- Introduction to Drools and Rule Engines
- What is Drools? Overview and Use Cases
- Drools Architecture and Key Components
- Installing and Setting Up Drools Environment
- Understanding the Rule Language (DRL)
- Working with Facts, Sessions, and Knowledge Bases
- Rule Execution Flow and Agenda Control
- Conclusion
Introduction to Drools and Rule Engines
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic approach to improving an organization’s processes to enhance efficiency, effectiveness, and adaptability. It involves analyzing, designing, implementing, monitoring, and optimizing business processes to meet organizational goals and customer needs. BPM focuses on processes rather than individual tasks, enabling organizations to streamline workflows, reduce costs, and improve service quality. By mapping out processes, businesses can identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies, allowing for continuous improvement. Modern BPM often integrates technology, Java Training such as workflow automation tools and software, to facilitate real-time process management and data-driven decision-making. This enables organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions, regulatory requirements, and customer expectations. Moreover, BPM fosters collaboration across departments by clearly defining roles and responsibilities within processes. This alignment helps ensure that everyone in the organization works towards common objectives. Ultimately, BPM is not just about automation but about creating a culture of ongoing process optimization and innovation. By embracing BPM, organizations can enhance agility, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve sustainable business growth.Drools is a powerful open-source Business Rule Management System (BRMS) and rule engine developed in Java.
To Earn Your Java Training Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Java Training Today!
What is Drools? Overview and Use Cases
Drools is an open-source Business Rule Management System (BRMS) and rule engine written in Java. It allows developers and business users to define, manage, and execute complex business rules separately from application code, enabling more flexible and maintainable software solutions. Drools uses a declarative approach where rules are expressed as “if-then” statements, Java Classes and Objects making it easier to capture business logic in a clear, human-readable format. At its core, Drools is powered by a rule engine that applies these rules to incoming data, or “facts,” to infer decisions or trigger specific actions. It leverages efficient algorithms, such as the Rete algorithm, trigger to quickly evaluate and match multiple rules, even in complex scenarios with large rule sets.
Drools supports a wide range of features, including rule versioning, event processing, decision tables, and complex event processing (CEP), making it suitable for applications like fraud detection, credit risk assessment, policy enforcement, and workflow automation. By externalizing business rules, Drools helps organizations respond quickly to changing business conditions without requiring extensive changes to application code. This improves agility, consistency, and transparency in decision-making processes, making Drools a popular choice for enterprises aiming to automate and optimize their business logic.
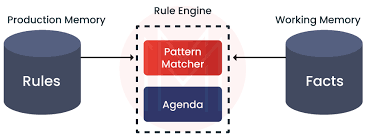
Drools Architecture and Key Components
Drools is composed of several interlocking components:
- Knowledge Base (KieBase): Stores compiled rules, processes, and models.
- Knowledge Session (KieSession): Runtime environment where facts are inserted and evaluated.
- DRL (Drools Rule Language): Text-based syntax to define conditions and actions.
- Decision Tables: Represent rules in Excel sheets for non‑technical rule authors HashMap in Java.
- Agenda: Manages rule execution order, offering control via salience, locking, etc.
- Working Memory: Stores ‘facts’ Java objects inserted into the session.
KIE Workbench adds a web interface for versioning, collaboration, and deploying rule assets as containers. The engine’s modular structure supports Stateless and Stateful sessions depending on use cases.
Would You Like to Know More About Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Now!
Installing and Setting Up Drools Environment
To start using Drools:
Add Maven dependencies to your pom.xml:
-
org.kie -
kie-api -
7.x.x.Final -
org.kie -
kie-dmn-core -
7.x.x.Final -
org.drools -
drools-compiler -
7.x.x.Final
Optionally, download and run KIE Workbench, a web app for managing rule projects.
- Create a .drl file under src/main/resources, and the Maven plugin (kie-maven-plugin) will compile and package it.
- For Spring Boot integration, include kie-spring-boot-starter and configure KieScanner for auto-updated rule reloading Socket Programming in Java.
- With dependencies resolved, you can load, compile, and execute rules within your Java application.
