
- AI and Machine Learning
- Quantum Computing
- Edge Computing
- Blockchain and Distributed Ledger
- Augmented and Virtual Reality
- Cybersecurity Advances
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Cloud Native Technologies
- Robotics Process Automation
- DevOps and AIOps
- Natural Language Processing
- Conclusion
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have revolutionized various industries, from healthcare to finance. AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines, enabling them to perform tasks like problem-solving, decision-making, and learning from experience. Machine Learning is a subset of AI where machines are trained to identify patterns in data, improving their performance over time without explicit programming. A web developer can leverage machine learning to create smarter, more personalized web applications that enhance user experience and functionality.
- Applications in Various Industries:
- Healthcare: AI is being used for predictive analytics, drug discovery, and personalized treatments. Machine Learning models can predict patient outcomes and help doctors make informed decisions.
- Finance: AI algorithms are used for fraud detection, risk assessment, and automated trading. Machine Learning models analyze vast datasets to predict market trends and optimize investments.
- Retail: Personalization engines powered by AI and ML provide personalized product recommendations based on customer preferences and behavior.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles, powered by AI, can navigate roads, detect obstacles, and make real-time decisions.
- Key Concepts:
- Supervised Learning vs Unsupervised Learning
- Neural Networks and Deep Learning
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Cryptography: Quantum computers can break current cryptographic systems, driving the development of quantum-safe encryption.
- Optimization: Quantum algorithms can be used for solving optimization problems in logistics, supply chain management, and more.
- Drug Discovery:Quantum simulations can provide insights into molecular structures and reactions, speeding up the process of discovering new drugs.
- Artificial Intelligence: Quantum Computing has the potential to enhance AI algorithms, making them more efficient and capable of handling larger datasets.
- IoT Devices: Edge Computing is used in IoT applications to process data locally on devices like smart cameras, sensors, and wearables.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Real-time data processing at the edge allows autonomous vehicles to make split-second decisions, like detecting obstacles.
- Smart Cities: Edge Computing supports traffic management, waste management, and energy-efficient solutions by processing data from various sensors in real time.
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the data, which increases security and transparency.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
- Public vs Private Blockchains: Public blockchains are open and anyone can participate, while private blockchains are restricted to authorized participants.
- Cryptocurrency: Bitcoin and Ethereum are built on blockchain, enabling decentralized currency transactions.
- Supply Chain: Blockchain improves transparency and traceability in supply chains, helping verify the origin of goods.
- Healthcare: Blockchain can store medical records securely, allowing easy access for authorized individuals.
- Gaming: VR is widely used in gaming for an immersive experience. AR games like Pokémon Go blend the real world with virtual objects.
- Healthcare: AR assists in surgeries by overlaying critical information like imaging data onto the surgeon’s view.
- Education: Both AR and VR provide interactive and immersive learning experiences, enabling students to visualize complex concepts and historical events.
- Retail: AR helps customers visualize products before purchasing, such as furniture or clothes.
- AI-Powered Threat Detection: Machine Learning algorithms are being used to detect abnormal network traffic or anomalies, helping in early detection of security breaches.
- Zero Trust Architecture: This security model assumes that no entity, either inside or outside the network, should be trusted. Access is continuously verified.
- Blockchain for Security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature can help improve security by eliminating centralized points of failure.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA is becoming a standard practice to prevent unauthorized access.
- Smart Homes: IoT-enabled devices like smart thermostats, lights, and security cameras make homes more efficient and secure.
- Healthcare: Wearable IoT devices track vital signs and send data to healthcare providers, enabling remote monitoring.
- Agriculture: IoT devices are used for precision farming, monitoring soil moisture, weather conditions, and livestock health.
- Industry 4.0: Industrial IoT (IIoT) is transforming manufacturing by enabling predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and supply chain optimization.
- Microservices: A design approach where applications are built as a collection of small, loosely coupled services.
- Containers: Technology like Docker enables developers to package applications and their dependencies into containers that can be easily deployed across different environments.
- Kubernetes: An open-source platform for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Applications:
- DevOps: Cloud-native technologies are foundational to DevOps practices, enabling continuous integration and deployment.
- Scalable Applications: These technologies allow applications to scale dynamically based on demand.
- Resilient Systems: Cloud-native applications are more fault-tolerant, as they can recover from failures quickly due to their distributed nature.
- Finance and Accounting: RPA can automate tasks like invoicing, transaction processing, and compliance reporting.
- Human Resources: RPA handles administrative tasks like employee onboarding and payroll processing.
- Customer Service: RPA chatbots are used to handle routine customer inquiries, improving response times and customer satisfaction.
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): DevOps practices focus on automating the integration and deployment of software.
- Automation: AIOps tools use machine learning to detect anomalies, predict failures, and automatically resolve issues.
- Collaboration: DevOps fosters collaboration between development and operations teams, improving efficiency and reducing silos.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: NLP powers chatbots like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, enabling them to understand and respond to user commands.
- Sentiment Analysis: NLP is used to analyze customer feedback, reviews, and social media posts to gauge sentiment.
- Translation Services: NLP is used in translation tools like Google Translate to convert text from one language to another.
To Earn Your web developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web developer courses Today!
Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in ways traditional computers cannot. Unlike classical bits, quantum bits (qubits) can exist in multiple states simultaneously, enabling quantum computers to solve complex problems much faster than classical computers. What Is a Software Developer by utilising the concepts of quantum physics, quantum computing technology is transforming the approach to solving complicated issues.Compared to traditional computers, this new area of quantum computing technology allows for faster data processing and more computational capacity. It is anticipated that the development of quantum computing technology would have a profound effect on sectors including artificial intelligence, medication development, and cryptography, spurring innovation and changing the course of technology.
