralized finance (DeFi).
Would You Like to Know More About Blockchain? Sign Up For Our Blockchain Training Course Now!
Data Structure and Blocks Explained
Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain Architecture
A blockchain’s core relies on its Consensus Mechanisms. There are several common types. One way involves miners racing to solve complex puzzles; the first to find the solution adds a new block and gets rewards. This process, called Proof of Work, is very secure but uses a lot of energy. Another method, Proof of Stake, selects validators based on how much cryptocurrency they hold and lock up. It uses less power and promotes honest behavior since participants have something to lose. Some systems use stakeholders to pick delegates who confirm blocks. This approach is faster but tends to be more centralized. Permissioned blockchains often use Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance, or PBFT, which works well when all participants are known. It can handle some faulty or malicious nodes without breaking down. Newer protocols are emerging too, like Proof of Authority, Proof of Elapsed Time, and hybrid models, each designed for specific needs.
Smart Contracts and Their Role in Blockchain Architecture
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code. They automate processes and enforce agreements without intermediaries.
The Role in Blockchain Smart contracts add a programmable layer to blockchain architecture, enabling complex decentralized applications (dApps).
Security Aspects of Blockchain Architecture
Explain the blockchain architecture security of blockchain is greatly influenced by its architecture and operation. The way data is stored in blocks is its primary strength. Each block contains a batch of data or transactions. After a block is created and added to the chain, it becomes very difficult to modify the data within it. If you wanted to change any information in that block, you would need to edit the block in question as well as each block after it. Fraud and manipulation are nearly impossible due to the enormous amount of computer power required for this operation. If someone tried to change the data, the entire chain would have to be redone, which is almost impossible to do at scale. Consortia and private blockchains operate somewhat differently. They focus on controlled access by limiting who can join the network and participate in validations. Usually, only approved users or reliable organizations are able to view and validate transactions. Strong access controls, such as user authentication systems, help safeguard sensitive data in workplace applications. This configuration increases security because fewer people can change the system or try to exploit it. Many businesses favor private blockchains because of their stronger privacy and control features, which are essential for handling sensitive data while still utilizing blockchain’s security features.
Are You Preparing for Blockchain Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Blockchain Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Conclusion
Architecture of Blockchain technology is the blueprint that defines the security, scalability, and functionality of blockchain networks. Explain the blockchain architecture its foundational components, like distributed ledgers and cryptography, to complex elements like consensus protocols and smart contracts, understanding blockchain architecture is essential for grasping how this transformative technology operates. As blockchain technical architecture advances, ongoing architectural innovations will address current limitations, enabling more scalable, interoperable, and efficient systems. Whether for cryptocurrencies, supply chain, healthcare, or government applications, blockchain technical architecture continues to be the cornerstone of the decentralized future.




