
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) is an enterprise resource planning (ERP) software suite that integrates various business functions such as finance, human resources, sales, supply chain management, and more. Developed by the German company SAP SE, it provides a centralized system to streamline processes, enhance data accuracy, and improve overall efficiency across organizations. SAP’s core component, SAP ERP Central Component (ECC), supports numerous industry-specific solutions and modules.
1. Explain the architecture of SAP.
Ans:
Three levels comprise the SAP architecture: the display layer, the application layer, and the database layer. This is based on a client-server design. SAP’s user interface is called the presentation layer (sometimes called the client layer). Using the SAP GUI, web browsers, or SAP Fiori applications, it may be viewed from a variety of platforms, including PCs, laptops, and mobile. Inputting user input, transmitting results back to the users, and coordinating with the application layer are all handled by this layer.
2. What are the key responsibilities of an SAP Basis Administrator?
Ans:
- Three levels comprise the SAP architecture: the display layer, the application layer, and the database layer.
- This is based on a client-server design. SAP’s user interface is called the presentation layer (sometimes called the client layer).
- Using the SAP GUI, web browsers, or SAP Fiori applications, it may be viewed from a variety of platforms, including PCs, laptops, and mobile.
- Inputting user input, transmitting results back to the users, and coordinating with the application layer are all handled by this layer.
3. What is the purpose of the SAP NetWeaver platform?
Ans:
- Offers a single technological platform for integrating several applications, both SAP and non-SAP.
- Application development, deployment, and execution environments are provided via development tools and environments.
- Ensures smooth communication across various IT environments and systems through interoperability.
- Business process management: Assists in planning, carrying out, keeping track of, and improving business processes.
- Data management: Enables adequate data access and management throughout the company.
4. Explain the difference between an application server and a message server in SAP.
Ans:
| Aspect | Application Server | Message Server |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Executes business logic and processes user requests. | Manages communication between multiple application servers. |
| Functionality | Handles transactions, batch processing, and system tasks. | Coordinates load distribution and failover for application servers. |
| Components | Includes work processes like dialogue, update, and background. | Maintains a list of active application servers and client requests. |
| Interaction | Interacts directly with the database to fetch and process data. | Facilitates communication and balances workload among servers. |
5. What are the different types of work processes in SAP?
Ans:
Work processes in SAP are specialized background jobs that manage particular kinds of system operations. Work processes come in many different forms; each intended to carry out a specific task. Taking user requests from the presentation layer, carrying them out, and providing the outcomes are the responsibilities of the Dialog work process (DIA). Batch jobs and other long-running or planned operations that don’t need instant human interaction are handled by the Background Work Process (BGD).
6. What is client administration in SAP?
Ans:
- Establishing new clients in the SAP system is known as client creation. Various departments, subsidiaries, or organizational units may be represented by distinct, independent entities known as clients.
- The process of copying client information, preferences, and configurations from one client to another is referred to as “client copy.” This is frequently done for training, testing, and setting up new environments, among other reasons.
- Client maintenance refers to the continuous administration of client setups, settings, and data. It covers tasks like user management, parameter modifications, and customization tailored to the client’s needs.
- When customers are no longer required, they are deleted from the SAP system. This process needs to be carefully planned and coordinated to ensure that any pertinent data is properly transferred or archived before being deleted.
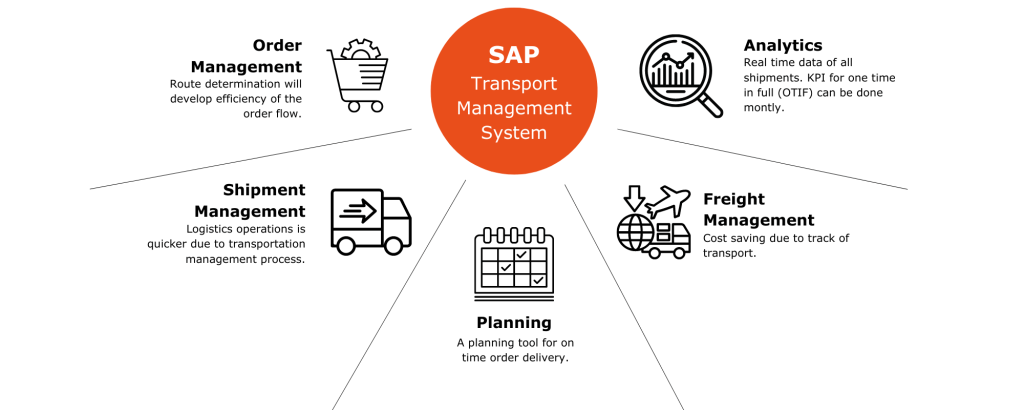
7. Explain the concept of SAP Transport Management System (TMS).
Ans:
The SAP Transport Management System (TMS) is a tool that manages the transport of changes and objects between different SAP environments, such as development, testing, and production. It ensures consistency and integrity by tracking transport requests and dependencies. TMS also facilitates rollback options, enhancing the safety and reliability of system updates and changes.
8. What are the different types of clients in SAP?
Ans:
There are three primary categories of clients in SAP: Production, Quality Assurance (QA), and Development (sometimes referred to as client 000). Every client in the SAP landscape has a distinct function. Application creation and modification, as well as configuration and customization, are handled by the Development client. Prior to being transferred to production production, performed changes by the development client are tested and validated by the quality assurance client.
9. How to monitor SAP system performance?
Ans:
- Numerous tools and methods, including SAP Solution Manager, SAP EarlyWatch Alert, and third-party monitoring tools, can be used to keep an eye on the performance of SAP systems.
- Response times, resource usage, database performance, and system utilization are examples of key performance indicators.
- Metrics, logs, and warnings are analyzed during monitoring in order to spot patterns, bottlenecks, and any problems.
