
- Introduction to Attributes in DBMS
- Entities and Attributes in DBMS
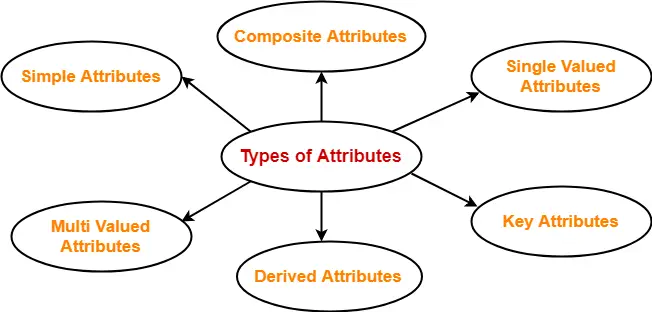
- Types of Attributes in DBMS
- Key Attributes in DBMS
- Multivalued Attributes in DBMS
- Complex Attributes in DBMS
- Common Attributes in DBMS with Example
- Conclusion
Introduction to Attributes in DBMS
In a Database Management System (DBMS), attributes are the defining properties or characteristics of an entity that help describe and distinguish it within the database. Each attribute represents a specific piece of information related to an entity, enabling the database to store detailed and organized data. For example, in a database representing students, the entity “Student” may have attributes such as Student ID, Name, Date of Birth, Email Address, and Phone Number. These attributes collectively provide a comprehensive description of each student. Attributes can be of different types, including simple (atomic) attributes that hold indivisible values, composite attributes that can be broken down into smaller sub-parts (like a full name into first and last name), single-valued attributes holding a single value for an entity, and multi-valued attributes that may hold multiple values (such as multiple phone numbers). Furthermore, attributes have Database Training, such as integers, strings, or dates, and constraints that ensure the accuracy and validity of the data, Types of Attributes like uniqueness or mandatory values. Properly defining attributes is crucial in database design because they directly impact how data is stored, retrieved, and maintained. Clear attribute definitions lead to efficient data management, better query performance, Entities and Attributes and the ability to accurately represent real-world objects in the database system.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Entities and Attributes in DBMS
Entities
- Represent real-world objects or concepts that can be distinctly identified.
- Examples include students, employees, products, or orders.
- Each entity is an instance within an entity set Self-Join in SQL.
- Entities are represented as rectangles in ER diagrams.
- Describe properties or characteristics of an entity.
- Examples include name, ID, age, and address.
- Can be simple (atomic), composite, single-valued, or multi-valued.
- Have specific data types like integer, string, date, etc.
- Help define the structure of an entity in the database.
Attributes
Types of Attributes in DBMS
There are numerous forms of attributes in DBMS, every with its precise traits and applications.
- Simple Attributes – Simple attributes are single-valued trends that can not be in addition split. In a scholar database, Data warehouses for example, the scholar`s call may be a easy attribute.
- Composite Attributes – Composite traits may be in addition subdivided into smaller sub-parts. A scholar`s address for example, may be in addition subdivided into a street, city, state, and zip code.
- Key Attributes – Key attributes are those who uniquely pick out a database entity. In a scholar database, for example, the roll quantity may be the important thing assets that uniquely identifies every scholar.
- Multivalued Attributes – Multivalued traits could have several values for the identical entity. A scholar, for example, can also additionally have many cellular smartphone numbers or e mail addresses.
- Derived Attributes – Derived attributes are the traits that originate from various attributes withinside the database. The date of delivery feature, for example, may be used to calculate a scholar`s age.
Key Attributes in DBMS
Key attributes are crucial in DBMS as they uniquely pick out an entity in a database. There are forms of key attributes
- Primary Key – A number one secret key asset that identifies every row in a desk individually. It needs to be precise for every row and can not be null. In a web buying database, for example, the Order ID may be the principal key.Primary keys make certain that every row in a database is awesome and without problems identifiable. They are essential for retrieving, sorting, and updating statistics. Foreign keys, on the opposite hand, are used to attach tables and assure that statistics is as it should be prepared and linked.
