
- What is pyodbc?
- Installing pyodbc
- Connecting to Databases
- Executing SQL Statements
- Fetching Results
- Working with Stored Procedures
- Error Handling and Debugging
- Conclusion
What is pyodbc?
pyodbc is a Python DB API-compliant module that allows Python programs to use ODBC to connect to almost any database. It’s widely appreciated for its ease of use, high performance, and compatibility with many platforms. It supports various SQL operations including DDL (Data Definition Language), DML (Data Manipulation Language), transactions, stored procedures, and batch processing.In modern software development, interacting with databases is crucial. pyodbc is a Python library that acts as a bridge between Python applications and databases using the ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) interface. ODBC is a standardized API for accessing DBMS (Database Management Systems) Python Training. pyodbc enables Python programs to connect seamlessly to databases like Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, SQLite, and PostgreSQL, provided the appropriate ODBC drivers are installed. This comprehensive guide will take you through the installation, usage, best practices, and advanced features of pyodbc, making it easier for developers to integrate databases into their Python applications. pyodbc is a popular open-source Python library that provides a simple and efficient way to connect Python applications to databases using the ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) interface. It allows Python programs to execute SQL queries, retrieve data, and manage database transactions across various database systems like SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle. pyodbc supports a wide range of databases through ODBC drivers, making it highly versatile for database interaction. It’s commonly used in data analysis, web development, Software Developer vs Software Engineer and enterprise applications to facilitate seamless communication between Python and relational databases.
Do You Want to Learn More About Python? Get Info From Our Python Online Training Today!
Installing pyodbc
- Prerequisites: Ensure you have Python and pip installed on your system.
- Install ODBC Driver: Install the appropriate ODBC driver for your database (e.g., SQL Server, PostgreSQL).
- Use pip to install pyodbc: pip install pyodbc
- Verify Installation: Open Python shell and run import pyodbc to check if installed correctly.
- Platform Notes: On Windows, ODBC drivers are often pre-installed; on Linux/macOS, you may need to install them separately Minimum Spanning Tree.
- Troubleshooting: For build errors, install system dependencies like unixodbc-dev on Linux.
- Virtual Environment: It’s recommended to install pyodbc inside a Python virtual environment to avoid conflicts.
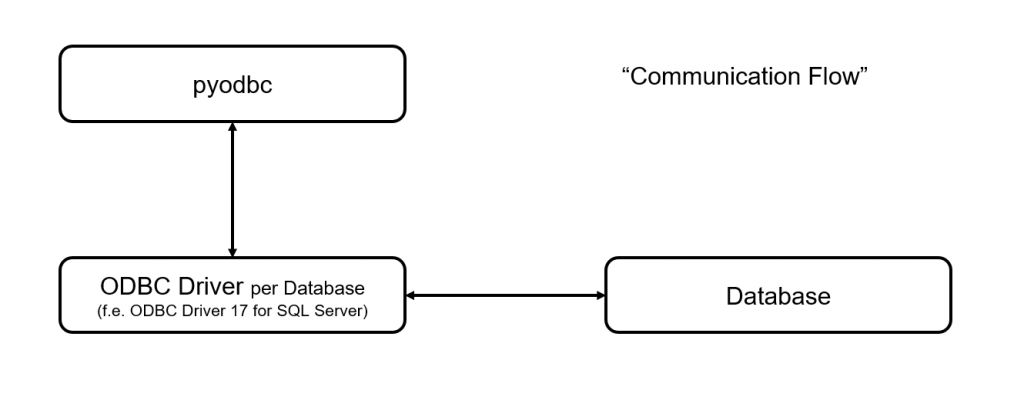
Connecting to Databases
The connection string defines how you connect to a database.GUI Tkinter Module It typically includes the driver, server name, database, username, and password.
Example for SQL Server:
- import pyodbc
- conn = pyodbc.connect(
- ‘DRIVER={ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server};’
- ‘SERVER=localhost;DATABASE=TestDB;UID=sa;PWD=Password123’
- )
Example for SQLite:
- conn = pyodbc.connect(‘DRIVER={SQLite3 ODBC Driver};DATABASE=test.db’)
- Using DSN (Data Source Name):
- conn = pyodbc.connect(‘DSN=MyDSN;UID=user;PWD=pass’)
Once connected, use conn.cursor() to create a cursor object.
Executing SQL Statements
Use cursor.execute() to run SQL commands. Always use placeholders (?) for parameters to prevent SQL injection Reverse C++ Vector .
Creating and inserting data:
- cursor = conn.cursor()
- cursor.execute(“CREATE TABLE Students (id INT, name VARCHAR(100))”)
- cursor.execute(“INSERT INTO Students VALUES (?, ?)”, (1, ‘Alice’))
- conn.commit()
You can also use .executemany() for batch inserts:
- data = [(2, ‘Bob’), (3, ‘Charlie’)]
- cursor.executemany(“INSERT INTO Students VALUES (?, ?)”, data)
- conn.commit()
Want to Pursue a Python Master’s Degree? Enroll For Python Master Program Training Course Today!