- Maintaining optimal system performance and ensuring smooth operations are made possible by proactive techniques, including infrastructure optimization, workload balance, and performance tuning.
- Frequent analysis and monitoring allow for prompt intervention and ongoing SAP system performance enhancement.
10. What tools are used for monitoring SAP system performance?
Ans:
SAP CCMS (Computer Center Management System), SAP EarlyWatch Alert, SAP Solution Manager, and third-party monitoring tools like Dynatrace, AppDynamics, and Nagios are often used tools for monitoring SAP system performance. Response times, system usage, and database performance resource usage are just a few of the performance metrics that these tools may help with. Enterprises may guarantee the smooth operation of their SAP landscapes, improve user experience, and optimize system performance.
11. What is the purpose of transaction code ST22?
Ans:
- The SAP ABAP runtime error analysis tool, commonly referred to as the ABAP Dump Analysis, can be accessed using transaction code ST22.
- Its main goal is to give comprehensive details regarding runtime faults that happen in the SAP system.
- A brief dump is produced by an ABAP program when an error occurs during execution. This dump includes details about the error, what caused it, and the state of the program at the time of the error.
- Administrators and developers can examine these brief dumps with ST22 in order to find the faults’ primary source and implement remedial measures to fix them.
12. How to analyze a short dump in SAP?
Ans:
- Access Transaction ST22: To access the ABAP runtime error analysis tool, log in to the SAP system and go to transaction code ST22.
- View Short Dump List: In ST22, a list of all systemic short dumps will be shown to you. Every entry denotes a distinct runtime error.
- Select Short Dump: Click on the short dump in the list that you wish to examine.
- Examine Short Dump Details: Examine the specifics of the chosen short dump, taking note of the error message, the application that caused the problem, the raised exception, and any other pertinent data.
13. What is the use of transaction code SM50?
Ans:
The SAP code for transactions uses SM50 to show details on the work processes within the SAP system. Entering SM50 will display a list of all work processes that are now operating in the SAP system. This list includes information about each work process, including its ID, kind (dialogue, background, update, etc.), user context, status, and the program it is presently executing. SM50 gives administrators real-time insight into the workload on the system, how resources are being used, and what each work process is doing.
14. How to manage and monitor background jobs in SAP?
Ans:
- To monitor and manage background jobs, log in to the SAP system and go to transaction code SM37.
- View Job Status: SM37 lists all planned background jobs in the system. Every job’s status is visible to you, indicating whether it is scheduled, ongoing, completed, or cancelled.
- Keep an eye on the job logs to see comprehensive details about each background task’s execution, including any error or warning messages that came up during processing.
- Jobs Cancel or Reschedule: You can easily cancel or reschedule background jobs from SM37 if necessary. This can be used to change work schedules or eliminate positions that are no longer needed.
- Examine the job pool requests: Spool is commonly generated by background jobs.
15. Explain the concept of workload balancing.
Ans:
In a SAP landscape, workload balancing is the process of allocating system tasks, resources, and workload among several servers or components in order to maximize resource consumption, assure scalability, and optimize performance. Workload balancing is primarily used to spread processing loads evenly and avoid overloading or bottlenecking any one component. This approach not only improves overall system reliability but also enhances user experience by ensuring consistent application responsiveness and reducing latency during peak usage times.
16. What is the importance of CCMS in SAP?
Ans:
SAP relies heavily on the Computer Center Management System (CCMS) for alerting, performance management, and system monitoring. It offers a single platform to monitor the SAP system’s hardware resources, database performance, work processes, and system logs. With the help of CCMS, administrators may ensure optimal system performance and availability by proactively detecting and addressing issues.
17. What is the use of transaction code ST06?
Ans:
- The operating system monitor in SAP may be accessed by using ST06, and it gives administrators comprehensive details about the hardware specifications and performance indicators of the SAP server.
- By displaying essential metrics, including CPU, RAM, disk I/O, and network activity, ST06 enables managers to keep an eye on the functionality and overall health of the server infrastructure.
- This data is essential for spotting possible bottlenecks, making the most use of available resources, and guaranteeing that the SAP system runs smoothly.
- Furthermore, ST06 offers trend analysis and historical data, which helps administrators prepare for upcoming system updates and optimizations and predict resource requirements.
18. How to monitor database performance in SAP?
Ans:
SAP database performance is tracked by programs like SAP Solution Manager, DBACockpit, and DBA Cockpit. To find performance bottlenecks and improve database performance, key metrics such as SQL statement execution times, database locks, buffer consumption, and disk I/O are tracked. Database speed is also increased by using performance-tuning strategies, including table partitioning, query optimization, and index optimization. Proactive management and regular monitoring with these tools help maintain database health.
19. Explain the steps involved in SAP system installation.
Ans:
- Assemble the installation media, download the installation files, and check the hardware and software specifications.
- Ascertain the system environment, encompassing the quantity of servers, client specifications, and system structure.
- Set up and install the database program on the database server (such as SAP HANA or Oracle).
- Launch the SAPinst installer to follow the instructions for choosing components, defining installation paths, and setting system parameters.
20. What is the use of the Software Provisioning Manager (SWPM)?
Ans:
SAP offers the Software Provisioning Manager (SWPM) as a tool for setting up, updating, or transferring SAP systems. The installation procedure is made simpler and more automated, and administrators are guided through the many processes needed to set up an SAP system. SWPM manages post-installation activities, system parameter configuration, and the deployment of required software components. It can handle a number of scenarios, such as distributed installations, system copy/migration procedures, and single-instance deployments.
21. How to perform an SAP system upgrade?
Ans:
- System analysis: Examine the installed components, add-ons, and customizations that make up the present system environment.
- Upgrade Planning: Create an upgrade plan that includes budgets, schedules, and risk analyses. Choose the intended SAP release and schedule any necessary downtime.
- Download Upgrade Media: Visit the SAP Support Portal or SAP Marketplace to get the required upgrade files and updates.
