
- Introduction to Kali Linux
- Prerequisites and System Requirements
- Downloading the Kali ISO
- Creating Bootable Media
- Dual Boot vs VM vs Live USB
- Installation Process Step-by-Step
- Initial Configuration Post-Install
- Tool Setup and Repository Updates
- Security Tips and Best Practices
- Final Check and First Steps
Introduction to Kali Linux
Install Kali Linux to unlock the full potential of one of the most powerful Debian-based distributions designed for digital forensics, penetration testing, ethical hacking, and security research. It comes preloaded with hundreds of tools that security professionals use worldwide to test vulnerabilities and strengthen cybersecurity defenses. With its flexibility, open-source nature, and strong community support, Kali Linux is suitable for both beginners learning cybersecurity and professionals performing advanced security assessments. To complement these capabilities with automation and scripting skills, exploring Python Training reveals how mastering Python empowers users to build custom security tools, streamline workflows, and enhance penetration testing efficiency. Knowing how to properly Install Kali Linux ensures a smooth setup and access to all of its features for training, research, or professional projects. Ultimately, mastering the process to Install Kali Linux gives you the foundation to explore ethical hacking, practice penetration testing, and advance your cybersecurity skills.
Interested in Obtaining Your Python Certificate? View The Python Developer Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before installing Kali Linux, it is crucial to verify that your system meets the minimum requirements to ensure smooth operation. Kali Linux typically requires at least a dual-core processor, 2GB of RAM (4GB or more recommended for graphical environments), and a minimum of 20GB of free disk space. Additionally, stable internet access is advised for downloading updates and tools. To streamline software builds and dependency management in such environments, exploring Gradle vs Maven reveals how these popular build tools differ in performance, flexibility, and configuration helping developers choose the right solution for automation and scalability. While Kali can run on various hardware platforms including ARM devices, laptops, desktops, and virtual machines, ensuring compatibility with your hardware such as network cards and graphics is important to avoid driver issues post-installation.
Downloading the Kali ISO
- The next step is to download the official Kali Linux ISO image, which contains the installation files. It is recommended to obtain the ISO directly from the official Kali website or trusted mirrors to avoid corrupted or malicious files. Kali offers different ISO versions such as full, light, and specialized ARM images.
- To simulate timed delays during automated installations or script executions, exploring Python Sleep Method reveals how developers can pause program flow for specific durations ideal for throttling tasks, managing retries, or sequencing operations in system scripts.
- Choose the version based on your needs, full ISO for a complete toolset, light ISO for minimal installations, or specific versions for embedded devices. Always verify the checksum (SHA256 or MD5) of the downloaded file against the official hashes to ensure integrity and security.
- Dual Boot: Kali Linux can be installed alongside an existing OS (like Windows), allowing users to select the OS at startup. This provides full hardware access but requires careful partitioning and bootloader management.
- Virtual Machine (VM): Installing Kali inside a VM using software like VMware or VirtualBox allows running Kali as an app within another OS. This is safe, convenient, and ideal for testing or learning without modifying your primary system.
- Live USB: Kali can run directly from a USB stick without installation, preserving your existing OS and allowing portability. However, performance may be slower, and changes may not be persistent unless a persistent storage partition is configured.
- Select Installation Mode: Options typically include Graphical Install, Text Install, and Live mode. Beginners should choose Graphical Install for ease.
- Configure Language and Location: Select preferred language, country, and keyboard layout.
- Network Configuration: Set up hostname, domain name, and network settings (DHCP or static IP).
- User Setup: Create a root or non-root user account with a strong password.
- Disk Partitioning: Choose partitioning method (guided or manual). For dual boot, manual partitioning is recommended to avoid overwriting existing OS.
- Install Base System: The installer copies core files to disk.
- Configure Package Manager: Select network mirrors and proxy if applicable to download updates during installation.
- Install GRUB Bootloader: Choose to install GRUB to the primary drive to manage system booting.
- Finish Installation: After installation completes, the system reboots into Kali Linux.
- Given Kali Linux’s powerful capabilities, following security best practices is critical. Avoid running Kali as root by default; instead, create and use non-privileged users to reduce accidental system changes. Regularly update your system and tools to patch vulnerabilities.
- Use strong passwords and consider enabling full-disk encryption during installation to protect data if the device is lost or stolen. When using Kali on public or insecure networks, employ VPNs and firewall configurations. Lastly, be aware that Kali should be used ethically and legally, only on systems you own or have permission to test.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Python Developer by Enrolling in Our Python Master Program Training Course Now!
Creating Bootable Media
To install Kali Linux on a physical machine, you need to create bootable installation media, usually a USB flash drive or DVD. Using tools like Rufus (Windows), Etcher, or UNetbootin, you can write the Kali ISO image to the USB drive. This process formats the USB and copies the installation files in a bootable format. For DVDs, burning the ISO with tools like ImgBurn ensures the disk boots correctly. To choose the right language for scripting installation tools or building cross-platform utilities, exploring Kotlin vs Python reveals how Kotlin offers strong type safety and Android integration, while Python excels in simplicity and rapid development helping developers align language choice with project goals. After preparing the bootable media, you can use it to start the installation process by booting the target system from the USB or DVD drive.
