
- Purpose of Constructors
- Default Constructor
- Parameterized Constructors
- Constructor Overloading
- Copy Constructor
- Delegating Constructors
- Constructor Initialization Lists
- Conclusion
Purpose of Constructors
In C++, a constructor is a special member function of a class that is automatically invoked when an object of that class is created. Its primary purpose is to initialize objects assigning values to variables, setting up resources, or performing startup tasks necessary for the object to function properly. Constructors share the same name as the class and do not have a return type, not even void. They provide a controlled way to ensure that an object starts its life in a valid and predictable state. Without constructors, object members would need to be initialized manually after creation, which increases the risk of uninitialized or inconsistent data Cloud Computing Training. C++ supports various types of constructors such as default constructors, parameterized constructors, copy constructors, and delegating constructors. These allow flexibility in how objects are initialized either with default values, user-provided values, copies of existing objects, or by reusing other constructors. constructors in C++ also support overloading, meaning a class can have multiple constructors with different parameter lists to suit different initialization needs. In addition, constructor initialization lists offer an efficient way to initialize member variables, especially when dealing with constants or reference members. Overall, constructors are fundamental in building robust, reliable, and efficient object-oriented applications in C++.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Course Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Course Today!
Default Constructor
A default constructor is a constructor that either takes no parameters or has all parameters with default values. It is automatically invoked when an object is created without arguments. If you do not define any constructor in your class, the Constructor in C++ compiler automatically generates a default constructor for you, which simply initializes built-in types to undefined values and calls default constructors for class-type members. However, if you explicitly define any other constructor (like parameterized or copy), the compiler will not generate the default constructor Prim’s Algorithm Explanation unless you specify it. Default constructors are particularly useful when creating arrays of objects, as the compiler will call the default constructor for each element. A default constructor in C++ is a constructor that takes no parameters and is used to initialize objects with default values. If no constructor is explicitly defined in a class, the C++ compiler automatically provides a default constructor. However, if you define any constructor (like a parameterized one), and still need a default constructor, you must declare it explicitly.
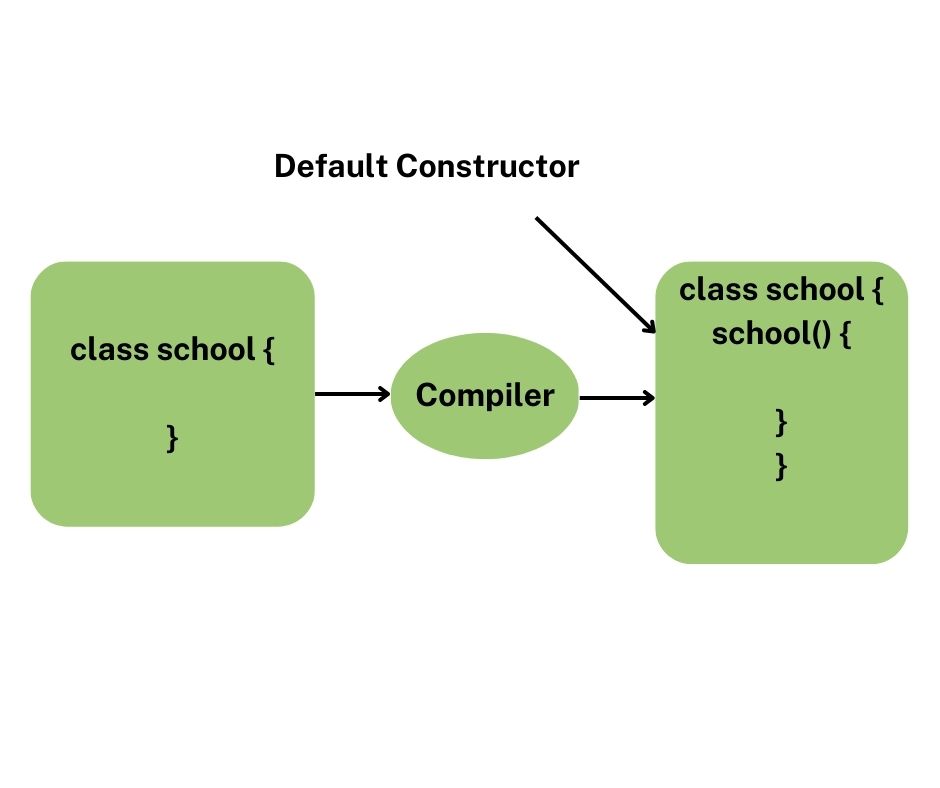
The primary role of the default constructor is to ensure that objects are created in a valid state, even when no initialization values are provided during object creation. It is particularly useful when creating arrays of objects or using classes with default initialization requirements.
Parameterized Constructors
- Used to Initialize Objects with Custom Values: Allows setting specific values for object attributes at the time of creation.
- Takes One or More Parameters: Unlike the default constructor, it accepts arguments to initialize data members.
- Defined Explicitly by the Programmer: The compiler does not generate a parameterized constructor automatically.
- Enables Constructor Overloading: Multiple constructors with different parameter lists can coexist in a class Cloud Computing Training.
- Can Be Combined with Default Parameters: Parameters can have default values, giving flexibility in object creation.
- Prevents Default Construction (If No Default Constructor Exists): If only a parameterized constructor is defined, objects cannot be created without arguments.
- Commonly Used for Object Initialization: Helps reduce the need for separate initialization functions after object creation.
- Purpose: Creates a new object as a copy of an existing object.
- Signature: Takes a reference to an object of the same class, typically ClassName(const ClassName &obj).
- Called When: An object is initialized using another object of the same class (e.g., ClassName obj2 = obj1;).