- Pre-Upgrade duties: Complete pre-upgrade duties like turning off background jobs, installing prerequisite updates, and shutting down non-essential services.
22. What is the purpose of a support package in SAP?
Ans:
- Bug Fixes: Support packages include updates and patches for SAP software. These are designed to resolve known problems, faults, and vulnerabilities, enhancing the system’s security, dependability, and stability.
- Enhancements: In addition to new features and functionality, support packages may also offer upgrades to current SAP modules. These improvements provide users with more options and enhance their experience.
- Legal Compliance: Updates to guarantee adherence to industry norms, legal mandates, and regulatory requirements are frequently included in support packages.
- Performance Optimization: SpecificSpecific support packages offer performance optimizations, parameter adjustments, and enhancements to improve system performance and scalability to improve system performance and scalability.
- Compatibility: Support plans guarantee that various SAP components, add-ons, and third-party connectors work together.
23. Explain the process of kernel upgrade in SAP.
Ans:
- Download Kernel Files: Visit the SAP Support Portal or SAP Marketplace to get the most recent versions of the SAP kernel files. Make sure the kernel version you get is compatible with the platform and SAP system.
- Stop SAP System: You can terminate the SAP system by either stopping the SAP services on each application server or by using transaction code SM21.
- Backup Current Kernel: Make a backup copy of all currently installed SAP kernel files, including libraries and executables, to a secure location. This makes restoration simple in the event of any problems during those.
24. What are the prerequisites for installing an SAP system?
Ans:
Before deploying a SAP system, a few requirements must be satisfied. First and foremost, there needs to be a hardware infrastructure that satisfies SAP’s hardware requirements. Servers, storage, and network components are all included in this. Second, the operating system needs to be set up and installed in accordance with the prerequisites and supported platforms of SAP. Furthermore, installation and configuration of the relevant database software—such as SAP HANA, Oracle, or Microsoft SQL Server—are required.
25. What is the SAP Add-on Installation Tool (SAINT)?
Ans:
The SAP NetWeaver Application Server ABAP stack includes the SAP Add-on Installation Tool, or SAINT, as it is more generally known. SAINT installs, updates, and manages SAP add-ons and support packages in a SAP system. It offers administrators an easy-to-use interface through which they can explore, pick, and apply new features to their SAP environment. By automating many of the installation stages, SAINT makes it easier to add new features, upgrades, or industry-specific solutions to an existing SAP system.
26. How to configure a new instance in SAP?
Ans:
- Planning: Establish the new instance’s goal (development, testing, Production, etc.), the hardware and software specifications, and the system landscape’s architecture.
- Installation: Set up the SAP program on the server that is assigned to the new instance. Make sure all criteria are met and that SAP’s installation guide is followed.
- Instance Profile: Either clone an already-existing profile or create a new instance profile via transaction RZ10. Set up the new instance’s specifications, including the hostname, instance number, and directories.
- Database Connection: In the instance profile’s database connection configuration, enter the database server hostname, port, and login information.
27. What is the purpose of the transaction code RZ10?
Ans:
SAP uses the transaction code RZ10, for instance, profile management and upkeep. The configuration options found in instance profiles, such as memory allocation, buffer settings, and directory paths, specify the behaviour and settings of an SAP instance. RZ10 offers an intuitive user interface for generating, viewing, and updating instance profiles. Configurations, instance profile modifications, and system parameter adjustments can all be made by administrators using RZ10.
28. Explain the concept of system landscape in SAP.
Ans:
Within an organization’s IT infrastructure, the arrangement and configuration of various SAP environments and systems is referred to as the “system landscape” in SAP. It includes all of the networked servers, systems, and parts that support business operations and SAP software deployments. Usually, there are several tiers or layers in the system landscape, each with a distinct function in the software development, testing, and production lifecycle.
29. What is user administration in SAP?
Ans:
Managing user accounts and their access to SAP systems and apps is known as user administration in SAP. To safeguard private information and system resources this entails setting up, changing, and removing user accounts, allocating suitable roles and permissions, and enforcing security regulations. To reduce the possibility of unauthorized access or data breaches, user administrators must both enforce the concept of least privilege and ensure that users have the rights necessary to carry out their jobs efficiently.
30. How do you create a new user in SAP?
Ans:
- Access User Administration: Log in to the SAP system using the proper login information to add new users. Use transaction code SU01 to access the User Administration transaction.
- Enter User Data: Enter the required user data, such as username, user type (dialogue user, system user, or service user), and user ID, in the User Maintenance panel.
- Assign User Roles and Profiles: To specify a user’s access permissions, assign roles and profiles to them. While profiles define extra factors like default settings and password rules, roles specify sets of authorizations needed for particular job functions.
- Set User Parameters: You can set up user-specific settings, the expiration date, and the initial password, among other things, as desired.
31. Explain the concept of roles and profiles in SAP security.
Ans:
- Roles: In SAP, roles are collections of authorizations that specify what operations users are permitted to carry out on the system. The particular features and information that users are able to access are determined by a set of parameters, permission objects, and transaction codes that are contained in each role.
- Profiles: In SAP, profiles serve as holding areas for extra configurations and parameters in addition to role authorizations. Profiles specify properties like password guidelines, printing defaults, and menu items that are visible to users. Profiles support roles, while roles are primarily concerned with defining access permissions.
32. What is the purpose of transaction code DB13?
Ans:
SAP’s transaction code uses DB13 for database administration functions. It offers a consolidated interface for carrying out several database management tasks, such as database backups, restores, and monitoring. Database administrators may manage database tablespaces and logs, schedule and carry out database backup processes, and monitor backup status and logs with DB13. Furthermore, DB13 enables administrators to carry out consistency tests, and other maintenance procedures to guarantee the database’s performance, and stability.
