
- Introduction to Hashing
- What is Hashing?
- Cryptographic Hash Functions Explained
- The Role of Hashing in Blockchain
- How Hashing Ensures Data Integrity and Security
- Popular Hash Functions in Blockchain
- Real-World Applications of Hashing Beyond Blockchain
- Challenges and Future of Hashing in Blockchain
- Conclusion
Introduction to Hashing
In the world of blockchain technology, security, transparency, and immutability are paramount. These qualities are largely possible due to a fundamental cryptographic process known as Hash Functions in Blockchain. Hashing is often described as the backbone of blockchain security. It is the process that links blocks securely, protects transaction data, cryptographic hash function and maintains Block Chain Training the integrity of the entire decentralized ledger.But what exactly is hashing? How does it work within blockchain? Why is it so critical? This article provides an in-depth exploration of hashing, cryptographic hash function breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand insights.
What is Hashing?
At its core, hashing is the process of transforming input data of any size into a fixed-length string of characters, typically a sequence of numbers and letters, using a mathematical function called a Hash Functions in Blockchain.The output is known as a hash value or digest. Best Blockchain Programming Language It acts like a unique digital fingerprint for the original data.
Key Properties of Hashing:
- Deterministic: The same input will always produce the same hash output.
- Fixed Output Length: Regardless of input size, output hash is always a fixed length (e.g., 256 bits).
- Fast Computation: Hash functions quickly convert input data into a hash.
- Pre-image Resistance: It’s computationally infeasible to reverse the hash to retrieve original input.
- Collision Resistance: It is extremely unlikely that two different inputs produce the same hash.
- Avalanche Effect: A tiny change in input drastically changes the output hash.
Do You Want to Learn More About Blockchain? Get Info From Our Blockchain Training Course Today!
Cryptographic Hash Functions Explained
A cryptographic hash function is a hash function that provides additional security properties required for cryptography, such as collision resistance and pre-image resistance. Each function has its own structure and characteristics but shares the core properties that ensure secure hashing. Bitcoin Mining Challenges These functions are vital for blockchain applications.
Popular Cryptographic Hash Functions Include:
- SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit): Widely used in Bitcoin and many other blockchains.
- SHA-3: A newer standard, designed as an alternative to SHA-2.
- Keccak: Basis for SHA-3, used in Ethereum.
- RIPEMD-160: Used in Bitcoin address generation.
- Linking Blocks Together: Each block contains the hash of the previous block’s header, creating a chain of blocks. This ensures that any change in a block’s data alters its hash and breaks the chain, making tampering obvious.
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners compete to find a nonce value that, when hashed with block data, produces a hash below a difficulty target.Block Chain Training This process relies entirely on hashing and is the core of Bitcoin’s security.
- Transaction Integrity: Transactions within a block are hashed and organized into a Merkle Tree structure. The root hash summarizes all transactions, enabling quick and secure verification.
- Address Generation and Digital Signatures: Hash functions help generate wallet addresses and verify signatures, ensuring secure ownership and transfer of cryptographic hash function .
- Immutability: Since blocks are chained by hashes, altering any transaction changes its hash and all subsequent hashes, alerting the network to tampering.
- Verification: Nodes independently compute hashes of blocks and transactions to verify authenticity without trusting a central authority What is Consortium Blockchain .
- Resistance to Fraud: Hashing makes it computationally impractical for attackers to modify data without detection.
- Efficient Data Validation: Merkle Trees and hashes allow nodes to verify transactions without downloading entire block data, enhancing scalability.
- Used by Bitcoin and many other blockchains.
- Produces a 256-bit hash output.
- Known for strong collision resistance and security.
- Basis of SHA-3, used primarily by Ethereum.
- Offers a different internal structure for improved security.
- Used in some newer blockchain projects like Zcash.
- Known for speed and security.
- Used for Bitcoin addresses.
- Produces shorter hashes used in address encoding.
