- Introduction to Tron Blockchain
- The Origin and Vision of Tron
- How Tron Blockchain Works
- Key Features and Technology
- The TRX Token and Economy
- Tron Ecosystem and dApps
- Use Cases and Real-World Applications
- Tron vs Other Blockchains
- Challenges and Criticisms
- Future Roadmap and Potential
- Conclusion
Introduction to Tron Blockchain
Tron is a blockchain-based decentralized platform primarily focused on building a free, global digital content entertainment system that leverages blockchain and peer-to-peer (P2P) technology. It aims to enable creators to publish, store, and own data while cutting out intermediaries, giving users more control over their content and revenues. Launched in 2017, Tron has rapidly evolved to support smart contracts and decentralized applications, positioning itself as a competitor to Ethereum and other blockchain platforms. It claims to offer high throughput, scalability, and low transaction fees, Tron Ecosystem and dApps making it attractive for developers and users alike.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Today!
The Origin and Vision of Tron
Tron was founded by Justin Sun in 2017. Sun, a prominent figure in the blockchain space, envisioned creating a decentralized internet where content creators have autonomy and users enjoy unrestricted access.
Key Milestones:- 2017: Tron project launched, raising $70 million via ICO.
- 2018: Tron mainnet went live, transitioning from Ethereum to its own blockchain.
- 2018: Acquisition of BitTorrent, a massive peer-to-peer file sharing platform.
- 2019-2020: Launch of Tron Virtual Machine (TVM) and expansion of dApps.
Tron’s vision is underpinned by the belief that the current internet architecture is dominated by intermediaries such as Google, Facebook, and YouTube, who control data, monetize user content, Tron Ecosystem and dApps unrestricted and impose restrictions. Tron Blockchain Works Tron seeks to disrupt this by enabling a truly decentralized web the “Web 3.0” era.
How Tron Blockchain Works
Tron operates on a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, which is more energy-efficient and faster than Proof of Work (PoW) used by Bitcoin.
Key Components:
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Tron uses a consensus model where TRX token holders vote for “Super Representatives” (SRs). These SRs validate transactions and produce blocks. There are 27 SRs at any time.
- Tron Virtual Machine (TVM): A Turing-complete virtual machine compatible with Ethereum’s EVM, allowing developers to deploy smart contracts written in Solidity.
Three-layer Architecture:
- Storage Layer: Manages blockchain data storage.
- Core Layer: Handles smart contracts, consensus, and account management.
- Application Layer: Hosts dApps and APIs.
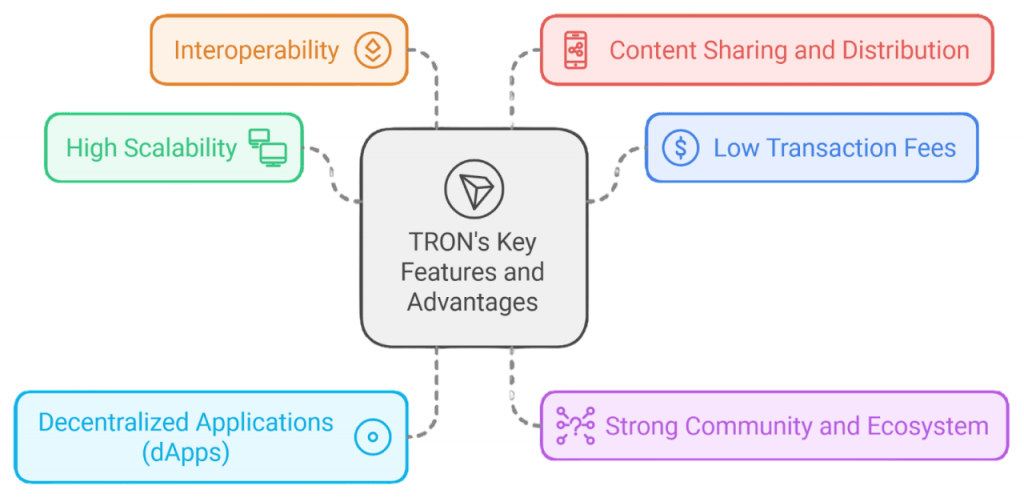
- High Scalability: With its DPoS consensus, Tron achieves faster transactions with low latency.