33. How to perform user authorization checks?
Ans:
- Choose the Authorization Object: Choose the authorization object that controls access to the specific report, transaction, or feature that the user wishes to utilize.
- Examine User Roles: Confirm the user’s assigned roles. Roles contain sets of authorizations that specify what users can douser’s assigned roles.
- Verify Authorization Values: Verify the particular authorization values that have been allocated to each user’s role for the authorization object that has been detected.
- Assess Authorization Data: This involves comparing the authorization values that the user has provided with the authorization data that the system object that the user wishes to access requires.
- Authorization Decision: This is made after the user’s roles and authorization have been assessed.
34. What is the purpose of the transaction code PFCG?
Ans:
In SAP, roles and permission profiles are managed and maintained using the transaction code PFCG. Profile Generator, also known as Profile Comparison, is an interface that makes it easy to create, edit, and assign responsibilities to people in the SAP system. Administrators can define role authorizations with PFCG by assigning transactions, reports, and other objects to roles, choosing appropriate authorization objects and values, and keeping track of role descriptions and documentation.
35. Explain the concept of authorization objects in SAP.
Ans:
In SAP, authorization objects stand for certain system functionality or data that has to be protected via authorization checks. They specify the fine-grained permissions that regulate the actions that users are allowed to take on these domains. Authorization fields are a collection of fields that correspond to various elements or features of an authorization object. For instance, the transaction code that the user is permitted to perform is represented by the authorization field “TCODE” in the authorization object S_TCODE (Transaction Code).
36. How do usesr analyze and resolve authorization issues in SAP?
Ans:
- To identify the issue, determine the exact activity or functionality that the user is trying to execute and the permission error message that was received.
- Examine Authorization Logs: To determine whether authorizations were lacking or insufficient and which led to the problem, review the authorization logs (transaction SU53).
- Examine the user’s allocated roles to determine whether they lack the required permissions to carry out the action at hand.
- Determine which fields and authorization objects were involved in the unsuccessful authorization check.
37. What are composite roles in SAP?
Ans:
- Authorization Aggregation: The authorizations of the separate roles that make up a composite role are combined.
- Role Hierarchies: Composite roles can be arranged hierarchically, with individual roles or lower-level composite roles contained within higher-level composite roles.
- Role Reuse and Maintenance: Administrators can save effort duplication and reuse current roles by constructing composite roles.
38. What is the purpose of transaction code SUIM?
Ans:
- User Reporting: Produce reports based on user master data, including names, email addresses, IDs, and other personal information.
- Authorization Analysis: Create reports on assigned roles, profiles, and authorizations in order to analyze user permissions and approvals.
- Role analysis: Generate reports on roles and role assignments to examine role utilization, dependencies, and conflicts.
39. How do users perform database backups in SAP?
Ans:
- Create a database backup plan that considers the business’s needs, including factors like retention times, backup kinds, and backup frequency.
- Log into the SAP system with the necessary database administration rights to use the database vendor’s tools.
- The database management tools allow you to automate the backup process by scheduling backup tasks.
- To guarantee that backups are carried out consistently and at the necessary frequency, configure backup schedules in accordance with the backup plan that has been established.
40. Explain the concept of database recovery in SAP.
Ans:
After a system breakdown, data corruption, or other significant occurrence, database recovery in SAP refers to bringing the database back to a consistent and useable state. In order to reduce downtime and data loss, the recovery procedure seeks to recover lost or damaged data and instantaneously bring the database back online. Recovering from backups, using database logs to roll forward changes, or doing point-in-time recoveries are some techniques that may be used, depending on how severe the problem is.
41. What is the purpose of transaction code DB02?
Ans:
SAP uses the transaction code DB02 for investigation and monitoring of database performance. It gives administrators knowledge about the functionality and efficiency of the underlying database system. Tablespaces, data files, indexes, memory use, and other database resource-related metrics, reports, and performance statistics are all accessible to administrators via DB02. Administrators may enhance system responsiveness and efficiency by tracking database performance trends, optimizing database configuration settings with DB02.
42. How to manage database tables in SAP?
Ans:
- Table Maintenance: To carry out maintenance operations on database tables, use transaction codes such as SE11 (Data Dictionary) or SE14 (Database Utility). Tables can be created, edited, or deleted, and table fields, data items, and domains can also be defined.
- Tablespace Management: To guarantee effective storage allocation and use, monitor and manage tablespaces. To maximize performance, examine tablespace utilization and growth patterns using transaction code DB02 (Database Performance Monitor). Then, modify tablespace settings as necessary.
- Data Archiving: To control database table performance and size, put data archiving techniques into practice. To construct archiving objects, configure retention periods, and schedule archiving processes to remove obsolete data from tables, use transaction code SARA (Archive Administration).
43. Explain the concept of database reorganization in SAP.
Ans:
Database reorganization in SAP aims to optimize the underlying database system’s performance, storage efficiency, and structure. Rearranging database tables, indexes, and tablespaces is a typical job that helps reduce fragmentation, recover underutilized space, and enhance data access performance. Through more effective data organization, reorganization seeks to improve system responsiveness, decrease storage overhead, and streamline database processes.
44. What are the common database types used with SAP?
Ans:
- SAP HANA is an in-memory database platform created primarily for use with SAP applications. Its high-speed data processing and analytics capabilities enable real-time insights and speedier application performance.
- Oracle Database is a widely used relational database management system (RDBMS) that is integrated with SAP systems. It offers strong characteristics for handling structured data, transaction processing, and scalability.
- When used with SAP applications, Microsoft SQL Server is another popular RDBMS. For SAP implementations, it provides scalability choices, and sophisticated analytics capabilities.
- Often utilized in extensive enterprise settings, IBM Db2 is a relational database management solution for SAP applications. It provides capabilities for optimizing performance, high availability, and support for multiple data.
45. How do you perform database migration in SAP?
Ans:
- Planning and Preparation: Before beginning the procedure, carefully consider the migration and make all necessary preparations.
