
BizTalk Server, developed by Microsoft, is a robust enterprise integration platform designed to automate business processes, facilitate seamless communication between disparate applications and systems, and enable the exchange of business documents across organizations. It supports various integration scenarios, including enterprise application integration (EAI) and business-to-business (B2B) integration, using XML-based messaging and adapters to ensure efficient data interchange.
1. What is BizTalk Server, and what is its primary purpose?
Ans:
Microsoft’s powerful integration tool, BizTalk Server, connects heterogeneous systems and efficiently automates a range of business activities. Its major objective is to facilitate enterprise application integration, enabling seamless business-to-business communication, and streamline business process automation. Advanced communications, orchestration features, and a range of adapter technologies that improve connectivity are used to do this.
2. Explain the critical components of BizTalk Server architecture.
Ans:
- Messaging Engine: Processes and routes messages through the system.
- Orchestration Engine: Executes business processes defined in orchestrations.
- Adapters: Enable communication with external systems and services.
- Pipelines: Handle message processing tasks like parsing and validation.
- BizTalk MessageBox: Stores and manages message routing and tracking.
- BizTalk Health Monitor: Monitors server and application health.
3. What are BizTalk artifacts, and how are they used?
Ans:
Schemas, maps, pipelines, orchestrations, and policies are examples of BizTalk artifacts. These parts allow data conversions, control message processing flows, define and modify message structures, and apply business rules inside the BizTalk Server. These artifacts are made available as BizTalk applications, which let businesses automate and effectively manage their business processes, leading to better integration and more seamless operations.
4. Describe the role of the BizTalk Administration Console.
Ans:
Managing on BizTalk Server environments, the BizTalk Administration Console is a complete administration solution. It enables administrators to successfully monitor message processing, manage host instances, and configure BizTalk applications. To improve system administration, the dashboard makes it possible to configure adapters and pipelines, monitor tracking data, and carry out operational operations like backup and restore.
5. How does BizTalk facilitate integration between different applications?
Ans:
- Providing adapters for connecting to various systems (like databases, FTP, and web services).
- Defining message formats and transformations using schemas and maps.
- Orchestrating business processes with visual orchestrations.
- Routing messages based on content, rules, and agreements.
- Monitor and track message flow for visibility and troubleshooting.
6. What is a BizTalk schema, and why is it important?
Ans:
The structure and data kinds of messages that are exchanged between different applications are defined by a BizTalk schema. It describes the elements, attributes, and relationships between them in the XML format of these communications. Schemas provide smooth communication and platform integration by standardizing message formats, ensuring system compatibility, and validating data integrity during message processing and translation.
7. Explain the concept of ports and their types in BizTalk.
Ans:
- Receive Ports: Accept incoming messages from external systems.
- Send Ports: Transmit outgoing messages to external systems.
- Logical Ports: Abstract endpoints used by orchestrations for message exchange.
- Direct Bound Ports: Connect orchestrations directly to receive or send ports.
8. What are pipelines in BizTalk, and how do they work?
Ans:
Pipelines in BizTalk are processing components that transform and process messages as they enter or exit the BizTalk Server. They consist of stages (e.g., decode, disassemble, validate, assemble) that perform specific message processing tasks like parsing XML, validating data, and applying encryption. Pipelines are configured in receive and send ports to handle message transformations and processing before routing to the MessageBox.
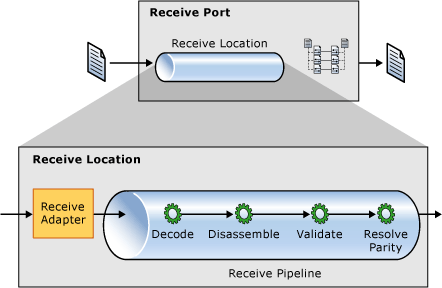
9. Describe the role of adapters in BizTalk Server.
Ans:
Adapters in BizTalk enable communication between BizTalk Server and external systems, services, or protocols. They provide connectivity by encapsulating protocol-specific details (like FTP, HTTP, SQL, and SAP) and handling message exchange operations. Adapters facilitate seamless integration by translating message formats, managing connections, and supporting reliable communication across diverse IT environments.
10. What are the considerations for choosing between BizTalk Server and Azure Integration Services?
Ans:
| Consideration | BizTalk Server | Azure Integration Services |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment Model | On-premises | Cloud-native |
| Integration Scenarios | Complex, on-premises integrations | Cloud-first, hybrid integrations |
| Scalability and Performance | Scalable with infrastructure management | Automatically scales based on demand |
| Development and Maintenance | Traditional with Visual Studio | Modern tools with Azure Portal and DevOps |
| Cost Considerations | Upfront licensing and infrastructure costs | Pay-as-you-go pricing |
11. What is the MessageBox database in BizTalk Server?
Ans:
One essential part of the BizTalk Server that keeps track of messages as they pass through the system is the MessageBox database. It performs the role of a message broker, assisting with crucial procedures including tracking, orchestration, and message routing. To ensure effective handling, messages are kept in the MessageBox until they are finished processing and sent to the correct location.
