- Origins and Evolution of C
- Setting Up Your C Environment
- Basic Syntax and Structure of a C Program
- Variables, Data Types, and Operators
- Using printf and scanf
- Functions and Recursion
- Conditional Statements (if, switch)
- Loop Constructs
- Debugging and Compiling
- Writing Efficient C Code
Origins and Evolution of C
The C programming language is one of the most influential and widely used programming languages in computer science history. It was developed in the early 1970s by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs as part of the UNIX operating system project. C evolved from an earlier language called B, which itself was derived from BCPL (Basic Combined Programming Language). To see how such foundational languages influence modern infrastructure, exploring Cloud Computing Training reveals how today’s systems leverage virtual machines, container orchestration, and distributed computing building on decades of programming evolution to deliver scalable, resilient cloud solutions. The main reason for C’s development was to create a language that could write system software, particularly the UNIX operating system, in a way that was both efficient and portable. Over time, C Programming Language became popular beyond operating systems and was adopted in areas such as embedded systems, game development, and application programming. In 1989, the ANSI C standard (C89) was established, followed by ISO C, ensuring a consistent specification across platforms. Later revisions such as C99 and C11 introduced features like inline functions, variable-length arrays, and multi-threading support, solidifying C’s role as a foundational language for software engineering.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Course Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Course Today!
Setting Up Your C Environment
To start writing and running C Programming Language, you need to set up a C development environment. This setup includes two main parts: a text editor for writing your code and a C compiler that changes your code into machine language. Popular compilers like GCC (GNU Compiler Collection), Clang, and Microsoft Visual C++ are widely used. If you’re on Linux or macOS, you might already have GCC installed, or you can easily add it using package managers. To ensure these tools perform reliably under sudden load conditions, exploring What is Spike Testing reveals how this QA technique evaluates system behavior during abrupt traffic surges helping developers identify bottlenecks, optimize performance, and prevent crashes. For Windows users, options like MinGW or full IDEs such as Code::Blocks, Dev-C++, or Visual Studio are good choices. After installing your preferred tools, create a .c file to write your code. You can compile this code through the terminal or use an IDE’s build feature. For terminal users, a simple command to compile your program looks like this: gcc program.c -o program, followed by ./program to run the executable. This process helps your C program to run smoothly on your system.
Basic Syntax and Structure of a C Program
A C program follows a structured format that consists of preprocessor directives, a main function, and statements inside curly braces {}. The #include directive is used to include header files like <stdio.h> that provide standard library functions. The main() function serves as the entry point of every C program, and the program execution starts from here. Statements inside the main function are terminated with semicolons. A simple program looks like:
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main() {
- printf(“Hello, World!\n”);
- return 0;
- }
In this example, #include <stdio.h> allows us to use the printf function, and return 0; indicates successful execution. C programs are case-sensitive, meaning Main and main are treated differently. To understand how mastering such foundational syntax translates into career opportunities, exploring Average Full Stack Developer Salary reveals how proficiency in both front-end and back-end technologies can lead to competitive compensation across industries.
Would You Like to Know More About Cloud Computing Course? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Course Now!
Variables, Data Types, and Operators
Variables in C act as named storage for data that your program manipulates. Each variable must have a data type that determines the kind of data it can hold and how much memory it occupies. Common data types include int for integers, float for floating-point numbers, char for single characters, and double for higher-precision floating numbers. To understand how such structured definitions apply to service communication, exploring What is WSDL in Web Services reveals how WSDL describes the operations, messages, and data types used in SOAP-based services enabling precise, interoperable interactions between systems.