Fetching Results
- Execute Query: After running a SQL query or stored procedure with cursor.execute(), the result set becomes available.
- Fetch One Row: Use cursor.fetchone() to retrieve the next row from the result set. Returns a single record or None if no more data.
- Fetch Multiple Rows: Use cursor.fetchmany(size) to fetch a specified number of rows at a time, useful for large datasets Python Training.
- Fetch All Rows: Use cursor.fetchall() to retrieve all remaining rows as a list of tuples.
- Iterate Results: You can iterate directly over the cursor to process rows one by one.
- Access Columns: Rows are usually tuples, accessed by index or column name (if supported).
- Close Cursor: After fetching results, close the cursor with cursor.close() to free resources.
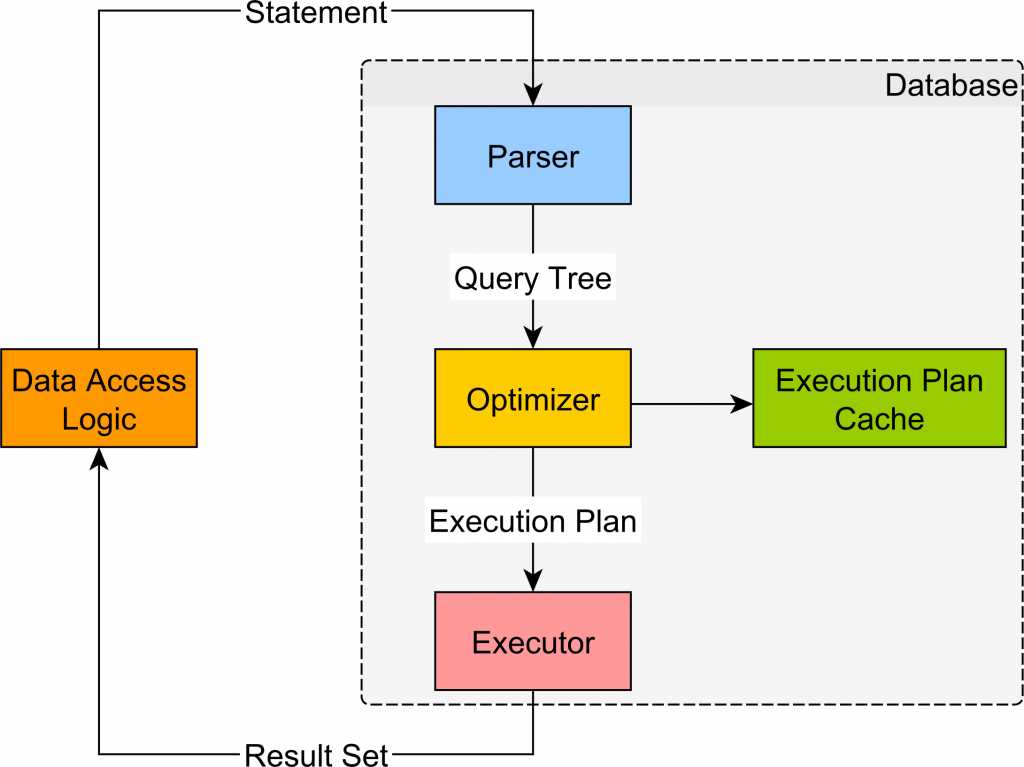
Working with Stored Procedures
Stored procedures are precompiled SQL code saved in the database, used to perform complex operations, improve performance, Data Structures & Algorithms and enhance security. SQL Server example: cursor.execute(“EXEC GetStudentById ?”, (1,)) row = cursor.fetchone() print(row) You can also handle output parameters and return values using database-specific syntax.
Error Handling and Debugging
- Use Try-Except Blocks: Wrap database operations in try-except to catch exceptions like connection errors or SQL syntax issues.
- Catch Specific Exceptions: pyodbc raises pyodbc.Error and subclasses like DatabaseError for more granular handling.
- Print Error Messages: Log or print the exception message to understand the issue.
- Enable Logging: Use Python’s logging module to track database operations and errors systematically Paging in Operating Systems.
- Check SQL Syntax: Verify SQL queries and stored procedure calls separately to isolate syntax problems.
- Close Connections Properly: Ensure cursors and connections are closed even on errors using finally or context managers.
- Use Debugging Tools: Leverage IDE debugging features or add debug prints to trace variable values and execution flow.
Preparing for a Python Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Python Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
pyodbc is a versatile and robust library for database access in Python. It provides efficient, secure, and scalable methods to interact with relational databases using ODBC drivers. Whether you are developing a web application, building an ETL process, or analyzing enterprise Connecting to Databases, pyodbc offers the flexibility and power needed for professional-grade development Python Training. With multi-platform support, Error Handling and Debugging, rich feature set, and ease of use, it remains one of the most reliable options for Python-database integration. To make the most of it, ensure your system is correctly configured with ODBC drivers, handle exceptions gracefully, and follow best practices for secure and maintainable code. In conclusion, mastering pyodbc not only simplifies your data workflows but also equips you with the tools to build scalable and robust data-driven applications in Python.