12. Explain the concept of message tracking in BizTalk.
Ans:
In BizTalk, message tracking is keeping a careful eye on how messages are sent and received across the board. It offers insightful visibility into all phases of message processing, such as message reception, routing, transformation, and delivery. Important information including message characteristics, route history, and processing status are all included in tracking data, and they are very helpful for auditing, debugging, and performance monitoring.
13. Describe the use of publish-subscribe messaging in BizTalk.
Ans:
- Publish-subscribe messaging in BizTalk enables loosely coupled communication between applications and services.
- Publishers send messages to topics, and subscribers receive notifications based on their subscriptions to these topics.
- It supports scalable and flexible communication patterns where multiple subscribers can independently receive relevant messages without direct dependencies on publishers.
14. What are BizTalk Hosts and Host Instances?
Ans:
BizTalk Hosts are logical processing containers for several kinds of BizTalk artifacts, such as adapters, orchestrations, and pipelines. The runtime versions of these BizTalk Hosts that carry out the artifacts’ actual execution are called Host Instances. They are in charge of allocating resources, guaranteeing scalability, and supplying isolation, all of which enable BizTalk Server to effectively and independently manage various processing jobs.
15. How to manage deployment in BizTalk Server?
Ans:
- Exporting BizTalk applications as MSI packages.
- Using BizTalk Deployment Wizard or PowerShell scripts for deployment.
- Configuring host instances, adapters, and bindings on target servers.
- Testing deployment with BizTalk Administration Console or scripts.
- Monitor and troubleshoot deployment issues using logs and tracking tools.
16. Explain the role of BizTalk Mapper in data transformation.
Ans:
BizTalk Mapper is a graphical tool for defining mappings between source and destination schemas in BizTalk Server. It facilitates complex data transformations by visually connecting elements from different schemas, applying functions (built-in functions), and defining logical conditions. The Mapper generates XSLT or .NET code for runtime transformation of messages.
17. What is a BizTalk orchestration, and how is it different from a pipeline?
Ans:
BizTalk orchestration is a graphical representation of a business process workflow in BizTalk Server. It defines message flows, conditional logic, exception handling, and interaction with external systems using visual programming. Orchestrations are long-running and stateful, managing business processes over time. BizTalk pipelines are linear processing components that execute discrete tasks such as message parsing, validation, and encoding.
18. Describe the purpose of BizTalk Parties and Agreements.
Ans:
- BizTalk Parties and Agreements facilitate B2B (Business-to-Business) communication by defining the identities and communication agreements between trading partners.
- Parties represent organizations or systems exchanging messages, while Agreements specify message exchange protocols, document formats, encryption, and other communication details.
- They streamline interoperability and ensure compliance with partner-specific requirements.
19. How does BizTalk support business process automation?
Ans:
- BizTalk supports business process automation by:
- Orchestrating end-to-end business workflows using visual orchestrations.
- Automating message routing, transformation, and validation based on business rules.
- Integrating disparate systems, applications, and data sources using adapters and connectors.
- Enabling real-time monitoring, tracking, and reporting of business processes.
20. Explain the role of the BizTalk Business Rules Engine (BRE).
Ans:
BizTalk Business Rules Engine (BRE) enables dynamic decision-making and policy enforcement within BizTalk Server. It separates business rules from application logic, allowing rules to be modified without code changes. BRE evaluates conditions and actions defined in policies, integrating with BizTalk orchestrations to enforce business rules at runtime. It enhances the flexibility, agility, and maintainability of business processes.
21. How to configure message routing in BizTalk Server?
Ans:
- Receive Ports: Define where and how incoming messages are received.
- Send Ports: Specify where and how outgoing messages are sent.
- Filters and Routing Rules: Define conditions based on message properties for routing.
- Distribution Lists: Route messages to multiple destinations based on subscriptions.
- Content-Based Routing: Route messages based on message content using orchestrations or pipelines.
22. Describe the role of BizTalk Health Monitor in monitoring and managing the server.
Ans:
Real-time monitoring of server and application health. Alerts and notifications for critical issues and performance bottlenecks. Historical data and performance metrics for analysis and troubleshooting. Management of BizTalk artifacts, host instances, and runtime components. Integration with System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) for enterprise monitoring.
23. What are the different types of BizTalk pipelines and their purposes?
Ans:
- Receive Pipeline processes incoming messages, including decoding, disassembling, and validating.
- Send Pipeline prepares outgoing messages for transmission, including assembling and encoding.
- Processing Pipelines perform specific message processing tasks such as encryption, decryption, and content-based routing.
- Pipelines are configured in receive and send ports to process messages according to defined stages and components.
