
- Introduction
- Understanding the Big Data Landscape
- Role of Java Skills in Hadoop Ecosystem
- Key Components of Hadoop
- Introduction to Hadoop Tools
- Learning Hadoop Frameworks
- Required Skills and Technologies to Master
- Training and Certification Options for Hadoop
- Real-World Use Cases for Hadoop Professionals
- Job Roles and Responsibilities in Hadoop Ecosystem
- Final Thoughts
Introduction
Switching Career from Java to Hadoop has become a popular choice in the constantly evolving world of technology, where professionals seek new opportunities aligned with emerging trends. One such transition is the shift from Java development to Big Data technologies like Hadoop. Java, while still highly relevant, is a general-purpose programming language, whereas Hadoop caters to the data-driven landscape that enterprises increasingly rely on. The growing importance of data analytics, machine learning, and large-scale data processing has made Hadoop a lucrative and future-ready career move. To prepare for this evolution, exploring Java Training reveals how mastering core Java principles, APIs, and enterprise frameworks builds the foundation needed to thrive in data-intensive roles and transition confidently into the Hadoop ecosystem. For Java professionals, Switching Career from Java to Hadoop is not only logical but also strategic, as it leverages existing skills while opening doors to high-paying and in-demand roles.
To Earn Your Java Training Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Java Training Today!
Understanding the Big Data Landscape
Big Data refers to data sets so large and complex that traditional data-processing applications are inadequate. The volume, velocity, and variety of modern data require specialized frameworks and tools to process, analyze, and store efficiently. Companies now generate data through digital interactions, IoT devices, transactions, and customer feedback across platforms. Big Data technologies, including Hadoop and Spark, enable organizations to gain valuable insights from massive data sets, driving decision-making, customer engagement, and operational efficiency. To extract relevant information efficiently from these vast datasets, exploring Searching in Data Structure reveals how linear and binary search techniques form the foundation for indexing, filtering, and optimizing data access in scalable analytics systems. The Big Data domain includes data engineers, analysts, architects, and scientists all depending on scalable solutions that Java developers are well-positioned to transition into.
Role of Java Skills in Hadoop Ecosystem
- Java plays a significant role in the Hadoop ecosystem. The core components of Hadoop, especially MapReduce, are written in Java. Professionals with Java expertise already have a head start in understanding Hadoop’s architecture, APIs, and processing logic. Knowledge of object-oriented programming.
- Exception handling, multithreading, and JVM-based execution is directly applicable when working with Hadoop. Additionally, Java’s integration capabilities make it easier for developers to work with Hadoop tools and APIs. This overlap simplifies the learning curve and allows for a smoother transition for Java professionals looking to specialize in Big Data.
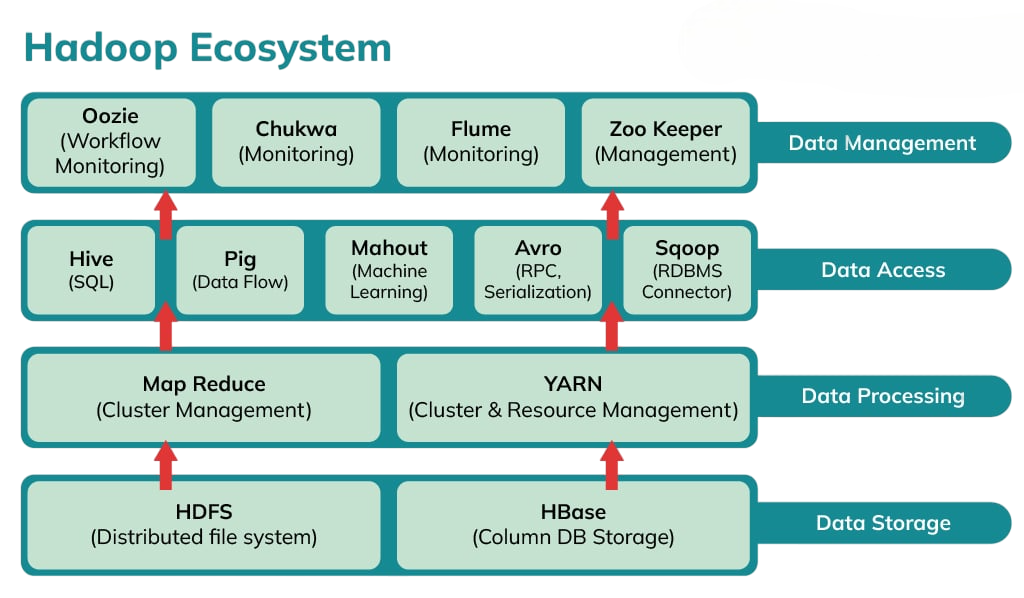
- HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System): It’s the storage layer of Hadoop. HDFS splits large files into blocks and distributes them across nodes in a cluster, ensuring fault tolerance and high availability.
- MapReduce: This is the processing layer. Java developers find MapReduce familiar as it involves coding mapper and reducer classes, similar to writing modular Java programs. It enables parallel data processing on distributed data.
- YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): YARN manages and allocates cluster resources efficiently. It acts as an operating system for Hadoop, running and monitoring multiple applications.