Understanding the Rule Language (DRL)
Rules in Drools are written in DRL, which has a simple structure:
package com.example.rules
- import com.example.model.Order
- rule “High Value Order”
- when
- $order : Order( total > 1000 )
- then
- System.out.println(“High value order: ” + $order.getId());
- modify($order) { setPriority(“HIGH”) }
- end
Each rule has a unique name.
- The when section defines matching conditions using Java-like expressions.
- The then section defines actions, Java Training such as modifying facts or calling services.
DRL supports rule attributes:
- salience for priority,
- no-loop to prevent self-triggering,duration or lock-on-active for special execution control.
- Comments (// or /* */) and DSL extensions can further enhance readability.
Are You Interested in Learning More About FullStack With Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Today!
Working with Facts, Sessions, and Knowledge Bases
In Drools, the core concepts of facts, sessions, and knowledge bases form the foundation for rule processing. Facts represent the data or information that the rule engine evaluates against the defined business rules. These facts are typically Java objects that hold the state of the system or input data relevant to decision-making. The Knowledge Base acts as a repository that contains all the compiled rules and processes. It stores and organizes these rules, making them accessible for execution. To execute rules, Drools uses a Session, Purpose Of Abstract Class Agenda Control which is a runtime environment where facts are inserted, and rules are fired. There are two main types of sessions: Stateful and Stateless.
Stateful sessions maintain the state of the inserted facts and can be used for long-running processes where facts and rule execution are continuously updated. Stateless sessions, by contrast, execute rules in a one-off manner without retaining state between invocations. When facts are inserted into a session, the rule engine evaluates them against the rules stored in the knowledge base, triggering the appropriate actions defined by matching rules. This architecture allows Drools to efficiently manage complex business logic and decision-making in a scalable and flexible way.
Preparing for Java Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Java Training Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
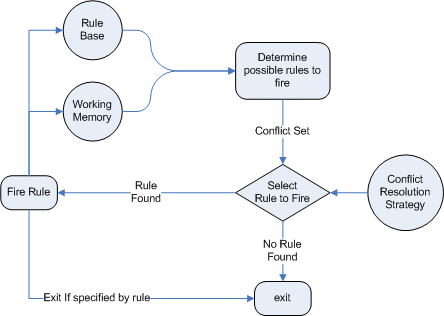
Rule Execution Flow and Agenda Control
Rule Execution Flow:
- Facts are inserted into the working memory (session).
- Rules are evaluated based on the conditions matching the facts.
- Matching rules are placed on the agenda for execution.
- Rules on the agenda fire according to priority and conditions.
- Rule actions execute, potentially modifying facts or inserting new facts
- The engine re-evaluates rules as facts change, repeating the cycle until no more rules match Reverse a String in Java .
- The agenda holds all activations (rules ready to fire).
- Rules can be prioritized using salience to control firing order.
- Developers can manipulate the agenda by halting, firing specific rules, or removing activations.
- Control flow operators like no-loop, lock-on-active, and auto-focus manage rule re-firing and agenda behavior.
- This allows fine-tuned control over rule execution, ensuring business logic executes as intended.
Agenda Control:
Conclusion
Drools offers a powerful paradigm for business rule management and execution. By separating decision logic from application flow, it empowers agile innovation and improves maintainability Understanding the Rule Language. Whether you’re using standalone Java applications, Spring Boot microservices, or full BPM suites, Drools provides the tools to declaratively express and evolve business policies. With a clear structure, robust testing mechanisms, and deep integration capabilities, Drools is an essential skill for developers working in regulated or logic-intensive domains. Armed with this guide, Java Training you’re now ready to start writing, testing, and scaling your rule-based solutions with Drools. Drools offers a robust framework for managing complex business rules through a clear separation of decision logic from application code. Understanding the rule execution flow and agenda control mechanisms is essential to harnessing its full power, enabling precise control over how and when rules fire. By effectively working with facts, sessions, and knowledge bases, organizations can build flexible, scalable, and maintainable rule-driven applications. This empowers businesses to quickly adapt to changing requirements, testing improve decision-making consistency, and automate critical processes, making Drools a valuable tool in modern enterprise solutions.