24. How does BizTalk handle EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) transactions?
Ans:
Using EDI schemas to parse, validate, and transform EDI messages. Supporting EDI-specific protocols and standards (like X12, EDIFACT). Configuring EDI receive and send pipelines for message processing. Mapping EDI data to internal schemas and formats for integration with enterprise applications. Implementing EDI-specific protocols for secure and reliable data exchange with trading partners.
25. Explain the use of Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) in BizTalk.
Ans:
BAM in BizTalk provides real-time visibility into business processes and key performance indicators (KPIs). Monitoring and tracking of business milestones, events, and transactions. Visualization of business process metrics and performance trends through dashboards and reports. Alerting and notification based on predefined thresholds and business rules. Analysis of process inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement.
26. Describe the integration capabilities of the BizTalk Adapter Pack.
Ans:
The BizTalk Adapter Pack extends the BizTalk Server’s integration capabilities by providing adapters for connecting to various enterprise applications and systems. It includes adapters for:
- SAP: Integration with SAP systems for data exchange and business process automation.
- Oracle Database: Connectivity to Oracle databases for data retrieval and update operations.
- SQL Server: Integration with SQL Server databases for data access and transaction processing.
27. What is the BizTalk Deployment Framework (BTDF), and how is it used?
Ans:
The BizTalk Deployment Framework (BTDF) is a set of tools and utilities used to streamline and automate the deployment of BizTalk applications. It provides: Automated deployment scripts and procedures for consistent application deployment. Configuration management for handling environment-specific settings and configurations. Versioning and rollback capabilities to manage application updates and changes.
28. How does BizTalk support B2B (Business-to-Business) integration?
Ans:
- Implementing EDI standards for structured data exchange with trading partners.
- Using AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) and other protocols for secure B2B communication.
- Defining trading partner agreements (TPAs) and agreements for message exchange.
- Orchestrating B2B processes for order processing, invoicing, and supply chain integration.
- Monitoring and tracking B2B transactions with visibility into message status and delivery.
29. Explain the concept of fault tolerance and scalability in BizTalk.
Ans:
Fault tolerance in BizTalk ensures continuous operation and resilience against failures by: Implementing high availability configurations with clustered host instances and databases. Configuring redundancy and failover mechanisms for critical components. Monitoring and alerting for system errors, performance degradation, and resource exhaustion. Scaling out host instances and load-balancing message processing for increased throughput.
30. Describe the role of BizTalk RFID (Radio Frequency Identification).
Ans:
- RFID device management and configuration for data collection and processing.
- Integration with business applications and processes for real-time visibility and tracking.
- Event-driven architecture for capturing RFID tag data and triggering business events.
- Analytics and reporting capabilities for RFID data analysis and operational insights.
- BizTalk RFID enhances supply chain visibility, asset tracking, and operational efficiency through RFID technology integration.
31. How does BizTalk handle long-running transactions and orchestrations?
Ans:
BizTalk handles long-running transactions and orchestrations by leveraging durable and stateful orchestrations. When orchestrating complex business processes that span extended periods, BizTalk uses persistence points to save the state of orchestration instances. This capability allows orchestrations to be suspended and resumed as needed without losing data or progress, ensuring continuity and reliability in handling lengthy operations.
32. What is Business Process Execution Language (BPEL), and what is its role in BizTalk?
Ans:
Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) is a standard language for defining executable business processes using web services. In BizTalk, BPEL is integral to orchestrations, where it serves as the primary language for defining workflows and business logic. BPEL allows developers to specify the sequence of activities, decisions, and interactions between services within an orchestration.
33. Explain the concept of BAM Alerts in BizTalk.
Ans:
BAM Alerts in BizTalk are essential for real-time monitoring and notification of critical business events or deviations from predefined performance metrics. They are triggered based on predefined conditions or thresholds set within Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) views. Alerts notify stakeholders, such as administrators or business users, about significant events that require immediate attention or action.
34. How does BizTalk integrate with cloud services like Azure?
Ans:
- Azure Logic Apps: BizTalk can leverage Azure Logic Apps connectors to seamlessly exchange messages and integrate with various Azure services, facilitating hybrid cloud scenarios.
- Azure Service Bus: BizTalk uses Azure Service Bus for reliable messaging and communication between on-premises BizTalk Server and Azure-hosted applications or services.
- Azure Functions: BizTalk can trigger serverless Azure Functions in response to events or messages processed within its orchestrations, enabling scalable and event-driven integration solutions.
- Hybrid Connections: BizTalk establishes secure connections via Azure Hybrid Connections to interact with Azure resources securely, extending its integration capabilities into the cloud.
35. Describe the role of BizTalk LOB (Line-of-Business) adapters.
Ans:
BizTalk LOB adapters play a crucial role in enabling seamless connectivity and integration between BizTalk Server and various Line-of-Business applications or systems. These adapters provide native connectivity to applications such as SAP, Oracle, SQL Server, and others, using their respective protocols and APIs. By supporting direct integration with LOB systems, BizTalk facilitates efficient data exchange, business process automation, and orchestration.
