- Introduction to Supply Chain Management in E-commerce
- Importance of Supply Chain in E-commerce
- Key Components of E-commerce Supply Chain
- Challenges in E-commerce Supply Chain Management
- Technology’s Role in E-commerce Supply Chain
- Best Practices for Effective E-commerce Supply Chain Management
- Case Studies of Successful E-commerce Supply Chains
- The Future of Supply Chain Management in E-commerce
- Conclusion
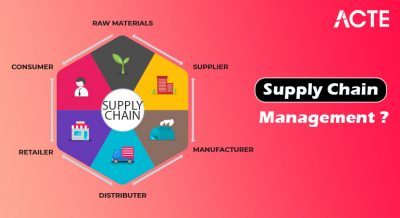
Introduction to Supply Chain Management in E-commerce
E-commerce has revolutionized consumer shopping by offering unprecedented convenience, choices, and speed. Underlying every seamless online purchase, however, lies a complex orchestration of activities collectively known as the supply chain. From sourcing raw materials and managing vendor relationships to warehousing, last-mile delivery, and reverse logistics, effective Supply Chain Management (SCM) ensures products reach customers quickly, accurately, and cost-effectively.
In e-commerce, where consumer expectations for rapid delivery and real-time tracking are high, SCM becomes a critical differentiator. This article examines the foundations, challenges, best practices, technology strategies, and future trends shaping SCM in e-commerce.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Importance of Supply Chain in E-commerce
In the fast-paced world of online shopping, managing the supply chain well is absolutely key to doing well in business. It really shapes how happy customers are and how smoothly everything runs day-to-day. When shoppers get their orders quickly, correctly, and can return things easily, they tend to stick around and trust the brand more. But if there’s any hiccup with shipping or if orders are wrong, customers get upset, and the company loses out on money. For online businesses, it’s also vital to focus on running things efficiently and keeping costs down. This means having operations that are lean, can grow, and make the most of packing and shipping, boost how much gets done in the warehouse, and cut down on having too much stuff sitting around. All this helps lower costs and boost profits. Having the right amount of stock on hand is another big deal. Getting this balance right stops the costly problems of running out of popular items or having warehouses filled with unsold goods. It saves money on storage while making sure products are always ready for customers. All the information collected from different parts of the supply chainlike predicting what will be popular and how shipments are going is incredibly useful. It helps make smarter choices about buying stock, shipping things better, and tracking important business numbers. Ultimately, the supply chain bridges brand promise and customer experience its design and efficiency directly impact revenue, costs, and brand reputation.
Key Components of E-commerce Supply Chain
Managing a robust e-commerce supply chain involves several interconnected components:
- Selecting reliable vendors, negotiating terms, and ensuring product quality are foundational. Strategic agreements (e.g., volume discounts or drop-shipping) help manage costs and flexibility.