- Backup: Completely back up the database, application data, and configuration settings of the current SAP system. This guarantees that you have a backup plan should anything go wrong during the migration process.
- Tools for Database Migration: Software Provisioning Manager and Database Migration Option in SAP Software Update Manager are two examples of tools and utilities that SAP offers to help with database migration.
46. How do users monitor database space utilization in SAP?
Ans:
SAP and the underlying database platform offer a number of tools and transactions that can be used to analyze database space use. Transaction DB02, which provides information about the size and growth patterns of database tablespaces, data files, and indexes, is a widespread technique. Administrators can monitor space allocation, free space, and growth history, among other specific information about tablespace consumption, in DB02.
47. Explain the concept of database buffering in SAP.
Ans:
In SAP, database buffering is a technique that lowers the number of database accesses needed for frequently accessed data, therefore improving system performance. Instead of accessing often-used database tables or data items from the database each time they are required, it entails keeping them in memory buffers within the application server. The system determines whether buffered data is available when a user demands it. If the data is located in the buffer, no database access is required because it is fetched straight from memory.
48. What is the Transport Management System (TMS) in SAP?
Ans:
One essential tool in SAP’s ecosystem for managing the transfer of development objects and configuration changes between various SAP systems is the Transport Management System (TMS). It makes it possible to move modifications made to the development system methodically and controlled to the production system via a variety of testing and quality assurance settings. Thanks to TMS, data integrity and system stability are preserved as changes are implemented consistently, traceably, and trustworthy.
49. How to configure TMS in SAP?
Ans:
- Verify that the SAP system has the TMS functionality turned on. You can use the SAP installation tool or transaction code STMS to accomplish this.
- As a logical collection of SAP systems with a shared transport directory and configuration, create a transport domain. To establish a new transport domain and designate a distinct domain controller for handling transport requests inside the domain, use transaction STMS.
- Set up the domain controller, which serves as the principal hub for controlling transport-related tasks inside the transport domain.
50. What is a transport request in SAP?
Ans:
Within a SAP landscape, a transport request is a container that holds configuration changes and development items that must be transported from one system to another. Any modifications made to the development system—whether new programs are written, old configurations are changed, or customizations are developed—are combined into a transport request and sent to other systems, such as Production, testing, or quality assurance systems.
51. Explain the different types of transport requests.
Ans:
Developed or changed repository objects in the SAP development environment, including ABAP programs, function modules, screens, and other objects, are transported using workbench requests. Usually, they begin life in the development system and proceed to the testing and production systems via the landscape. Customizing Request Configuration changes made in the SAP customizing environment (transaction SPRO) are transported using customizing requests.
52. How to create and release a transport request?
Ans:
- Access Transport Organizer (SE01): In the SAP GUI, navigate to the Transport Organizer by entering transaction code SE01. You can make a request by using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + F10 or by navigating to “Request/Task” -> “Create” in the Transport Organizer interface.
- Add Objects: After the transport request is established, it is possible to include objects in it. To include objects, navigate to “Request/Task” -> “Include Objects” or press Ctrl + F11. From the object list, pick the development objects or settings you wish to include in the transport request.
53. What is the purpose of transaction code SE09?
Ans:
- Show Transport Requests: SE09 allows users to see comprehensive details about transport requests, such as their release history, contents, status, and transport logs.
- Examine Transport Logs: The transport process is documented in the transport logs, which are accessible by SE09 and include messages, warnings, and problems produced throughout the release and import of transport requests.
- Track Transport Requests: With SE09, users can monitor the status of transport requests sent to various SAP systems. The flow of changes across the transport landscape may be tracked, and users can keep an eye on the status of several types of transports, including confirmed, imported, and released.
54. How do usesr import transport requests in SAP?
Ans:
Users can import transport requests in SAP by following these steps:
- Access the Transport Management System (TMS) through the SAP GUI.
- Navigate to the “Transport Organizer” using transaction code SE09 or SE10.
- Select the transport request to be imported and choose the “Import” option.
- Specify the target system and confirm the import, which will process the request.
- Monitor the import logs for any errors or warnings to ensure successful completion.
55. What are the different transport routes in SAP?
Ans:
- Transport Route for Single System: This kind of route removes items inside a single SAP system. Andisand is usually used to transfer changes between various clients.
- Sequential Transport Route: These routes specify a straight line that moves objects via several systems in a particular order. Sequentially, objects are transferred from the development system to the quality assurance system and finally to the production system.
- Parallel Transport channel: This type of transport channel enables the simultaneous delivery of things to several target systems. When providing updates to distributed or regional contexts, for example, this kind of route can be helpful in distributing changes to several systems simultaneously.
56. How to troubleshoot transport errors in SAP?
Ans:
- Examine Transport Logs: To begin, look over the transport logs for the transfer requests that were unsuccessful. To access the Transport Organizer and get to the logs for unsuccessful requests, use transaction codes SE01 or STMS. Examine the logs to find any warnings or error messages that arose during the transport process.
- Recognize Error Messages: Watch for error messages in the transport logs, as they frequently hint at the reason behind the transport’s failure. Seek out particular error codes, descriptions, and timestamps to identify the issue’s origin.
- Examine Object Status: Confirm the current state of the objects that were part of the unsuccessful transport requests. To verify that each item is consistent across systems and to monitor its state, use transaction code SE03.
57. Explain the concept of transport logs in SAP.
Ans:
Transport logs in SAP offer comprehensive documentation of all the actions and occurrences that take place when objects are moved between systems and configurations are changed inside the SAP environment. These logs are an invaluable resource for monitoring the status of transport requests, identifying problems and errors, and recording the transport procedure.
58. How to perform system refresh in SAP?
Ans:
- In order to synchronize the target system with the most recent configurations and data from the source system, copying data from a source system—such as a production system—to a target system—such as a development or quality assurance system—is the process of performing a system refresh in SAP.