36. How to implement error handling and tracking in BizTalk?
Ans:
- Exception Handling: Orchestrations use try-catch and exception handling shapes to capture and gracefully manage errors during process execution.
- Fault Handling Policies: Receive and send ports employ fault handling policies to define actions for message routing and processing errors, ensuring resilience and fault tolerance.
- Tracking Profiles: Configurable tracking profiles capture detailed information about message flows, processing times, and error details, facilitating comprehensive monitoring and analysis.
- Integration with BAM: Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) provides real-time visibility into error trends and their impact on business processes, enabling proactive error management and resolution.
37. Explain the use of Business Rules Composer in BizTalk.
Ans:
Business Rules Composer in BizTalk is a graphical tool designed to define and manage business rules independently of application code. It enables business analysts and subject matter experts to create, update, and validate business rules using a user-friendly interface. These rules govern decision-making within BizTalk orchestrations and processes, guiding behavior based on changing business conditions or requirements.
38. Describe the role of BAM activities and views in monitoring business processes.
Ans:
- Defined Process Steps: Activities represent specific steps or milestones within monitored business processes, offering granularity and clarity in process monitoring.
- Real-Time Tracking: BAM views visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) and performance metrics in real-time, enabling stakeholders to monitor process health and performance trends.
- Drill-Down Capabilities: Users can drill down into individual process instances or data points within BAM views to investigate issues, identify bottlenecks, and analyze root causes.
- Custom Dashboards and Reports: Customizable dashboards and reports offer tailored insights into business process performance, supporting informed decision-making and continuous process improvement.
39. How does BizTalk integrate with SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)?
Ans:
BizTalk leverages SSIS adapters to connect directly to SQL Server databases and data sources, enabling seamless data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) operations. SSIS packages can be invoked from BizTalk orchestrations to perform complex data transformations, integration tasks, and workflow automation. BizTalk and SSIS collaborate in hybrid environments, where SSIS handles data processing and integration tasks.
40. Explain the concept of dynamic send ports and subscriptions in BizTalk.
Ans:
Messages are routed dynamically at runtime based on content, context, or message properties rather than predefined static configurations. Subscriptions define criteria or filters that determine the destination endpoints or processing routes for messages, allowing for dynamic adaptation to changing business requirements. Dynamic routing supports scalable architectures where message flows and destinations can evolve dynamically.
41. What are the performance tuning strategies for BizTalk Server?
Ans:
- Optimizing Host and Host Instances: Distributing workload across multiple hosts and instances.
- Pipeline and Orchestration Optimization: Streamlining message processing and reducing latency.
- Database and Disk I/O Optimization: Improving database performance and minimizing disk I/O bottlenecks.
- Throttling and Resource Management: Managing system resources to prevent overload and ensure consistent performance.
42. Describe the architecture of a high-availability BizTalk environment.
Ans:
- Load-Balanced Host Instances: Multiple BizTalk hosts are distributed across servers to handle incoming traffic.
- Clustered Databases: SQL Server databases configured in a failover cluster for data redundancy and availability.
- Redundant Messaging Components: Duplicate receive locations, send ports, and orchestrations for seamless failover.
- Disaster Recovery (DR) Setup: Geo-redundant configurations or hot standby environments for business continuity.
43. How does BizTalk support hybrid cloud integration scenarios?
Ans:
Leveraging Azure Service Bus and Azure Logic Apps for seamless cloud-to-on-premises and cloud-to-cloud integration. Establishing secure connections between on-premises BizTalk Server and Azure resources using Azure Hybrid Connections. Enabling connectivity with various cloud services and applications through native adapters. Triggering serverless functions in response to events processed by BizTalk orchestrations.
44. Explain the integration of BizTalk with IoT (Internet of Things) devices.
Ans:
Using Azure IoT Hub to ingest data from IoT devices and route it to BizTalk for processing. Developing custom adapters or leveraging existing IoT protocols (e.g., MQTT) to connect with diverse IoT devices. Orchestrating data flows between IoT devices and backend systems using BizTalk orchestrations and pipelines. Processing and analyzing IoT data in real-time using BAM and other BizTalk components for actionable insights and decision-making.
45. Describe the role of BizTalk in real-time data analytics and decision-making.
Ans:
- Business Activity Monitoring (BAM): Monitoring KPIs and critical business processes in real time.
- Complex Event Processing (CEP): Analyzing streaming data and triggering actions based on predefined rules and patterns.
- Integration with Analytics Platforms: Sending processed data to analytics platforms like Power BI or Azure Synapse Analytics for further analysis.
- Operational Intelligence: Providing operational dashboards and reports to stakeholders for informed decision-making based on real-time data insights.
46. How does BizTalk handle complex event processing (CEP)?
Ans:
- Rules Engine Integration: Using the Business Rules Engine (BRE) to define rules for event correlation and pattern detection.
- Event Stream Processing: Processing and correlating real-time events from multiple sources to identify meaningful patterns or anomalies.
