
- Introduction to Data Independence
- Importance of Data Independence in DBMS
- Types of Data Independence
- Logical Data Independence – Explained
- Physical Data Independence – Explained
- Differences Between Logical and Physical Data Independence
- Levels of Abstraction in DBMS
- Real-Life Examples of Data Independence
- Benefits of Data Independence
- Challenges in Achieving Data Independence
- Role of Data Independence in Database Design
- Conclusion
Introduction to Data Independence
In a database management system (DBMS), data independence refers to the ability to change the schema at one level of a database system without affecting the schema at the next higher level. This concept is critical to ensuring flexibility, scalability, and manageability in modern database applications.In simple terms, data independence allows Database Training systems to evolve without breaking existing applications. It separates the physical storage of data from how it’s logically organized, role of data independence in database design giving developers and administrators more freedom and efficiency in database handling.The capacity to alter a database’s structure at one level without influencing other levels is known as data independence. It facilitates easy database maintenance and modification by ensuring logical and physical data independence. This idea ensures flexibility, efficiency, and system stability by permitting modifications to storage or data organization without affecting application programs.
Importance of Data Independence in DBMS
Here are the key reasons why data independence is important:
- System Flexibility: Changes in storage structures don’t require rewriting application logic.
- Reduced Maintenance Cost: Applications need minimal changes when database design is altered.
- Data Integrity: What is Data Control Language It encourages modular design, which enhances reliability and consistency.
- Ease of Upgrade: Hardware or software upgrades become easier to manage.
- Performance Tuning: Physical optimizations can be done without affecting the user interface or logic.
- Logical Data Independence
- Physical Data Independence
- The internal level deals with the physical storage of data, such as file structures and indexing methods.
- The conceptual level provides a logical view of the entire database, describing what data is stored and the relationships among data.
- The external level defines user-specific views, allowing different users to access only the data relevant to them.
- Complex Mapping: Translating between logical and physical layers requires accurate metadata.
- Performance Trade-offs: Abstracting layers can introduce overhead.
- Schema Evolution: Maintaining backward compatibility with logical changes can be tricky.
- Legacy Applications: Older systems may not be designed for modular updates.
- Tool and DBMS Limitations: Some database tools may not fully support all abstraction levels.
- Supports normalization by allowing logical changes without affecting apps.
- Improves scalability by decoupling data access from structure.
- Facilitates data migration and integration across systems.
- Helps maintain API stability, even as underlying data evolves.
- Empowers DBAs to fine-tune systems with confidence.
Interested in Obtaining Your Database Certificate? View The Database Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Types of Data Independence
Data independence is generally divided into two main types:
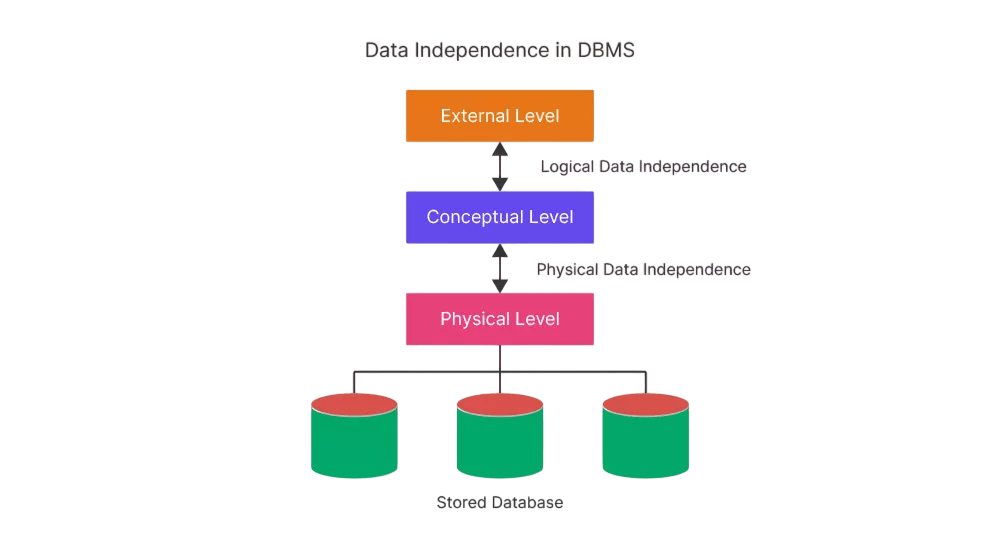
It sounds like you’re describing the three-schema architecture of a database system, which divides the Database Training architecture into different layers, each handling a different aspect of data management.
Logical Data Independence – Explained
Definition
The ability to change the logical schema (e.g., tables, fields, relationships) without requiring changes to the external schema or application programs.
Example
Cassandra The Buzzword in Database Management , supports operations like adding a new column to a table or merging tables without altering existing user views or application logic.
Importance
It allows the database to evolve without affecting how users or programs interact with the data.
Physical Data Independence – Explained
Definition
The ability to change the internal schema (e.g., file storage, indexing, compression) without changing the logical schema.