- A few phases are usually included in the system refresh process: client copy, system backup, system export/import, and post-refresh actions. Initially, a complete backup of the original system is made to guarantee the integrity and recoverability of data.
59. What is the purpose of transaction code SPAD?
Ans:
To utilize SAP’s Spool Administration function, enter the transaction code SPAD. The administration of the print and spooling system in a SAP environment is the primary goal of SPAD. Printer configuration, printer device definition, print queue management, and spool request monitoring are all accomplished by system administrators using SPAD. Network, virtual, and local printers are just a few of the output devices for which administrators can configure printers using SPAD.
60. How do you manage SAP printers and spool administration?
Ans:
- Spool Administration (SPAD): To access the SAP Spool Administration feature, enter the transaction code SPAD.
- Define Output Devices: In SPAD, specify which printers and print queues the different output devices should go to. Indicate the host printer, destination settings, device type, and access method, among other details.
- Print Queue Configuration: Create print queues to oversee the flow of print jobs and handle spool requests. For every print queue, define parameters such as the maximum number of spool requests, the priority settings, and the output device assignments.
61. Explain the concept of operation modes in SAP.
Ans:
Operation modes in SAP serve as a tool for defining and controlling how the system employs resources in response to various operational scenarios or business needs. By configuring operating modes, system administrators can improve system performance and resource consumption based on multiple scenarios. These configuration options include performance parameters, background processing priority, and resource allocations. The definition of operation modes, usually depends on variables like system load, the time of day, or business activity.
62. How do users configure and manage operation modes?
Ans:
To configure and manage operation modes in SAP, follow these steps:
- Open the operation modes configuration using the transaction code SM63 in the SAP GUI.
- Create new operation modes or modify existing ones by specifying their names, descriptions, and relevant parameters such as the processing type.
- Assign application servers to the defined operation modes, determining which instances will operate under each mode based on load balancing and resource management.
- Configure specific parameters for each operation mode, such as maximum parallel processes and priority levels, to optimize performance and resource allocation.
- Regularly monitor the performance of operation modes through transaction ST03N or ST06, making adjustments as necessary to improve efficiency and address any system issues.
63. What is the use of transaction code SM21?
Ans:
- Viewing System Logs: SM21 allows users to see what’s in the system log and look at entries for particular systems, periods, or log categories. Users can follow system events and activities over time by viewing the system log entries in chronological order.
- Log Entry Filtering: SM21 offers the ability to filter log entries according to several parameters, including message type, severity level, component name, and user ID. Users can tailor others to highlight particular messages or occurrences and omit unrelated data.
- Examining Error Messages: SM21 is used by system administrators and support staff to examine warnings and error messages in the system log. By reviewing log entries, users can troubleshoot, diagnose, and discover issues.
64. How to perform system log analysis in SAP?
Ans:
In SAP, system events, failures, warnings, and other pertinent data can be found by reviewing, filtering, and analyzing log entries using the System Log tool (transaction code SM21). In order to narrow down the analysis to particular criteria, administrators set log parameters including the time range, log type, severity level, and component. The System Log tool allows administrators to export log entries for further analysis or reporting, facilitating better decision-making and troubleshooting.
65. Explain the purpose of transaction code SMLG.
Ans:
- Defining Logon Groups: Within an SAP system landscape, administrators can use SMLG together to form logon groups. Each login group consists of one or more application servers that share the same set of SAP services and resources.
- Setting up Load Balancing: Logon groups make load balancing possible by evenly dividing user logon requests among the group’s application servers. SMLG makes configuring load balancing factors, including server priorities, load distribution methods, and user session management settings, more accessible
66. How do usesr configure logon groups in SAP?
Ans:
- Maintenance of Access Logon Groups (SMLG): Using the SAP GUI’s transaction code SMLG, launch the Logon Group Maintenance tool.
- Form New Logon Groups: On the Logon Group Maintenance screen, click the “Create” button or choose the “New Entries” option to form new login groups.
- Add Application Servers: When assigning application servers to login groups, provide the server name, instance number, and any other pertinent information.
67. What is the role of transaction code SM59?
Ans:
SM59 enables users to add additional RFC destinations to connect SAP and non-SAP systems or other SAP systems. Users can specify connection parameters, including communication protocol, target host, altering connection parameters, or altering communication settings are some ways that users can utilize SM59 to keep their current RFC destinations active. This involves upgrading destinations to account for modifications to the network or system architecture.
68. How to apply support packages in SAP?
Ans:
Examine the Support Package Documentation: To comprehend the modifications, additions, and requirements related to a support package, go over the release notes, documentation, and installation instructions that SAP has supplied before deploying a support package. Get the Support Package here. You can also get the necessary support package files by visiting the SAP Software Download Center or SAP Support Portal. Make sure that the support package version and components you download are appropriate for the SAP system landscape.
69. What is the difference between support packages and enhancement packages?
Ans:
Assistance Bundles:
- Provide updates, patches, and bug fixes for SAP software that is already in use.
- It was Primarily focused on enhancing system security, dependability, and stability.
- They are usually issued often to fix known bugs and vulnerabilities.
- They are applied to SAP systems to guarantee that the most recent patches and bug fixes are installed.
Packages for Enhancement:
- Provide more features, solutions tailored to a particular industry, and enhancements to company procedures.
- Give businesses the freedom to decide which new features to activate and implement according to their own business requirements.
- Released, typically every 12–18 months, less frequently than support packages.
- After installation, extra procedures for activation and configuration are required in order to make new features functional.
70. How do users handle SPAM/SAINT update issues?
Ans:
- Examine Log Files: Look through the log files produced by the SPAM/SAINT update procedure to find any informational, warning, or error messages. Examining the log files can give important information about the type and source of the update problems.