- Event Aggregation: Aggregating related events over time windows or sequences to derive actionable insights.
- Dynamic Event Routing: Routing events dynamically based on CEP outcomes to appropriate destinations or orchestrations.
47. What are the best practices for versioning and deploying BizTalk applications?
Ans:
Using source control systems (e.g., Git) to manage artifacts and configurations. Utilizing tools like BizTalk Deployment Framework (BTDF) for automated deployments and version management. Maintaining separate environments (development, testing, production) to control deployments and minimize risks. Implementing backup strategies and rollback plans to revert changes in case of deployment failures.
48. Explain the role of BizTalk Adapters for Enterprise Applications.
Ans:
- SAP: Connecting to SAP systems (ERP, CRM) using SAP adapter for bi-directional data exchange and orchestration.
- Oracle: Integrating with Oracle databases and applications through Oracle adapter for transactional operations and data synchronization.
- Other ERP/CRM Systems: Supporting adapters for Microsoft Dynamics, Salesforce, and other enterprise applications to facilitate business process automation.
- Protocol Support: Providing connectivity via industry-standard protocols (e.g., OData, SOAP) for interoperability with diverse enterprise systems.
49. How does BizTalk support message encryption and secure communication?
Ans:
Implementing SSL/TLS for secure communication between BizTalk Server and endpoints. Encrypting sensitive data within messages using cryptographic algorithms (e.g., AES) before transmission. Managing X.509 certificates for authentication and encryption purposes across BizTalk environments. Supporting secure protocols such as AS2, SFTP, and HTTPS for encrypted data exchange with external partners.
50. Describe the process of upgrading BizTalk Server to newer versions.
Ans:
Review system requirements and compatibility with existing solutions. Perform a full backup of BizTalk databases, configurations, and applications. Install the new version of BizTalk Server on designated servers. Migrate configurations, schemas, maps, and orchestrations to the new environment. Conduct thorough testing of migrated applications and integrations to ensure functionality.
51. Explain the concept of BAM in tracking key performance indicators (KPIs).
Ans:
- Monitoring: Capturing real-time data from BizTalk Server and external systems.
- Analysis: Analyzing data to measure performance against predefined KPIs and thresholds.
- Visualization: Visualizing KPIs through dashboards and reports in BAM Portal or custom applications.
- Alerting: Triggering alerts based on KPI deviations or predefined business rules.
- Decision Support: Providing insights for timely decision-making and process optimization.
52. How does BizTalk handle message validation and schema enforcement?
Ans:
- Schema Definition: Defining XML schemas (XSD) for message structure and data validation.
- Receive Pipeline: Using receive pipelines to validate incoming messages against defined schemas.
- Schema Cache: Caching schemas for efficient validation and enforcement during message processing.
- Error Handling: Routing invalid messages to designated error handling processes or suspending them for manual review.
53. Describe the integration of BizTalk with SharePoint for document management.
Ans:
Routing documents from BizTalk Server to SharePoint libraries based on business rules. Synchronizing metadata between BizTalk messages and SharePoint document properties. Triggering SharePoint workflows based on events or data processed by BizTalk orchestrations. Enabling document search and retrieval from SharePoint within BizTalk applications. Managing document versions and access control policies through SharePoint integration.
54. What are the considerations for disaster recovery planning in BizTalk?
Ans:
Regularly backing up BizTalk databases, configurations, and applications. Replicating BizTalk artifacts and databases to a secondary data center or cloud environment. Implementing clustering and load balancing for BizTalk servers to ensure failover capabilities. Conducting periodic disaster recovery drills and testing failover procedures. Documenting disaster recovery plans, procedures, and contacts for quick response during emergencies.
55. Explain the role of Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) in BizTalk.
Ans:
- Process Modeling: Graphically modeling business processes using standardized BPMN notation.
- Orchestration Design: Designing orchestrations to automate business processes and workflows.
- Visualization: Visualizing process flows, activities, decisions, and message flows within BizTalk orchestrations.
- Execution: Execute BPMN-compliant processes using BizTalk orchestrations and integrate them with external systems.
- Business Agility: Enhancing business agility by modeling, analyzing, and optimizing business processes using BPMN standards.
56. How does BizTalk support asynchronous messaging patterns?
Ans:
- Receive Locations and Ports: Configuring receive locations to receive messages from external systems asynchronously.
- Messaging Pipelines: Using receive and send pipelines to process messages asynchronously, including validation and transformation.
- Message Queues: Queuing incoming messages for processing and decoupling message senders and receivers.
- Orchestration Patterns: Designing orchestrations to handle asynchronous message processing and long-running transactions.
57. Describe the role of BizTalk EDI/AS2 Runtime in B2B communication.
Ans:
Supporting Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) standards (e.g., X12, EDIFACT) for partner communication. Enabling secure and reliable exchange of EDI messages over the Internet using AS2 protocol. Validating incoming EDI messages against predefined schemas and business rules. Generating and sending acknowledgments (e.g., MDN) for received AS2 messages. Managing trading partner agreements, certificates, and configurations for EDI exchanges.