- Low Transaction Fees: Transactions on Tron cost a fraction of a cent, making microtransactions feasible.
- Smart Contracts: Supports Ethereum-compatible smart contracts through TVM.
- Decentralized Storage: Through BitTorrent File System (BTFS), enabling decentralized file sharing.
- Governance Model: TRX holders have voting power to elect SRs and influence the protocol.
- Cross-chain Compatibility: Tron bridges allow asset transfers across blockchains like Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain.
- Medium of Exchange: Used for transaction fees, smart contract deployment, and incentivizing network participation.
- Staking: TRX holders can stake tokens to vote for SRs and earn rewards.
- Governance: Voting power is proportional to TRX holdings.
- Token Economy: Tron supports the creation of TRC-10 and TRC-20 tokens, enabling new projects and assets within its ecosystem.
- Decentralized Content Sharing: By integrating BitTorrent, Tron is enabling decentralized content distribution, allowing creators to monetize their content directly with minimal fees.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi):Tron’s fast and cheap transactions make it an ideal platform for DeFi services, competing with Ethereum-based projects.
- Gaming and NFTs: Tron hosts blockchain games and NFT marketplaces, catering to a growing community interested in digital collectibles and play-to-earn mechanics.
- Micropayments and Streaming:Tron’s infrastructure supports micropayments for streaming and tipping, revolutionizing how creators monetize their audience.
- Consensus: Tron uses DPoS (fast, low energy); Ethereum currently PoW transitioning to PoS.
- Transaction Speed: Tron ~2000 TPS; Ethereum 15-30 TPS.
- Fees: Tron’s fees are much lower.
- Smart Contracts: Both support Solidity and EVM compatibility.
- Both use DPoS-like models with fast transactions and low fees.
- BSC is tightly integrated with Binance exchange; Tron emphasizes decentralized content.
- Plagiarism Allegations: Tron faced accusations of copying code from other projects.
- Competition: Tron faces fierce competition from Ethereum, BSC, Solana, and others.
- Regulatory Risks: As with all blockchain projects, regulatory scrutiny remains a risk.
- Improve scalability and interoperability.
- Expand DeFi and NFT ecosystems.
- Enhance governance mechanisms.
- Increase adoption in emerging markets.
This architecture supports high throughput, with Tron claiming up to 2000 transactions per second (TPS) compared to Ethereum’s 15-30 TPS.
To Explore Database in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Database Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Key Features and Technology
Tron’s technology stack includes several features that make it attractive:
The TRX Token and Economy
The native cryptocurrency of Tron is TRX (Tronix), TRX has gained substantial market capitalization and liquidity, Tron Blockchain Works making it one of the top cryptocurrencies by trading volume.which plays a vital role in the ecosystem:
Use Cases and Real-World Applications
Tron vs Other Blockchains
Tron vs Ethereum
Challenges and Criticisms
Centralization Concerns: Critics argue Tron’s DPoS leads to fewer validators, reducing decentralization.
Want to Learn About Database? Explore Our Database Interview Questions and Answers Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Future Roadmap and Potential
Tron continues to evolve, with plans to:
Conclusion
Tron Blockchain represents a bold effort to reshape the internet by decentralizing content ownership and fostering a thriving ecosystem of dApps and digital assets. With fast transaction speeds, low fees, Tron Blockchain Works and a growing community, Tron has carved out a unique niche in the blockchain space. While challenges remain, the project’s vision and technical innovations offer exciting opportunities for creators, Tron Ecosystem and dApps developers, and users to participate in a truly decentralized digital future.