- int age = 25;
- float height = 5.9;
- char grade = ‘A’;
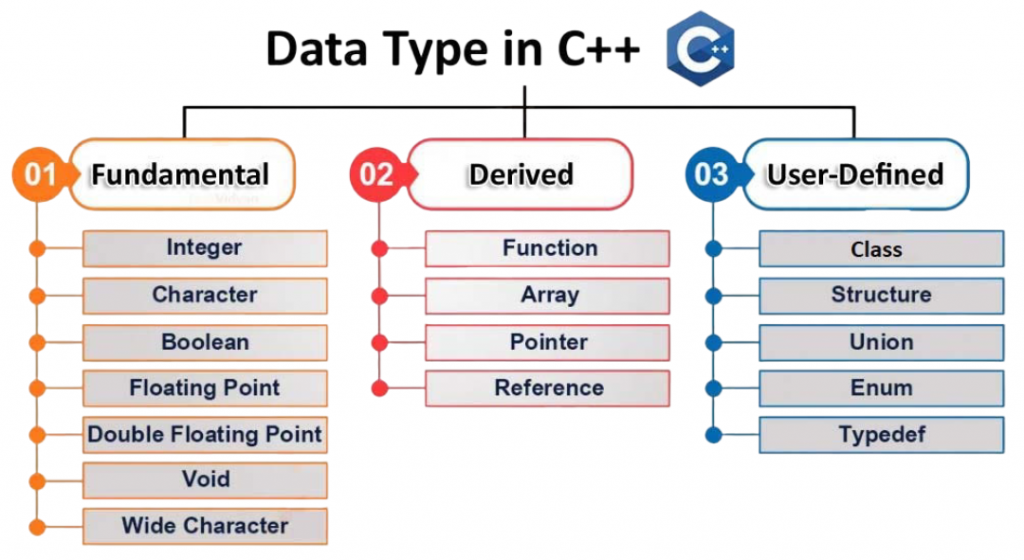
C is a powerful programming language that provides a variety of operators to help you perform different tasks in your code. These include arithmetic operators like addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), and modulus (%). You also have relational operators such as equality (==), not equal (!=), less than (<), and greater than (>), which let you compare values. Additionally, logical operators like AND (&&), OR (||), and NOT (!) help you create complex conditions. Finally, assignment operators, including standard assignment (=) as well as compound assignments like plus-equals (+=) and minus-equals (-=), allow you to update variable values effectively. By mastering these operators and learning to combine them with variables, you will improve your ability to write clear, logical, and functional programs in C.
Using printf and scanf
In C Programming Language, two essential functions for handling input and output are printf and scanf. The printf function is responsible for displaying information to the console, allowing programmers to share messages, variables, and results with users. For instance, using printf, you can easily format and present data, such as: printf(“The result is: %d\n”, result);. To scale such output-driven logic into distributed environments, exploring Cloud Computing Training reveals how cloud platforms handle logging, monitoring, and real-time data presentation across virtualized systems enhancing visibility, performance, and collaboration. On the other hand, scanf is used to gather input from the user. This function captures data, such as numbers or strings, and stores it in variables for further processing.
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main() {
- int age;
- printf(“Enter your age: “);
- scanf(“%d”, &age);
- printf(“You are %d years old.\n”, age);
- return 0;
- }
In scanf, format specifiers like %d (integer), %f (float), and %c (character) are used to indicate the type of data being read. The & symbol is important because it passes the memory address of the variable where the input will be stored. To explore how data acquisition and control systems handle such input dynamically, Virtual Instrumentation using Labview reveals how graphical programming enables real-time monitoring, hardware interfacing, and automated testing across engineering applications.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course Now!
Functions and Recursion
Functions in C allow you to organize your code into reusable blocks. A function has a return type, a name, a parameter list, and a body. For example: To understand how build tools apply similar modular principles to software automation, exploring Gradle vs Maven reveals how these tools differ in configuration style, performance, and dependency management helping developers streamline compilation, testing, and deployment workflows.
- int add(int a, int b) {
- return a + b;
- }
Functions can be called from main() or from other functions. C also supports recursion, where a function calls itself directly or indirectly. Recursion is useful for tasks like factorial calculation, traversing data structures, and solving mathematical problems. However, recursion should be used carefully to avoid stack overflow errors.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing Course? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Course Today!
Conditional Statements (if, switch)
C Programming Language provides if, else if, and else statements to execute code blocks conditionally. For example: To understand how timing and conditional logic can be coordinated in other languages, exploring Python Sleep Method reveals how developers can pause execution for specified durations enabling controlled delays, task scheduling, and smoother flow in Python scripts.