58. Explain the use of WCF (Windows Communication Foundation) adapters in BizTalk.
Ans:
Connecting to and consuming WCF services hosted on-premises or in the cloud. Supporting various communication protocols (e.g., HTTP, TCP, MSMQ) for interoperability with WCF services. Supporting request-response and one-way messaging patterns for service invocation. Implementing transport and message-level security mechanisms (e.g., SSL/TLS, message encryption) for secure communication.
59. How does BizTalk handle business rule validation and execution?
Ans:
- Business Rules Engine (BRE): Defining and managing business rules using the BRE in BizTalk Server.
- Rule Composer: Using the Business Rules Composer to author, test, and deploy rules based on policies.
- Integration: Integrating business rules with BizTalk orchestrations and messaging pipelines for rule execution.
- Policy Evaluation: Evaluate rules at runtime based on incoming data and message context.
- Logging and Monitoring: Log rule execution results and monitor rule performance for optimization.
60. Describe the process of integrating BizTalk with third-party APIs and services.
Ans:
- Adapter Configuration: Configuring BizTalk adapters (e.g., WCF, HTTP) to connect with external APIs.
- Message Transformation: Mapping and transforming data formats between BizTalk schemas and API payloads.
- Protocol Handling: Supporting communication protocols (e.g., REST, SOAP) used by external APIs.
- Security Integration: Implementing authentication and authorization mechanisms required by APIs.
- Error Handling: Managing exceptions and errors during API communication and ensuring reliable messaging.
61. How to implement a file-based integration solution using BizTalk Server?
Ans:
Configuring receive locations to monitor and retrieve files from specified directories. Using file adapters to manage file operations (e.g., read, write, delete) and handle file-based messaging. File contents are processed through receive pipelines for validation, transformation, and enrichment. Routing processed messages to appropriate destinations based on business rules and content.
62. Explain the integration of BizTalk with CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems.
Ans:
Configuring CRM adapters in BizTalk Server. Synchronizing customer data, leads, opportunities, and other CRM entities with back-end systems. Triggering CRM workflows and processes based on events or data changes from integrated systems. Implementing custom mappings, transformations, and business rules specific to CRM integration. Supporting real-time data updates and bidirectional synchronization between BizTalk and CRM.
63. Describe a scenario in which BizTalk would be used for integrating supply chain management systems.
Ans:
- Supplier Integration: Automating purchase orders, invoices, and payment processing between suppliers and ERP systems.
- Inventory Management: Updating inventory levels, tracking shipments, and managing warehouse operations in real-time.
- Logistics Coordination: Routing transportation and logistics data across supply chain partners and systems.
- Demand Forecasting: Sharing demand forecasts, sales orders, and production schedules between manufacturers and suppliers.
64. How to implement real-time inventory tracking using BizTalk RFID?
Ans:
- RFID Device Integration: RFID readers and tags are integrated with the BizTalk server through RFID adapters.
- Event Processing: Capturing RFID tag events and data (e.g., location, timestamp) in real-time.
- Data Processing: RFID tag data is processed through BizTalk orchestrations for validation and enrichment.
- Inventory Updates: Updating inventory databases and systems with real-time RFID tag readings and location updates.
65. Explain the process of migrating legacy integration solutions to BizTalk.
Ans:
Assessing existing integration architecture, components, and dependencies. Mapping legacy integration workflows, data mappings, and transformations to BizTalk equivalents. Converting data schemas, message formats, and protocols to BizTalk-compatible standards. Conducting rigorous testing, including functional, performance, and integration testing of migrated solutions.
66. Describe the implementation of EDI transactions and partner agreements in BizTalk.
Ans:
Configuring EDI-specific adapters for exchanging EDI messages. Defining EDI document schemas to parse and validate incoming and outgoing messages. Establishing partner profiles, agreements, and communication protocols in BizTalk. Routing EDI messages to appropriate destinations based on trading partner agreements and business rules. Ensuring compliance with EDI standards and regulatory requirements.
67. How to handle batch processing and data aggregation in BizTalk?
Ans:
- Batch Orchestration: Using BizTalk orchestrations to process large volumes of data in batches.
- Batching Components: Implementing batching components to aggregate data based on predefined criteria.
- Message Aggregation: Aggregating multiple smaller messages into larger batches for efficient processing.
- Scheduled Processing: Scheduling batch processing jobs to run at specified intervals or based on triggers.
68. Explain the integration of BizTalk with custom line-of-business applications.
Ans:
- Adapter Development: Developing custom adapters or using existing adapters (e.g., WCF, SQL) to connect with LOB systems.
- Data Mapping: Mapping data formats and structures between BizTalk schemas and LOB application data models.
- Event Handling: Triggering events and workflows in LOB applications based on data changes or business rules in BizTalk.