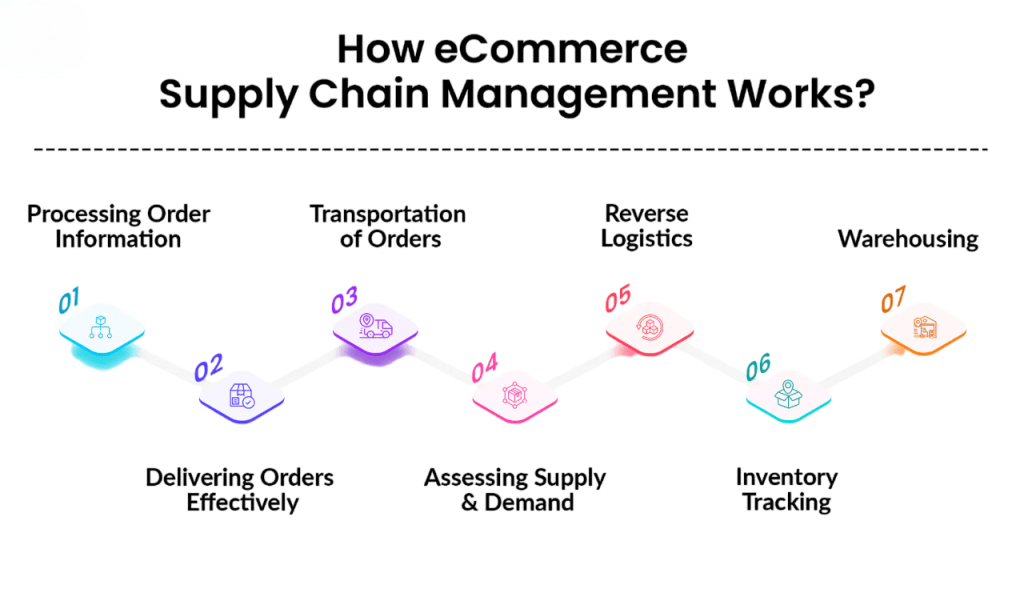
- E-commerce often utilizes both centralized (mega-fulfillment centers) and decentralized (local distribution centers or dark stores) warehousing. Efficient layout, inventory tracking, automation, and picking strategies are key to volume handling.
- OMS coordinates order intake, validation, routing, and fulfillment. Integration with marketplaces and e-commerce platforms ensures a single, consolidated view of orders and their statuses.
- Involves processes for picking, packing, and preparing products for shipment. High-volume players rely on technologies like barcode scanning, pick-to-light, robotics, and conveyor systems for enhanced speed and accuracy.
- Covers delivery from warehouses to customers. Logistics players may be in-house or third-party carriers. Last-mile strategies might include route optimization, varied shipping options, and smart parcel lockers.
- Efficient returns processing, restocking, refurbishing, or disposal is critical in e-commerce with high return rates (~20–30%). Streamlined reverse flows reduce cost and enhance customer trust.
- Measuring key metrics includes fulfillment speed, inventory turnover, delivery times, cost-per-order, return rate, and customer satisfaction. Real-time dashboards help identify issues early.
- Retail events, trends, and seasonality create significant demand fluctuations. Incorrect forecasting leads to stockouts or excessive warehousing costs.
- Same-day or next-day delivery expectations strain warehousing and courier setups, especially for remote or rural areas.
- High return volumes require robust systems for reverse logistics, inspections, repackaging, and restocking adding cost and complexity.
- Synchronizing inventory across online stores, marketplaces, and physical stores is tricky but essential to avoid overselling or inconsistent stock updates.
- Serving wide geographies introduces challenges like import/export laws, lead time variations, customs, and multi-currency considerations.
- Transportation, storage, packaging, labor, and returns incur costs. Balancing these with margins, pricing, and customer expectations requires continuous optimization.
- Connecting various systems E-commerce platforms, OMS, warehouse automation, CRM, and 3PL providers requires robust integration to ensure data flow and visibility.
- With its expansive fulfillment center network, same-day delivery (Prime Now), robotics, and real-time inventory, Amazon has set the bar for fulfillment efficiency. Innovations include drone delivery pilots, automated sortation, and algorithmic replenishment.
- Focused on customer experience, Zappos integrated an efficient reverse logistics process. They offer free and extended returns, using centralized fulfillment centers designed for swift processing and restocking.
- Flipkart developed regional warehouses and predictive inventory distribution to manage diverse geography. Their Smart Fulfillment Centers reduce cost and improve delivery performance in semi-urban and rural regions.
- Adopting direct-to-consumer (DTC) model, Warby Parker built micro-fulfillment centers near urban hubs for same-day shipping and quick returns, enhancing customer experience and footprint flexibility.
- AI-powered systems will dynamically select warehouses and couriers based on customer preferences and context. Smart packaging customized in real-time may emerge.
- Advanced analytics will anticipate demand anomalies, optimize deliveries before issues occur, and proactively manage exceptions.