- if (age > 18) {
- printf(“You are an adult.\n”);
- } else {
- printf(“You are a minor.\n”);
- }
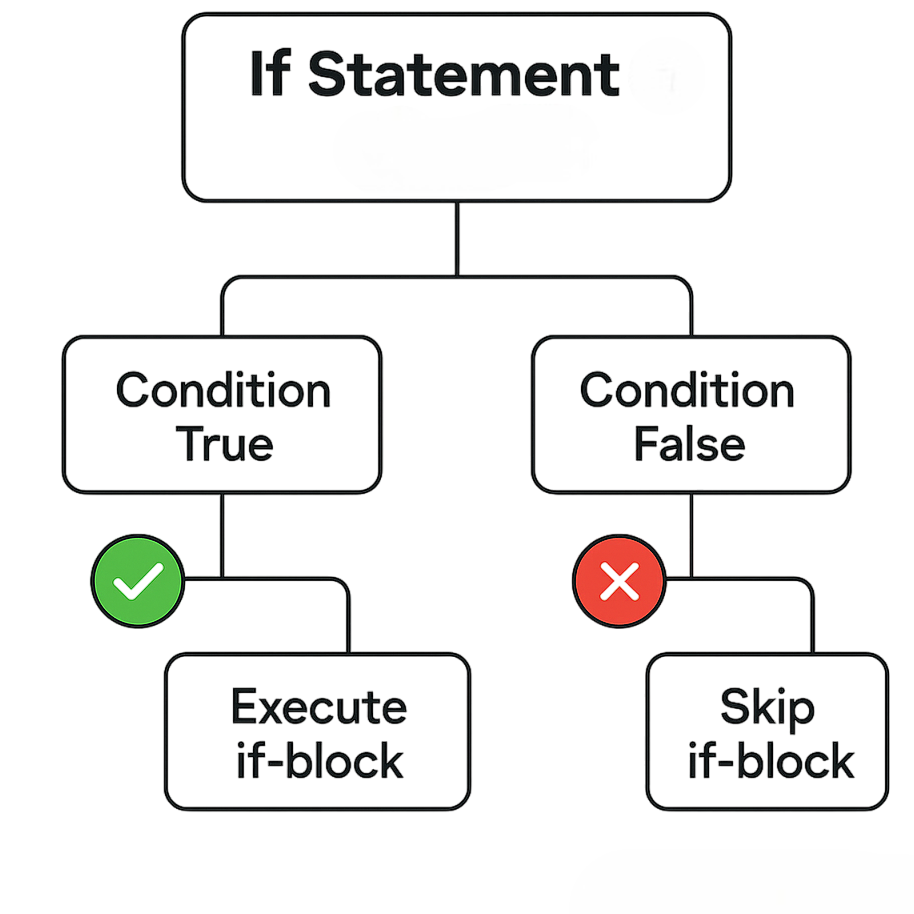
The switch statement is useful when you have multiple possible values for a single variable:
- switch (grade) {
- case ‘A’:
- printf(“Excellent!\n”);
- break;
- case ‘B’:
- printf(“Good.\n”);
- break;
- default:
- printf(“Invalid grade.\n”);
- }
Both constructs help control the program’s flow based on conditions.
Preparing for Cloud Computing Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Loop Constructs
C offers several loop constructs: for, while, and do-while. Loops are used for repeated execution of code. For example: To compare how modern languages handle iteration and control flow, exploring Kotlin vs Python reveals how Kotlin’s concise syntax and null safety contrast with Python’s readability and dynamic typing helping developers choose the right tool for scalable, maintainable logic.
- for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
- printf(“%d\n”, i);
- }
The while loop runs while a condition is true, and the do-while loop guarantees at least one execution before checking the condition. Loop control statements like break and continue allow you to exit loops or skip iterations.
Debugging and Compiling
Debugging is essential to fix errors in your C programs. Tools like GDB (GNU Debugger) allow you to set breakpoints, inspect variables, and step through code. Compiling with gcc -Wall program.c helps catch warnings that can indicate potential bugs. Common issues include syntax errors, logical errors, and runtime errors like segmentation faults. To understand how modern frameworks simplify debugging and development, exploring Spring Boot vs Spring MVC reveals how Spring Boot’s auto-configuration and embedded server model compare with Spring MVC’s manual setup helping developers choose the right approach for building scalable Java applications.
Writing Efficient C Code
To achieve efficiency in C Programming Language, it’s important to understand memory management. A clear approach can greatly improve performance. Start by identifying and using the const modifier for values that don’t change, as this helps the compiler optimize your code. To scale such optimization strategies across distributed systems, exploring Cloud Computing Training reveals how virtualized resources, elastic infrastructure, and deployment automation empower developers to build high-performance, cost-efficient applications in the cloud. It’s also vital to avoid unnecessary loops, focus on using efficient algorithms to cut down processing time. In performance-critical sections, minimize function calls to speed up execution. Always remember to free any allocated memory to prevent leaks that can waste resources. Writing modular code not only makes maintenance easier but also improves speed, allowing your applications to run more smoothly and efficiently.