Example
Moving data to a As outlined in the Guide to Choosing an Enterprise Data Strategy, changes like using a different storage device or changing the way data is indexed can be made without impacting the overall database structure. or queries.
Importance
It enables performance improvements and hardware upgrades without disrupting user operations.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Differences Between Logical and Physical Data Independence
| Feature | Logical Data Independence | Physical Data Independence |
|---|---|---|
| Affects | External schema and user views | Internal schema and storage mechanisms |
| Harder to Achieve | Yes | No |
| Examples of Change | Adding/removing columns, altering tables | Changing file organization, indexing |
| Application Impact | Can be significant if not well designed | Minimal to none |
| Role in System Flexibility | High | Medium |
Levels of Abstraction in DBMS
In a Database Management System (DBMS), As explained in in Why NoSQL is the Ultimate Solution for Database, the levels of abstraction help manage data complexity by separating how data is stored from how it is viewed by users. Or a slightly more detailed version: According to NoSQL is the Ultimate Solution for Database Management one of the strengths of NoSQL systems is the use of abstraction levels, which help manage data complexity by decoupling storage mechanisms from user-facing data views. There are three levels of abstraction: the internal level, the conceptual level, and the external level.
This layered approach ensures data independence, simplifies database design, and improves security and maintainability.
Real-Life Examples of Data Independence
Banking System (Logical Data Independence)
A bank adds a new field “credit score” to its customer database. Existing applications like transaction processing or loan approval continue to work without changes because they don’t use this new field.
E-commerce Website (Physical Data Independence)
An online store switches its product database storage from local servers to a cloud-based system. the context of Real-Time Big Data Converts , the change improves performance, but customers and staff continue to access product data the same way, without altering their existing workflows or user experience.the application interface.
University Database (Logical Data Independence)
A university updates its student records to include “emergency contact details.” Existing applications for grading, attendance, and course registration remain unaffected.
Hospital Management System (Physical Data Independence)
A hospital upgrades its database to use a new indexing method for faster patient record retrieval. The change boosts speed but doesn’t affect how doctors or staff access records.
Benefits of Data Independence
For database administration, data independence provides a number of important advantages. Improved system flexibility, One of the primary benefits highlighted in the NoSQL vs SQL comparison is schema flexibility, which permits data structure modifications without impacting application programs.. Every time the database changes,internal schema this minimizes the time and expense required to update the software.
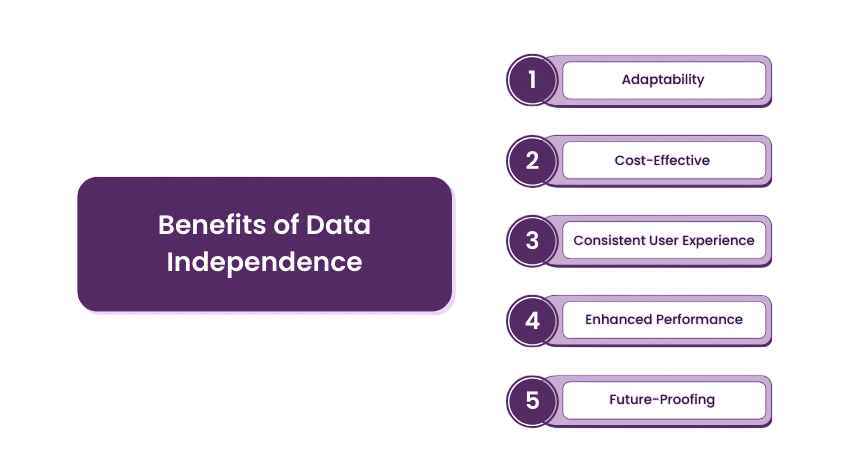
Because developers can Data Independence in DBMS alter the database’s logical or physical design, it also improves maintainability. Furthermore, data independence facilitates data abstraction, which makes database design and use simpler by separating how data is utilized from how it is stored. Additionally, it guarantees system stability because user applications continue to work even when the database structure changes, strengthening and expanding the system over time.
Challenges in Achieving Data Independence
Despite its advantages, implementing data independence can be challenging:
Want to Pursue a Graduate Degree in Database Studies? Enroll For Database Training Today!
Role of Data Independence in Database Design
In database design, data independence:
Conclusion
Data independence is not just a technical feature, it’s a strategic advantage. It allows developers, administrators, and organizations to build resilient, adaptable, and efficient Database Training systems.By separating the logical view of data from its physical implementation, DBMS systems provide the flexibility needed in today’s fast-changing digital environments. As businesses grow and technologies evolve, the databases behind them must evolve too without breaking everything.Whether you’re a student learning Data Independence in DBMS, a developer designing applications, or a database administrator optimizing systems, internal schema understanding and implementing data independence is a core skill that will serve you in the long run.In conclusion, role of data independence in database design is vital for efficient database management. It allows structural changes without affecting application functionality, promoting system flexibility and ease of maintenance. By separating data from application logic, it ensures adaptability to future needs, reduces downtime, and enhances the overall reliability and scalability of database systems.