Dual Boot vs VM vs Live USB
There are multiple ways to run Kali Linux, each with its advantages: from direct installation on hardware to using virtual machines or bootable USB drives. To build and manage such environments effectively, exploring Skills Needed for Full Stack Developers reveals how proficiency in operating systems, backend logic, frontend frameworks, and deployment tools empowers developers to create secure, scalable, and responsive applications across platforms.
Choose the method that best fits your use case and hardware.
Are You Preparing for Python Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Python Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Installation Process Step-by-Step
Once booted from the Kali installation media, the installation wizard guides you through several steps: selecting language, configuring partitions, setting up users, and installing packages. To integrate such systems with web-based dashboards or remote APIs, exploring What is Axios in React reveals how Axios simplifies HTTP requests in React applications enabling seamless data fetching, error handling, and asynchronous communication with backend services.
Carefully reading prompts and confirming options ensures a successful installation.
Initial Configuration Post-Install
After booting into Kali for the first time, some essential configurations help stabilize and personalize the system. Set up system locales, time zones, and additional user accounts if needed. Running apt update and apt upgrade commands updates package lists and installs the latest patches. Configuring network settings and verifying internet connectivity ensures access to repositories. To extend these system administration skills with automation and scripting capabilities, exploring Python Training reveals how Python can streamline updates, manage configurations, and build custom tools for efficient Linux operations. It is advisable to change the default root password if you created one and consider creating a non-root user for day-to-day tasks to enhance security.
Tool Setup and Repository Updates
After booting into Kali for the first time, some essential configurations help stabilize and personalize the system.
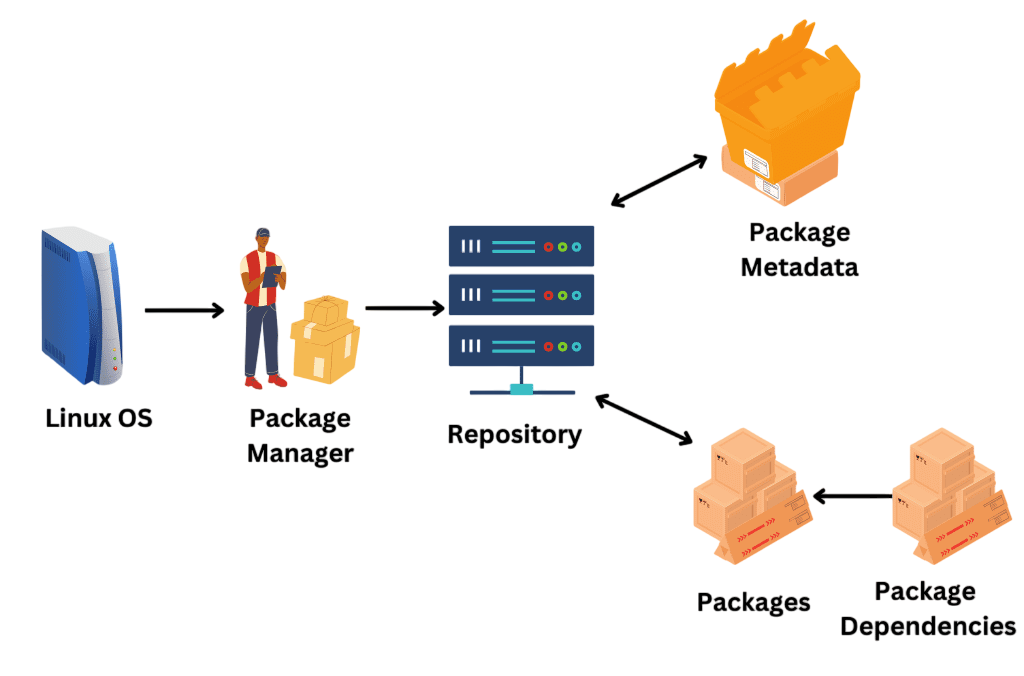
Set up system locales, time zones, and additional user accounts if needed. Running apt update and apt upgrade commands updates package lists and installs the latest patches. Configuring network settings and verifying internet connectivity ensures access to repositories. To build full-featured web applications that interact with such backend systems, exploring What is MEAN Stack reveals how MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js work together to deliver scalable, JavaScript-powered solutions from database to frontend. It is advisable to change the default root password if you created one and consider creating a non-root user for day-to-day tasks to enhance security.
Security Tips and Best Practices
Final Check and First Steps
After you Install Kali Linux and complete the initial setup, perform a final system check to ensure everything works smoothly. Verify that all hardware components (sound, Wi-Fi, display) function properly, and test basic commands and tool execution. As part of the process when you Install Kali Linux, familiarize yourself with the desktop environment, file system, and essential tools. To complement your system-level skills with programming expertise, exploring Python Training reveals how mastering scripting, automation, and tool integration in Python can enhance your efficiency in cybersecurity, data analysis, and system administration. It is also advisable to set up regular backups and configure automated updates for stability and security. Finally, once you Install Kali Linux, explore the official documentation and community resources to learn advanced usage and stay informed about new releases and security advisories.





