
- Sparse Matrix in Data Structure
- What is a Sparse Matrix?
- Characteristics of Sparse Matrices
- Types of Sparse Matrices
- Representation Methods
- Linked List Representation
- Triplet Representation
- Applications of Sparse Matrices
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Sparse Matrix Operations
- Conclusion
Sparse Matrix in Data Structure
In the field of computer science and applied mathematics, the concept of a sparse matrix is fundamental when working with large-scale data systems and numerical simulations. Sparse matrices are a specialized type of data structure that help optimize both memory usage and computational efficiency. They are used extensively in areas such as machine learning, graph theory, computer graphics, and scientific computing. As datasets continue to grow in size and complexity, understanding sparse matrices and their practical applications has become increasingly important.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Structures and Algorithms Training Certificate? View The Data Structures and Algorithms Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
What is a Sparse Matrix?
A sparse matrix is a two-dimensional array or matrix in which the majority of the elements are zero. In contrast to a dense matrix, where most of the elements are non-zero, a sparse matrix contains a relatively small number of non-zero elements. This concept is especially relevant in high-dimensional data analysis, where efficient modeling techniques are crucial. To explore how ensemble methods handle such complexity, check out Random Forest Algorithm a powerful machine learning approach that builds multiple decision trees to improve accuracy, reduce overfitting, and handle sparse data effectively. Due to this property, special techniques are employed to store and manipulate sparse matrices efficiently, focusing only on the non-zero elements.
This approach helps to reduce memory usage and computational cost. For example, consider a 1000×1000 matrix where only 1% of the entries are non-zero. Storing such a matrix in a conventional two-dimensional array format would result in a significant waste of memory. Instead, sparse matrix representations provide a way to store only the meaningful, non-zero values and their positions.
Characteristics of Sparse Matrices
Sparse matrices exhibit several key characteristics that distinguish them from dense matrices: they contain a high proportion of zero-valued elements, require specialized storage techniques, and are optimized for memory efficiency. To better understand how such data is organized and manipulated, explore What is Linear Data Structure a foundational guide that explains arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues, which form the backbone of efficient data representation and access in computer science.
- High Proportion of Zeroes: The defining characteristic is that a large number of elements in the matrix are zero.
- Storage Efficiency: Due to the prevalence of zero values, storage methods are optimized to avoid storing them.
- Computational Efficiency: Algorithms are adapted to skip zero elements during operations, improving speed.
- Memory Conservation: Specialized storage methods consume less memory.
- Dynamic Structure: Often, sparse matrices are stored in data structures that can dynamically grow or shrink, such as linked lists or dictionaries.
- Index Mapping: Efficient access to non-zero elements is achieved through indexing techniques.
- Diagonal Matrix: Non-zero elements are confined to the main diagonal.
- Tri-diagonal Matrix: Non-zero elements are on the main diagonal and the diagonals immediately above and below it.
- Band Matrix: A generalization of diagonal matrices, where non-zero values are within a certain bandwidth around the main diagonal.
- Block Sparse Matrix: Contains blocks of non-zero submatrices interspersed with zero blocks.
- Symmetric Sparse Matrix: Elements are symmetric around the main diagonal, allowing for optimized storage.
- Random Sparse Matrix: No particular pattern, but still contains a small fraction of non-zero elements.
- Original Matrix:
- [0 0 3]
- [4 0 0]
- [0 0 5]
- CSR Format:
- Values: [3, 4, 5]
- Column Indices: [2, 0, 2]
- Row Pointers: [0, 1, 2, 3]
- Row index array
- Column index array
- Value array
- Efficient Storage: Reduces memory requirements significantly.
- Faster Computation: Skipping zero elements leads to performance gains.
- Dynamic Resizing: Especially in linked list representation.
- Scalability: Suitable for very large datasets and computations.
- Complex Implementation: Requires more effort to implement compared to dense matrices.
- Access Overhead: Indirect indexing can slow down access to elements.
- Limited Library Support: Not all languages or libraries support all sparse matrix formats.
- Inefficiency for Dense Matrices: Using sparse techniques for dense data can lead to worse performance.
- Addition and Subtraction: Only non-zero elements are considered; requires matching indices.
- Multiplication: Sparse matrix multiplication algorithms skip zeroes to minimize computations.
- Transpose: Changes the row and column indices; can be efficiently performed on triplet and CSR formats.
- Matrix-Vector Multiplication: Frequently used in scientific computing and machine learning.
- Solving Linear Systems: Specialized solvers like Conjugate Gradient and GMRES are used.
- Conversion Between Formats: Conversion between CSR, COO, and other formats as per application needs.
Types of Sparse Matrices
There are several types of sparse matrices, each suited to different applications: coordinate format (COO), compressed sparse row (CSR), and compressed sparse column (CSC), among others. These formats are optimized for memory efficiency and computational speed in large-scale data environments. To understand how algorithmic strategies can be applied to such data structures, explore Dynamic Programming Explained a beginner-friendly guide that breaks down recursive problem-solving, memoization, and optimal substructure principles used in efficient algorithm design.