- Digital Signatures: Hashes are signed rather than entire messages to optimize speed.
- Data Deduplication: Identifies duplicate data blocks in storage systems.
- File Integrity Verification: Checks if files have been altered during transfer.
- Certificate and Public Key Infrastructure: Ensures trust in digital certificates.
- Quantum Computing Threats: What is Decentralized Finance Quantum computers may break traditional hash functions, pushing the need for quantum-resistant hash functions.
- Increasing Efficiency: New hash algorithms aim to reduce energy consumption in PoW systems.
- Enhanced Scalability: Hashing combined with data structures like Merkle proofs continues to improve blockchain scalability.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Research is ongoing to design hash functions that withstand quantum attacks.
Would You Like to Know More About Blockchain? Sign Up For Our Blockchain Training Course Now!
The Role of Hashing in Blockchain
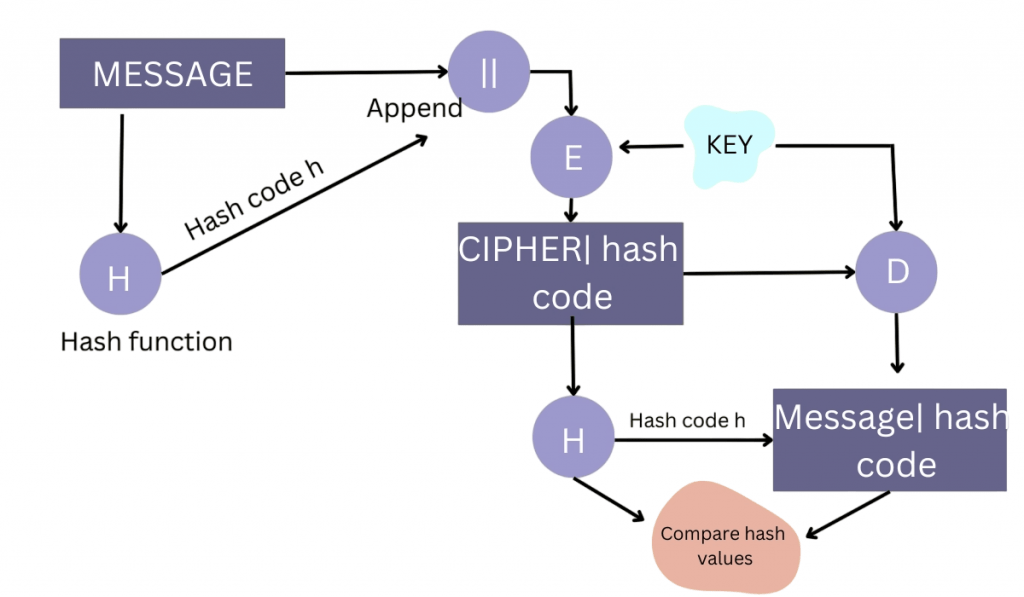
How Hashing Ensures Data Integrity and Security
Data integrity means that information remains accurate and unaltered over time. Hashing guarantees this in blockchain through:
Popular Hash Functions in Blockchain
SHA-256
Keccak-256
Blake2b
RIPEMD-160
Are You Preparing for Blockchain Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Blockchain Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Real-World Applications of Hashing Beyond Blockchain
Password Storage: Hashing passwords ensures that even if a database is breached, original passwords remain secure.
Challenges and Future of Hashing in Blockchain
While hashing provides robust security, it faces evolving challenges:
Conclusion
Hashing is the unsung hero of blockchain technology. It ensures every piece of data is uniquely identified, Data Integrity , verifiable, and immutable. By linking blocks, securing transactions, cryptographic hash function and enabling decentralized consensus, hashing underpins the trustless and secure nature of blockchains.As blockchain adoption grows, Hash Functions Block Chain Training in Blockchain cryptography understanding hashing is key to grasping how this revolutionary technology protects data and maintains integrity in a decentralized world.