- Examine Error Messages: To determine the underlying reason for the update problems, examine the error messages recorded in the log files. Determine whatever prerequisites, conflicts, or dependencies might be causing the update procedure to fail or encounter issues.
- Check Dependencies: Make sure that the update process’s prerequisites and dependencies have all been satisfied. Before attempting to deploy updates via SPAM/SAINT, be sure that all necessary software components, add-ons, support packages, and system customizations are in place.
71. What is the purpose of the SAP Support Portal?
Ans:
- Product Documentation Access: For SAP software products, users get complete access to user manuals, installation instructions, configuration manuals, release notes, and technical specifications.
- Software Downloads: The SAP Support Portal offers patches, updates, support packages, and downloads for SAP software products. Users can download the most recent software patches, updates, and versions to maintain security and keep their SAP systems up-to-date.
- Knowledge Base and SAP Notes: Users can search the SAP Knowledge Base and access SAP Notes to find information, solutions, and suggestions for fixing difficulties, troubleshooting issues, and implementing best practices for SAP systems.
72. How to use the Maintenance Optimizer?
Ans:
To go to the Maintenance Optimizer, go to the Software Downloads area of the SAP Support Portal after logging in. Use the Software Logistics Toolset to access the Maintenance Optimizer tool. Decide on the System Landscape: Select the SAP system landscape for which you wish to optimize maintenance. Indicate the kind of system (Production, development, quality control, etc.) and the SAP Solution Manager system that is connected to the landscape in question.
73. What is the role of the Solution Manager in patch management?
Ans:
Patch Landscape Analysis: The SAP Solution Manager analyzes the existing patch landscape to find the installed software components, their versions, and any potential dependencies or conflicts. This study helps administrators better grasp the system landscape’s present condition and make plans for any modifications. The SAP Solution Manager suggests the most recent software updates, patches, and support packages for the installed components based on its study of the patch landscape.
74. How do users apply kernel patches in SAP?
Ans:
- Examine SAP Note: Before implementing a kernel patch, go over the relevant SAP Note that SAP has provided. The SAP Note includes important details about the patch, including compatibility requirements and installation guidelines.
- Get Kernel Patch Here: To get the kernel patch files, go to the SAP Software Get Center or SAP Support Portal. Make sure the kernel patch version you download is appropriate for your operating system and SAP system.
- Backup System: Make a complete system backup, including a database and file system backup, prior to implementing the kernel patch. This ensures that you have a backup copy of the system in case the patching procedure encounters problems or mistakes.
75. What is the purpose of transaction code SPAM?
Ans:
- Support Package Management: SAP software components’ bug fixes, upgrades, and additions are managed using a centralized interface called SPAM.
- Add-On Installation: SPAM not only makes support packages easier to install, but it also makes it easier to install extensions and add-ons for SAP applications.
- Resolution of Conflicts: Prior to applying support packages or add-ons, SPAM looks for dependencies, conflicts, and prerequisites.
76. Explain the role of the Web Dispatcher in SAP.
Ans:
As a reverse proxy server, SAP’s Web Dispatcher routes inbound HTTP and HTTPS requests from clients to the relevant SAP system elements, including SAP NetWeaver systems or application servers. SSL encryption, speed optimization, request filtering, and load balancing improve system security. It also allows URL redirection and single sign-on, which enhances user experience and makes it easier for customers and SAP systems to communicate together.
77. What is the significance of the SUM tool?
Ans:
- Because it simplifies and automates the process of applying software upgrades, patches, and updates throughout the SAP system landscape, SAP’s Software Update Manager (SUM) product is essential.
- SUM makes it easier to carry out strenuous activities like version upgrades, database migrations, and system maintenance by combining multiple update and upgrade tools into a single interface.
- Its relevance stems from its capacity to avoid manual errors, limit downtime, and guarantee the seamless and effective deployment of software upgrades, all of which contribute to improved system performance, reliability, and compliance with SAP standards.
78. Explain the concept of high availability in SAP.
Ans:
The ability of a SAP system to continue functioning and being available to users with the least amount of downtime or interruption—regardless of hardware malfunctions, software bugs, or other disruptions—is referred to as high availability in SAP. By optimizing system uptime and reducing the effect of outages on business operations, the idea seeks to guarantee the ongoing availability of crucial SAP systems and business processes.
79. What are the different high-availability solutions for SAP?
Ans:
- Automatically moves workloads from faulty servers to working ones within a cluster using clustering technologies to guarantee continuous availability of SAP services.
- Examples are SAP HANA System Replication with SUSE Linux Enterprise Server for SAP Applications (SLES HA) and SAP HANA System Replication (HSR).
- In the event that the primary system fails, SAP HANA System Replication enables failover to the secondary system.
- It can be configured to be synchronous or asynchronous and replicates SAP HANA databases between primary and secondary systems.
- To guarantee the availability of crucial SAP Business Suite components like Enqueue Server and Message Server, SAP Enqueue Replication Server (ERS) and SAP Central Services (SCS) are implemented.
80. How to configure SAP for high availability?
Ans:
- Evaluate Requirements: List the essential SAP components, services, and business operations that need to be highly available. For every component or service, ascertain the recovery time objectives (RTOs), uptime targets, and availability requirements.
- Select High Availability Solution: Consider the infrastructure, financial restrictions, and requirements when selecting the best high availability solution. Solutions for disaster recovery, hardware redundancy, clustering technologies, and SAP HANA System Replication are among the options.
- Create Redundant Architecture: Create a redundant architecture for SAP systems by setting up redundant network devices, servers, storage systems, and power supplies, among other hardware elements. Implement clustering and failover techniques to provide smooth failover in the event of hardware failures.
81. Explain the concept of disaster recovery in SAP.
Ans:
- Risk Assessment and Planning: To detect any threats, weaknesses, and hazards to SAP systems and operations, a thorough risk assessment must be carried out. Create a disaster recovery strategy that outlines the tactics, steps, and resources needed to respond to and recover from disasters based on the assessment.