- Applications and Impact:
Edge Computing
Edge Computing is a distributed computing framework where data processing happens closer to the data source (edge of the network) rather than being sent to a centralized data center. This reduces latency, optimizes bandwidth, and enhances real-time processing capabilities. Guide to Git and Version Control Edge computing benefits lie in its ability to process data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making. One major Edge Computing Benefits is enhanced performance for applications like autonomous vehicles and IoT devices, where speed and reliability are critical. Overall, the Edge Computing Benefits enables more efficient bandwidth use and supports smart city initiatives by enabling faster, localized data processing.
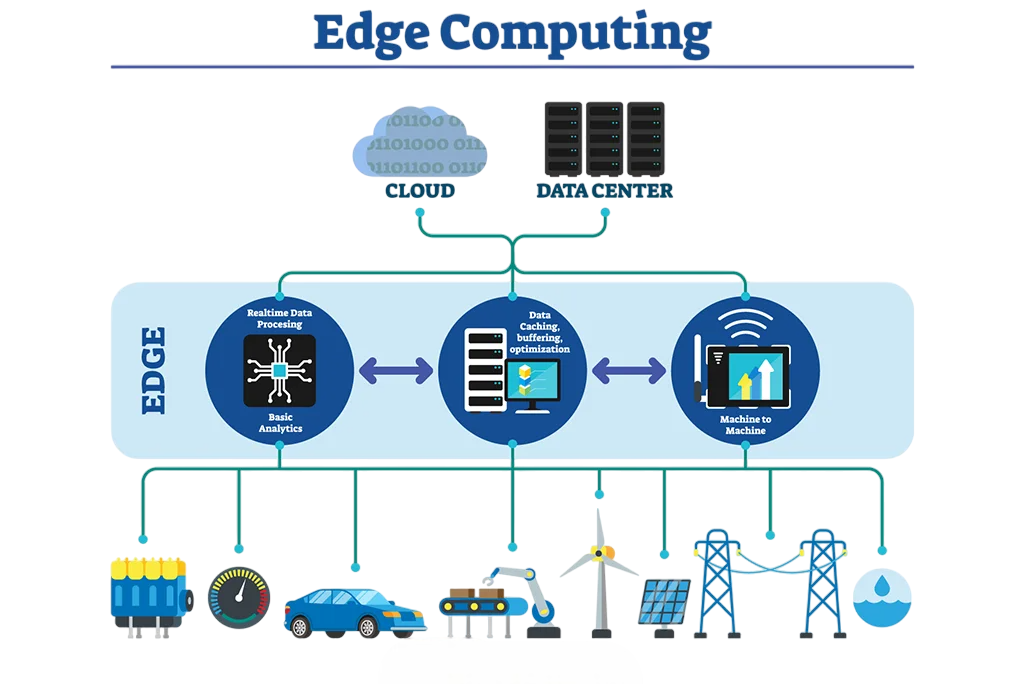
- Applications:
Would You Like to Know More About Web developer? Sign Up For Our Web developer course Now!
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed ledger system that ensures data integrity, transparency, and security. What are Microservices? It allows secure transactions without the need for a central authority, making it popular in areas like cryptocurrency, supply chain, and finance.
- Key Concepts:
- Applications:
Augmented and Virtual Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are immersive technologies that enhance or replace the user’s perception of the world. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, while VR creates a fully simulated environment.
- Applications:
Cybersecurity Advances
With the rise of digital transformation, cybersecurity has become more critical than ever. Advances in cybersecurity focus on securing data, applications, networks, and systems from cyberattacks, breaches, and unauthorized access. A web developer must stay updated on these advancements to build secure websites and applications that protect user data and maintain trust.
Trends in Cybersecurity:Are You Interested in Learning More About FullStack With Web developing? Sign Up For Our Web developing Today!
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnection of everyday devices, allowing them to send and receive data. IoT has become an integral part of smart homes, cities, and industrial applications.

Cloud Native Technologies
Purpose Of Abstract Class cloud-native technologies refer to the design and development of applications that are built to run in a cloud environment. They utilize microservices, containers, and orchestration tools like Kubernetes to achieve scalability, resilience, and flexibility.
- Core Concepts:
Preparing for Web developer Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Web developer Training Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Robotics Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the use of software robots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks. RPA improves efficiency, reduces human error, and frees up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Applications:
DevOps and AIOps
DevOps is a set of practices that combine software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to shorten the systems development life cycle and provide continuous delivery with high software quality. AIOps, or Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations, enhances DevOps by using AI to automate and optimize IT operations.
- Key Concepts:
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Prim’s Algorithm natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field of AI focused on the interaction between computers and human language. NLP allows machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- Applications:
Conclusion
The fields mentioned above are reshaping industries and economies globally. As technologies continue to evolve, their applications will only expand, creating new opportunities and challenges. The convergence of AI, quantum computing, edge computing, blockchain, and other innovations will drive the next wave of digital transformation across the globe.Because of ground-breaking discoveries and growing demand for faster, smarter, and more efficient technology, computer science is changing quickly. A web developer benefits from these advancements by utilizing modern tools and frameworks to build more dynamic, responsive, and intelligent web applications. Professionals, researchers, and students all need to be knowledgeable and flexible. A world that is smarter, more connected, and more inventive will result from the ethical and responsible adoption of these technologies.