- Foreign Key – An overseas secret is a key function that refers to any other desk`s major key. It connects tables. In a web buying database, for example, the Customer ID may be the overseas key that pertains to the Customer desk`s number one key.Key traits are essential to a Database Training integrity and consistency. They make a contribution to the precise identity of every entity and the correct definition of entity relationships.We can broaden a greater efficient, logical, and user-pleasant database via way of means as it should be figuring out and organizing critical attributes.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Multivalued Attributes in DBMS
Candidate keys and remarkable keys are vital thoughts in database control systems. A candidate secret is a set of 1 or extra traits that may be used to uniquely discover a database entity. A unmarried entity may have severa candidate keys.
- In contrast, remarkable keys are collections of houses that may be applied to uniquely discover a row in a desk.
- A remarkable key may be minimum or now no longer, Data Mart vs Data Warehouse because of this that it’d have extra houses than are required to uniquely discover a row.
- Here are the number of the important thing variations among the candidate keys and remarkable keys.
- Candidate keys are minimum units of attributes which can uniquely discover an entity, at the same time as remarkable keys can also additionally or won’t be minimum.
- A candidate key may be a remarkable key, however now no longer all remarkable keys may be candidate keys.
- A desk may have above one candidate keys, however handiest one number one key.
- Candidate keys may be used as a reference for overseas keys in different tables.
- Understanding candidate keys and remarkable keys is vital for properly database layout and maintenance. We can expand an efficient, logical, and user-pleasant database with the aid of using accurately defining and organizing candidate keys and remarkable keys.
Complex Attributes in DBMS
Complex attributes are the ones which can be made of more than one sub-components and may be in addition divided into sorts
- Nested Attributes: Nested attributes are those who include different attributes inside them. For example, in a product database, a product may have nested attributes like Brand (nested characteristic inside Product) and Manufacturer (nested characteristic inside Brand).
- Repeating Groups: Repeating companies include more than one times of the equal characteristic.For example, in a purchaser database, a purchaser may have more than one addresses (Home Address, Office Address, etc.), every with its set of attributes (Street, City, State, Zip Code).
- Complex Attributes: These assist to symbolize complicated relationships among entities and offer extra specific records approximately them.By nicely defining and organizing complicated attributes, Database Partitioning Techniques we will create a database this is extra efficient, logical, and smooth to use.Understanding the one-of-a-kind styles of attributes in DBMS is vital for powerful database layout and control.
By nicely defining and organizing attributes, which includes complicated attributes, we will create a database that is simple to use, maintain, and expand. Whether you’re a database developer, administrator, or user, having a complete information of attributes and their sorts assist you to to make the maximum of your database and gain your dreams effectively.
Common Attributes in DBMS with Examples
In a Database Management System (DBMS), attributes are used to describe the properties of entities and are essential for defining the structure and content of a database. Some of the most common attributes include names, IDs, dates, and contact information, which are widely used across different types of databases. For example, in an Employee entity, typical attributes might include Employee ID (a unique identifier), Name, Designation, Department, Email, and Phone Number. In a Student entity, common attributes could be Student ID, Full Name, Date of Birth, Course Enrolled, and Address. Each of these attributes holds specific data about the entity and helps distinguish one record from another. Attributes can also be categorized based on their characteristics. For instance, Employee ID is a unique attribute often used as a primary key, while Name is a simple attribute made up of text. Address can be a composite attribute, Between DBMS and RDBMS as it may include sub-parts like street, city, and postal code. Understanding and properly defining these common attributes is crucial for creating effective and organized databases, ensuring data consistency, and enabling efficient data retrieval and reporting.
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Finally, characteristics are critical in Database Training management systems. They aid in the identification and differentiation of numerous entities, as well as the description of their various properties. Understanding the different attributes in DBMS allows to create and maintain databases that match the demands of the organization. We hope that this explanation has given you a better grasp of characteristics and their types in DBMS. So, start exploring and utilizing these techniques to develop your database management skills!