- Backup and Recovery: Implement backup and recovery strategies to periodically back up important components, configurations, and data from SAP systems. Ensure that backups are safely kept and can be swiftly restored in the event of a disaster, system failure, or data corruption.
- Data Replication and Redundancy: Replicating SAP system configurations and data to off-site sites or backup data centres through the use of data replication and redundancy technologies. In the event that the primary data centre fails or there is data loss, this guarantees data availability and permits quick recovery.
82. What are the steps involved in disaster recovery planning?
Ans:
- Define Recovery Objectives: For SAP systems and activities, set recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). Assign each system a maximum allowable downtime and data loss tolerance, then order recovery efforts based on those values.
- Create a Comprehensive Disaster Recovery Plan: Create a comprehensive plan that outlines resources, protocols, and tactics for responding to and recovering from disasters. Establish roles dut,ies and procedures for communication, escalation, and recovery.
83. How do usesr perform system failover testing in SAP?
Ans:
In order to confirm that failover mechanisms and recovery procedures are working as intended, SAP system failover testing requires meticulous design and execution of simulated disaster situations. This procedure entails establishing the parameters and goals of the test, informing relevant parties, setting up a test environment, initiating failover mechanisms, keeping an eye on the failover process, verifying the success of failover, carrying out recovery procedures, recording test results, going over and evaluating the results, and repeating testing on a regular basis.
84. What is the use of the Central Instance in high availability?
Ans:
The Central Instance (CI) is a key component of the high availability (HA) setup in SAP since it acts as the central hub for monitoring and directing all system operations. The CI hosts important parts like the Enqueue Server and Message Server, as well as core services like the SAP Gateway and Internet Communication Manager (ICM). These parts are necessary for locking mechanisms, user request routing to the right application servers, and system communication.
85. How is a clustered environment configured for SAP?
Ans:
- Set Up Shared Storage: SAP data files, executables, and shared resources can be hosted on shared storage (SAN, NAS, etc.). Set up the cluster so that it can access shared storage and that each cluster node’s data is consistent and intact.
- Set Up Virtual IP Addresses: Give each cluster node a virtual IP address (VIP) so that they may all access SAP services through a single virtual endpoint. Set up the cluster so that it can oversee the distribution and failover of VIPs among cluster nodes in the event of a node failure.
- Configure Heartbeat and Quorum: To monitor the well-being and condition of cluster nodes, configure heartbeat and quorum settings. Establish quorum rules to guarantee cluster stability and avoid situations in which separate nodes assert resource ownership.
86. What is the purpose of synchronous and asynchronous replication in SAP?
Ans:
Data changes are committed to the original database and instantly replicated to the secondary database via synchronous replication. For the primary database to declare a transaction complete, the secondary database must ensure that the modifications have been correctly replicated. Asynchronous replication commits data changes to the primary database without requiring confirmation from the secondary database. Later, changes are asynchronously propagated to the secondary database.
87. How to ensure data consistency in a high-availability setup?
Ans:
High-availability setups can guarantee data consistency by implementing synchronous replication techniques, transaction logging, quorum and consensus methods, checksums, and data validation to preserve data integrity. Data consistency is ensured by adhering to the ACID principles and building transactions and applications to provide atomicity, consistency, and isolation durability.
88. What is the purpose of transaction code SE38?
Ans:
- The transaction code To run ABAP programs in SAP, utilize SE38.
- This allows developers and system administrators to create, modify, display, and run ABAP programs directly within the SAP system.
- ABAP code, including reports, function modules, classes, and other program objects, can be easily developed and maintained using the SE38 interface.
- With SE38, users can display program source code, update already-written ABAP programs, and run applications for Production or testing.
89. How do users perform ABAP dump analysis?
Ans:
- Get the Tool for Dump Analysis Here: To use the “ABAP Runtime Error” investigation tool, use transaction code ST22. This transaction provides a list of the system-generated short dumps.
- Choose the Appropriate Dump: On ST22’s first screen, a list of recent runtime problems appears. You can examine the dump you wish by clicking on its date and time entry or using the filters to refine the list.
- Examine the dump’s specifics: The dump details screen provides complete details regarding the error, such as the kind of mistake, the program in which it happened, and the precise code line that caused the problem.
90. What is the use of transaction code RZ20?
Ans:
- System Monitoring: RZ20 offers a thorough overview of the state of the operating system, database, hardware, and SAP apps on the system. Administrators can monitor a variety of metrics and performance indicators in real-time.
- Alert Management: Depending on the level of severity, the transaction shows alerts for various system components. Critical issues impacting system availability and performance can be promptly detected by administrators, who can then take appropriate action.
- Customizable Monitoring Trees: Users can customize the monitoring trees to concentrate on particular areas of interest. This adjustment allows for more focused monitoring, freeing up administrators to focus on important system components and performance indicators.
91. Explain the concept of SAP Fiori and its architecture.
Ans:
With a contemporary, user-friendly, and uniform interface across platforms, SAP Fiori is a user experience (UX) framework that aims to improve the usability of SAP applications. One component of its architecture is the SAP Fiori Launchpad, which functions as a central point entry and includes tiles that may be customized for various applications. SAP Fiori also emphasizes role-based access, allowing users to see only the applications and data relevant to their specific tasks, further enhancing efficiency and productivity.
92. What is the purpose of the transaction code SICF?
Ans:
Internet Communication Framework (ICF) services are managed and configured in SAP using the transaction code SICF. Web-based services and applications like SAP Fiori, SAP Web Dynpro, and SAP NetWeaver Business Client are made possible by ICF services. Administrators can set up, deactivate, and activate different HTTP, HTTPS, and SOAP services needed for these apps through SICF. It also permits controlling user authentication and security settings, as well as establishing service nodes and changing service parameters.