- Transaction Management: Ensuring transactional consistency and integrity between BizTalk and LOB applications.
- Legacy System Integration: Modernize legacy systems by integrating them with BizTalk for improved interoperability and efficiency.
69. Describe a scenario in which BizTalk would be utilized for healthcare data integration.
Ans:
Integrating electronic health records (EHRs) between healthcare providers and hospitals. Automating the processing and adjudication of insurance claims between payers and providers. Facilitating secure exchange of medical information across disparate healthcare systems. Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations (e.g., HIPAA) for data privacy and security.
70. How does BizTalk facilitate integration between on-premises and cloud applications?
Ans:
Using BizTalk adapters (e.g., Azure Service Bus, Azure Blob Storage) for seamless integration with cloud services. Leveraging Azure Logic Apps, Azure Functions, and Azure API Management for cloud-based integrations. Acting as a message broker to route and transform messages between on-premises and cloud environments. Implementing hybrid integration patterns such as cloud-to-ground, ground-to-cloud, and cloud-to-cloud.
71. Explain the implementation of BAM for tracking order processing metrics in BizTalk.
Ans:
- Activity Definitions: Defining BAM activities to monitor critical stages and milestones in order processing workflows.
- Tracking Profiles: Creating tracking profiles to capture relevant data and performance metrics during order processing.
- Data Collection: Collecting and storing BAM data in the BAM database for real-time monitoring and analysis.
- Dashboard Creation: Creating BAM views and dashboards to visualize order processing metrics and performance indicators.
72. Describe the process of implementing a publish-subscribe architecture using BizTalk.
Ans:
- Messaging Patterns: Using messaging patterns such as publish-subscribe (pub/sub) for asynchronous communication.
- Message Broker: Configuring BizTalk orchestrations or Azure Service Bus for message routing and subscription management.
- Topic Subscriptions: Subscribing to message topics based on specific criteria (e.g., message type, content).
- Event Handling: Publishing events or messages to topics and notifying subscribers based on their subscriptions.
- Scalability: Scaling the publish-subscribe architecture to handle varying message volumes and subscriber loads.
73. How to monitor and troubleshoot performance issues in BizTalk Server?
Ans:
Monitoring BizTalk-specific performance counters (e.g., CPU usage, memory usage, message processing rates). Review BizTalk Server event logs for errors, warnings, and performance-related events. Using the BizTalk Health Monitor tool to analyze server health, performance, and configuration. Configuring tracking profiles and using BAM to monitor message processing and orchestration performance.
74. Explain the use of BAM Alerts for proactive monitoring and notification.
Ans:
Setting thresholds and criteria based on key performance indicators (KPIs) monitored by BAM. Configuring alert rules to trigger notifications when thresholds are exceeded or specific conditions are met. Sending alerts via email, SMS, or integrating with external systems for real-time notification. Monitoring BAM activities and viewing alerts in the BAM portal or customized dashboards.
75. Describe the integration of BizTalk with mobile applications for real-time updates.
Ans:
- Mobile Backend Integration: Using BizTalk adapters (e.g., REST, WCF) to connect with mobile backend services.
- Push Notifications: Push notifications from BizTalk are sent to mobile devices using platforms like Azure Notification Hubs.
- Data Synchronization: Implementing data synchronization between on-premises systems or databases and mobile clients.
- Offline Support: Supporting offline capabilities in mobile apps with data caching and synchronization mechanisms.
76. How to implement secure messaging and authentication in BizTalk?
Ans:
- Transport Security: Using secure protocols such as HTTPS, FTPS, or AS2 for message transport encryption.
- Message Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data within BizTalk using certificates or encryption algorithms (e.g., AES).
- Authentication: Implement authentication mechanisms (e.g., Windows Authentication, OAuth) to verify sender and receiver identities.
- Access Control: Configuring access control lists (ACLs) and permissions to restrict access to BizTalk artifacts and resources.
77. Explain the role of the Business Rules Engine in dynamically adjusting business logic.
Ans:
Allowing business analysts to define and manage business rules using a graphical interface (Business Rules Composer). Evaluating conditions and actions based on incoming message data during runtime. Enforcing policies and regulations by applying dynamic business rules to incoming messages or processes. Making real-time decisions and routing messages based on business rules without requiring code changes.
78. Describe the implementation of a scalable and fault-tolerant BizTalk solution.
Ans:
Deploying BizTalk in a clustered environment with redundant servers and load balancing. Implementing database clustering or mirroring for BizTalk databases to ensure data redundancy and failover. Establishing disaster recovery (DR) sites or using Azure Site Recovery for replicating BizTalk environments. Scaling BizTalk by adding additional host instances or servers to distribute workload and handle peak loads.
79. How to handle dynamic routing and message enrichment in BizTalk?
Ans:
- Routing Configuration: Configuring dynamic send ports and receive locations based on message content or properties.
- Content-Based Routing: Using message properties, context properties, or XPath expressions to route messages to appropriate destinations.