- Core Hadoop (HDFS, YARN, MapReduce)
- SQL & Hive for querying big data
- Apache Spark for fast processing
- Scripting languages like Python (optional but helpful)
- ETL tools (Sqoop, Flume)
- NoSQL databases like HBase and Cassandra
- Cloud platforms (AWS EMR, Azure HDInsight, GCP BigQuery)
- Monitoring & deployment tools (Ambari, Cloudera Manager)
- Basics of Linux and shell scripting
- Cloudera Certified Associate (CCA) and Cloudera Certified Professional (CCP)
- Hortonworks Hadoop Certification (now merged with Cloudera)
- MapR Certified Hadoop Developer
- Coursera, Udemy, Edureka, Simplilearn offer hands-on courses with real-time projects
- Apache Spark Certifications via Databricks
- Retail & E-Commerce: Customer behavior analysis, recommendation engines, sales predictions
- Healthcare: Medical data analytics, diagnostics, clinical trials
- Banking & Finance: Fraud detection, credit risk modeling, transaction monitoring
- Telecom: Call data record (CDR) analysis, churn prediction
- Government & Public Sector: Population analysis, traffic prediction, emergency response planning
Would You Like to Know More About Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Now!
Key Components of Hadoop (HDFS, MapReduce, YARN)
Understanding Hadoop begins with its three core components: HDFS for storage, MapReduce for processing, and YARN for resource management. As you dive deeper into data workflows, knowing how to structure and access data efficiently becomes essential. Exploring Python List vs Tuple reveals how mutable lists and immutable tuples serve different roles in memory optimization, data integrity, and performance especially when handling large-scale datasets in distributed systems like Hadoop.
Understanding how these components interact is foundational for anyone moving from Java to Hadoop. It sets the stage for mastering other tools in the ecosystem.
Introduction to Hadoop Tools
The Hadoop ecosystem includes various tools that make data processing easier beyond its main components. Hive offers a simple SQL-like interface for querying data, which helps users who are familiar with structured databases. Pig, on the other hand, uses a scripting language called Pig Latin. This language turns complex Java code into simpler scripts, making data flow management easier. To understand how these transformations work under the hood, exploring Java Training reveals how mastering core Java syntax, control structures, and data handling techniques equips developers to write efficient code and transition seamlessly into big data scripting environments like Pig. Sqoop is essential for transferring data efficiently between Hadoop and traditional relational databases like MySQL and Oracle. Flume is great at taking in large amounts of log and event data into Hadoop’s HDFS.
Learning Hadoop Frameworks: Apache Spark and Others
While Hadoop is a good starting point for Big Data processing, many projects now choose more effective frameworks like Apache Spark. Spark processes data in memory, making it much faster than Hadoop MapReduce. It is versatile; it supports batch processing and real-time data streaming through Spark Streaming.
Additionally, Spark has strong libraries for machine learning (MLlib) and graph processing (GraphX). Other useful frameworks to consider include Kafka for real-time data ingestion, HBase for NoSQL storage, and Zookeeper for coordination. To build efficient data workflows and solve complex problems, exploring Recursion in Data Structures reveals how recursive algorithms simplify tasks like tree traversal, graph exploration, and dynamic computation making them essential for scalable, distributed systems. For managing workflows, tools like Airflow or Oozie are very helpful.
Are You Interested in Learning More About FullStack With Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Today!
Required Skills and Technologies to Master
To succeed in the Hadoop domain, transitioning Java developers should focus on acquiring the following skills: understanding distributed computing principles, mastering data ingestion tools like Kafka, and learning frameworks such as Spark and Hive. To complement these backend capabilities with modern API development, exploring FastAPI Explained reveals how Python’s FastAPI framework enables rapid, scalable, and asynchronous API creation ideal for integrating data services into real-time analytics pipelines.
Understanding data formats such as Avro, Parquet, ORC, and working knowledge of JSON, XML, and CSV is also beneficial.
Training and Certification Options for Hadoop
Formal training can accelerate your Hadoop learning curve. Numerous reputable platforms offer structured training and certification:
These certifications not only provide conceptual knowledge but also validate your practical ability, making your resume stand out in job searches.
Preparing for Java Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Java Training Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Real-World Use Cases for Hadoop Professionals
Hadoop has transformed how businesses manage and interpret data. Real-world use cases include: fraud detection, recommendation engines, customer segmentation, and predictive maintenance. To enhance data accuracy and pattern recognition in these applications, exploring Understanding Hamming Distance reveals how comparing binary strings helps identify errors, measure similarity, and optimize algorithms in large-scale data environments.
Hadoop professionals work with vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, turning raw information into actionable insights.
Job Roles and Responsibilities in Hadoop Ecosystem
After switching to Hadoop, Java developers can explore various job roles. As a Hadoop Developer, you’ll write MapReduce programs and Spark jobs, while also integrating important tools. If you decide to be a Data Engineer, your job will involve building and maintaining data pipelines and managing ETL workflows. For those interested in administration, a Hadoop Administrator manages clusters to ensure top performance and uptime. On the architectural side, a Big Data Architect designs Big Data solutions that span multiple platforms. To optimize data flow and processing efficiency across these roles, exploring Sorting in Data Structures reveals how algorithms like quicksort, mergesort, and heapsort are essential for organizing data, improving query performance, and enabling scalable analytics. Data Analysts, who are skilled in Hive and Spark SQL, work to extract valuable insights from large datasets.
Final Thoughts
Switching Career from Java to Hadoop is a smart move for developers aiming to future-proof their careers. This transition leverages existing Java skills while expanding capabilities into one of the most in-demand tech domains. The Hadoop ecosystem offers diverse roles, high salaries, and opportunities to work on impactful, large-scale data projects. As the world continues to generate and rely on massive volumes of data, professionals with Big Data skills will find themselves at the forefront of innovation. To build a strong foundation for this transition, exploring Java Training reveals how mastering core Java concepts, APIs, and frameworks equips developers to thrive in data-centric environments and unlock high-growth career paths. By focusing on learning, gaining practical experience, and pursuing certifications, Switching Career from Java to Hadoop becomes not only achievable but also highly rewarding.