- Green packaging, electric vehicles, and real-time carbon counting will enable “green shipping” initiatives and eco-conscious branding.
- Pop-up mini-hubs located closer to consumers (stores, lockers) will boost speed and reduce transportation cost.
- Immutable ledgers will power transparent supply chains from origin to doorstep vital for regulated goods and ethical sourcing.
- AR glasses and wearable scanners will help warehouse workers accelerate picking, reduce errors, and improve ergonomics.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Challenges in E-commerce Supply Chain Management
Despite its advantages, e-commerce SCM faces some unique challenges:
Technology’s Role in E-commerce Supply Chain
Technology is truly transforming modern supply chain management, bringing about a revolution in how operations are carried out thanks to sophisticated automation and intelligent systems. Warehouse automation and robotics have largely replaced traditional supply centers, with auto-guided vehicles and robotic picking systems significantly boosting throughput. Meanwhile, conveyor systems, automated storage, and packing machinery make order processing incredibly fast. Furthermore, Internet of Things devices and sensors provide an unprecedented level of visibility by continuously monitoring factors like temperature, integrity, and product conditions. This is especially crucial for perishable and high-value items. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also boosting supply chain efficiency. They power forecasting models that adapt to changing demand, optimize inventory plans, and enable dynamic pricing strategies. AI-based route optimization further reduces transit times and fuel costs substantially. Cloud-based SCM platforms, such as SAP SCM, Oracle Netsuite, and ODOs, offer comprehensive end-to-end logistics automation. These provide scalable, cost-effective solutions with real-time analytics capabilities, perfectly suited to growing business needs. Finally, blockchain technology and smart contracts are bringing essential transparency and traceability, particularly vital for sensitive products like food and luxury goods. They also automate payments and seller verification based on real-time milestones.
Want to Pursue a PMP Master’s Degree? Enroll For PMP Master Program Training Course Today!
Best Practices for Effective E-commerce Supply Chain Management
Putting a complete plan in place for managing your stock needs a smart mix of efficiency and keeping customers happy. One way to do this is by setting up a flexible system of warehouses that thoughtfully uses both central and local storage spots. This helps cut down on delays getting products to customers quickly, while also keeping storage costs and stock levels just right. This solid base makes it easier to predict what customers will want and when, so you can restock automatically and avoid the expensive problem of running out of items. Plus, having your stock levels sync up across all the places you sell ensures everyone sees the same real-time updates. This gets rid of the risk of accidentally selling items you don’t have and helps customers trust that the products they want are actually available. Making your warehouse run smoother is possible with tech like barcodes, RFID tags, and conveyor systems. These tools make picking items, packing orders, and restocking shelves much more efficient, and let you keep an eye on how productive everything is so you can always find ways to improve. And finally, having a flexible shipping plan that offers different delivery speeds and uses smart rules (like considering the order value, where the customer is, and what they prefer) helps find the sweet spot between keeping costs down and making customers happy, which ultimately helps your business grow and stay ahead of the competition.
Case Studies of Successful E-commerce Supply Chains
Preparing for a PMP Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on PMP Interview Questions and Answers
The Future of Supply Chain Management in E-commerce
Conclusion
Supply Chain Management is the engine of e-commerce profitability and customer satisfaction. To thrive, businesses must invest in strategic SCM practices from resilient sourcing and warehouse automation to dynamic routing and transparent returns. Leveraging technology like AI, IoT, cloud platforms, and robotics gives companies the ability to meet rising customer expectations efficiently and sustainably. In an increasingly competitive marketplace, a well-oiled supply chain isn’t just operational, it’s a strategic advantage that empowers growth, resilience, and differentiated experience. Overall, a well-managed supply chain is a critical part of any successful e-commerce business today. It is not just about getting products on shelves but about creating a strategic advantage. Through smart planning, the right technology, and continuous improvement, companies can build a supply chain that supports growth, keeps customers happy, and sets them apart from the competition.