- Orchestration: Implementing BizTalk orchestrations to dynamically enrich messages by adding or modifying message content.
- Message Enrichment: Enriching messages with additional data from external systems or databases during message processing.
80. Explain the role of BizTalk in data synchronization and master data management.
Ans:
- Data Integration: Integrating disparate systems and databases to synchronize data across enterprise applications.
- Master Data Hub: Acting as a master data hub to centralize and manage master data entities (e.g., customer, product) across systems.
- Data Transformation: Transforming data formats and structures to ensure consistency and compatibility during synchronization.
- Real-time Updates: Enabling real-time data updates and propagation between systems to maintain data accuracy and currency.
81. What are the advantages of using BizTalk Server for enterprise integration?
Ans:
Supports a wide range of integration patterns including message transformation, routing, and orchestration. Extensive support for adapters and protocols to connect with diverse systems, databases, and applications. Enables automation of business processes through orchestration of workflows and integration of disparate systems. Includes tools like BizTalk Administration Console and BAM for monitoring and managing integrations.
82. Explain the role of adapters and connectors in BizTalk integration solutions.
Ans:
Adapters provide connectivity to various systems (e.g., databases, SAP, Salesforce) using specific protocols. Facilitate seamless exchange of data between BizTalk and external systems by handling communication protocols and data formats. Support for industry-standard protocols like HTTP, FTP, SOAP, and specialized adapters for ERP, CRM, and other enterprise systems.
83. How does BizTalk support compliance with industry standards and regulations?
Ans:
Facilitates Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) transactions that are compliant with standards like ANSI X12, EDIFACT, and HL7. Implements security measures such as message encryption, digital signatures, and secure communication protocols (e.g., AS2) to ensure data privacy and integrity. Provides auditing capabilities through BAM and logging mechanisms to track message flow and ensure regulatory compliance.
84. Describe the impact of BizTalk on business agility and operational efficiency.
Ans:
- Streamlining Processes: Automates workflows and business processes, reducing manual intervention and improving process efficiency.
- Faster Integration: Accelerates integration projects with pre-built adapters, reusable components, and visual development tools.
- Real-time Visibility: Provides real-time monitoring and analytics through BAM for proactive decision-making and performance optimization.
- Scalability: Scales seamlessly to handle growing data volumes and transaction loads, ensuring business continuity and operational scalability.
85. What are the challenges of implementing BizTalk in a heterogeneous IT environment?
Ans:
- Integration Complexity: Managing integration with diverse systems, protocols, and data formats can be complex and require specialized knowledge.
- Version Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between different versions of BizTalk, operating systems, databases, and third-party applications.
- Customization and Extensibility: Customizing BizTalk for specific business requirements may involve developing custom adapters, orchestrations, or pipelines.
- Performance Tuning: Optimizing performance across heterogeneous systems and maintaining scalability under varying workloads.
86. Explain the future trends and advancements expected in BizTalk technology.
Ans:
Enhanced support for hybrid cloud deployments and cloud-native integration solutions. Integration with AI and ML technologies for predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and intelligent automation. Adoption of microservices architecture for modular, scalable, and agile integration solutions. Emphasis on event-driven architectures for real-time data processing and responsiveness.
87. How does BizTalk ensure message reliability and consistency across systems?
Ans:
Supports transactional processing to ensure atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID properties). Uses reliable messaging protocols like MSMQ, Azure Service Bus, and WCF to guarantee message delivery. Provides message tracking capabilities to monitor message flow, identify failures, and ensure message integrity. Implements automatic retry mechanisms for failed message delivery attempts to improve reliability.
88. Describe the role of BizTalk in digital transformation initiatives.
Ans:
- Integration Backbone: This is an integration platform that connects legacy systems, cloud applications, and IoT devices.
- Process Automation: Automating business processes and workflows to improve operational efficiency and reduce manual effort.
- Data Integration: Integrating diverse data sources and formats to enable real-time data exchange and analytics-driven insights.
- Customer Experience: Enhancing customer experience by enabling seamless data flow and integration across customer touchpoints.
89. How does BizTalk handle message routing and processing?
Ans:
- Routing messages based on content, message properties, and configured rules.
- Using receive and send ports to manage message entry and exit points.
- Applying pipelines for message validation, transformation, and enrichment.
- Orchestrating message flows through business processes defined in orchestrations.
- Persisting message status and tracking data in the MessageBox database for monitoring and auditing purposes.
90. Explain BizTalk’s role in enabling interoperability between diverse systems.
Ans:
Supporting various protocols (e.g., HTTP, FTP, SOAP) and data formats (e.g., XML, JSON, EDI) to bridge communication gaps between systems. Providing adapters for connecting with ERP systems (e.g., SAP, Oracle), CRM systems (e.g., Salesforce), databases, and custom applications. Implementing message routing, enrichment, and transformation to ensure data compatibility and relevance across integrated systems.