Representation Methods
When it comes to computational efficiency, the way a sparse matrix is represented is essential for optimizing both memory usage and computational speed. To handle these data structures, researchers and engineers mainly use three methods: array representation, linked list representation, and triplet representation. Out of these, the array representation is a highly advanced method to a great extent. To understand how data retrieval operates across these formats, explore Searching in Data Structure Explained a practical guide that covers key search techniques like linear and binary search, and how they adapt to various structural representations for optimal performance. In fact, CSR (Compressed Sparse Row) and CSC (Compressed Sparse Column) are two such techniques that enable the exact storage of non-zero elements of a matrix through the use of three one-dimensional arrays which represent row indices, column indices, and values respectively.
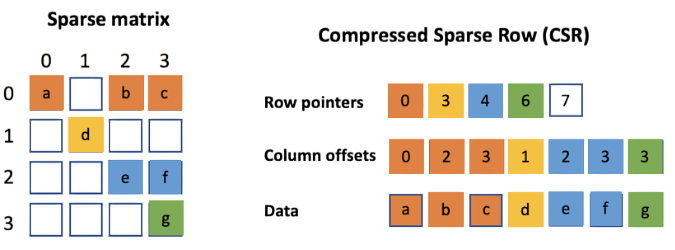
For example, CSR not only keeps non-zero values but also their column indices and additionally it has pointers that indicate the beginning of each row thus, it achieves a very compact and efficient way of data storage.
Example of CSR:
In this process, the memory overhead is greatly reduced while the computational speed is still very high; therefore, this method has become indispensable in areas like scientific computing and machine learning applications.
Are You Preparing for Python Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Data Structures Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Linked List Representation
Sparse Matrices using a linked list is an efficient and memory-saving way that adjusts easily to changes. Every non-zero number is stored in a node which holds the main data: the row number, the column number, and the value itself, plus a pointer that connects to the next node. This new method is quite good, especially when you have a matrix in which the non-zero elements are just a few and are scattered because it allows you to store and get the data exactly without taking extra memory. Not only does this method save memory by storing only non-zero elements, but it also enables quick access and updates through the pointer references, thus making it an efficient solution for dealing with large sparse matrices in various applications.
Triplet Representation
Triplet representation (also known as coordinate list or COO format) involves storing the matrix in the form of three arrays or a list of tuples. This representation is particularly simple and intuitive, making it suitable for input and output operations or for initial construction before conversion to more efficient formats. To understand how recursive logic can be applied to such structural patterns, explore Recursion in Data Structures a foundational guide that explains how recursive calls navigate nested structures, solve divide-and-conquer problems, and optimize traversal in sparse matrix formats.
This representation is particularly simple and intuitive, making it suitable for input and output operations or for initial construction before conversion to more efficient formats.
Applications of Sparse Matrices
Sparse matrices are clever data structures that have become a key computational tool with in-depth applications in research and technology sectors. These structures are capable of handling big and complicated data that have mostly zero values and thus open up a wide range of applications in different areas. In scientific computing, sparse matrices are used for numerical simulations at a high level, whereas machine learning algorithms employ these matrices for advanced methods such as Support Vector Machines and recommender systems. To understand how hierarchical data structures support these computational models, explore Types of Trees in Data Structure a comprehensive guide that explains binary trees, AVL trees, B-trees, and other variants used for efficient data organization, indexing, and decision-making processes. Natural language processing gets a lot of help from sparsity in representations, especially in term-document matrices, and graph theory depends on them to depict complex network relationships. Sparse matrices are being utilized in computer graphics and Geographic Information Systems to demonstrate their wide applications in complex mesh processing, image manipulation, and spatial data analysis. Through the reduction of computational overhead and memory, sparse matrices are a vital technological breakthrough that has opened the way for scientists and engineers to solve the most challenging problems of computation in different fields.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Sparse Matrix Operations
Operations on sparse matrices are tailored to maintain their efficiency and avoid unnecessary computations. Common operations include: matrix addition, transposition, and multiplication each optimized to skip zero-valued elements and reduce memory overhead. To understand the foundational elements that support such optimizations, explore Important Data Structures a comprehensive guide that covers arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, and graphs, all of which play a critical role in efficient algorithm design and data manipulation.
Summary
Sparse matrices are a cornerstone in the optimization of computational tasks involving large data sets, where storing and operating on numerous zeroes would be inefficient. Their special representations, including array-based methods like CSR and CSC, and structures like linked lists or triplets, allow for significant savings in both memory and computation time. Despite some complexities in implementation and occasional performance trade-offs, the advantages of sparse matrices in domains such as machine learning, scientific computing, and graph theory are undeniable. As the demand for processing large-scale and high-dimensional data continues to rise, the importance of understanding and effectively using sparse matrices becomes even more critical.