- An object is passed by value to a function.
- An object is returned by value from a function.
- Default Copy Constructor: Provided by the compiler if not explicitly defined. Performs a shallow copy Kruskal Algorithm in DAA (member-wise copy).
- Custom Copy Constructor: Needed when deep copy is required (e.g., when the class contains pointers).
- Prevents Issues: Helps avoid problems like double deletion and dangling pointers when copying objects.
- class Point {
- int x, y;
- public:
- Point(int a, int b) : x(a), y(b) {}
- };
Would You Like to Know More About Cloud Computing Course? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Course Now!
Constructor Overloading
Constructor overloading in C++ is the process of defining multiple constructors within the same class, each having a different parameter list. This allows the creation of objects in different ways depending on the available data at the time of instantiation. The compiler determines which constructor to call based on the number and type of arguments passed. For example, a Book class might have one constructor that sets the title and author, another that sets the title, author, and price, and a default constructor that initializes default values. This flexibility makes code more user-friendly and adaptable. Constructor overloading in constructors in C++ allows a class to have multiple constructors with different parameter lists.
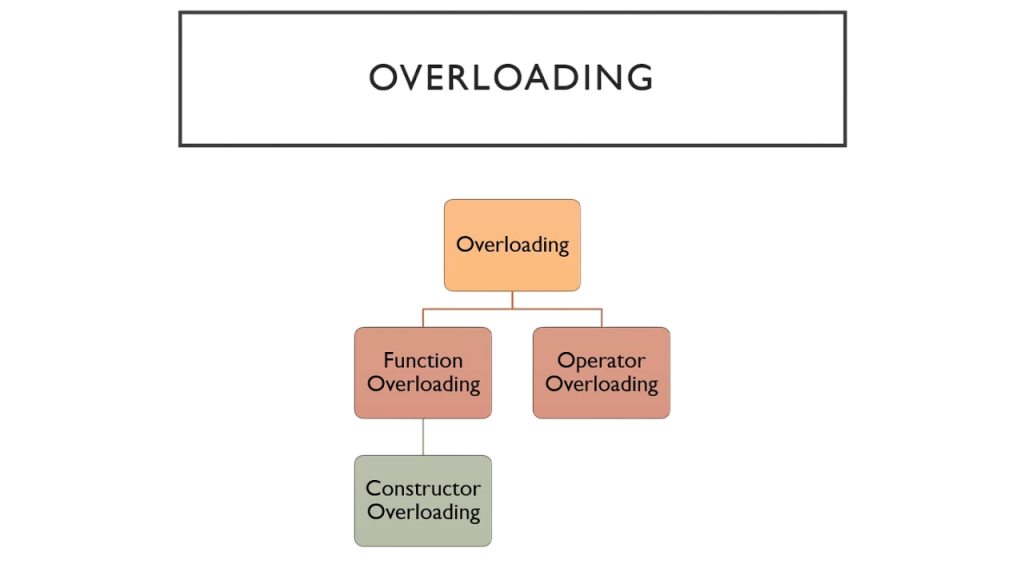
This enables objects to be initialized in various ways depending on the number or type of arguments passed Fibonacci Series in Python . Each overloaded constructor must differ in its parameter signature to avoid ambiguity. It improves flexibility and usability by allowing developers to create objects with default values, specific values, or copied values. For example, one constructor may take no arguments, while another accepts parameters to initialize object attributes. Constructor overloading enhances code readability and supports efficient object creation in different situations within the same class.
Copy Constructor
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course Now!
Delegating Constructors
C++11 introduced delegating constructors, which allow one constructor to call another constructor in the same class. This helps to avoid code duplication and makes it easier to maintain the class. For instance, you may have a parameterized constructor that performs most of the initialization, and your default constructor can call it with default arguments. This ensures that all initialization logic is centralized in one place, reducing the chances of bugs when changes are made in the future PPC Analyst Salary . Delegating constructors allow one constructor to call another constructor within the same class to reuse initialization code. Introduced in C++11, this feature helps avoid code duplication and simplifies constructor management. When a delegating constructor is called, it first invokes the target constructor, which performs the actual initialization. This approach is useful when multiple constructors share common setup steps but differ in parameters. It enhances code maintainability and clarity by centralizing initialization logic. Delegating constructors cannot create recursive calls, as that would lead to infinite loops. Overall, they streamline object construction in complex classes.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing Course? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Course Today!
Constructor Initialization Lists
A constructor initialization list is a more efficient way to initialize class data members, especially constant members, reference members, or members of classes without default constructors. IT Engineer Salary in India Instead of assigning values inside the constructor body, you can initialize them directly in the list following the constructor’s parameter list. For example:
This approach avoids unnecessary default construction followed by reassignment, improving performance and ensuring proper initialization order. It is also the only way to initialize const data members and references in a class.
Preparing for Cloud Computing Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Constructors are fundamental components in constructors in C++ that ensure objects are correctly initialized when they are created. They provide a structured way to set up an object’s initial state, promoting code clarity and reliability. The default constructor allows for basic object creation without requiring parameters, while parameterized constructors give flexibility by enabling initialization with specific values. This versatility is further enhanced by constructor overloading, which permits multiple constructors with different parameter lists in the same class, catering to various initialization needs. The copy constructor plays a critical role when objects are copied, ensuring a proper copy of an object’s data, especially Cloud Computing Training when dealing with dynamic memory or pointers. Without a custom copy constructor, shallow copies can lead to issues like double deletion or memory corruption. Introduced in C++11, delegating constructors help reduce code duplication by allowing one constructor to call another within the same class, centralizing initialization logic and improving maintainability. Together, these constructor types help developers write clean, efficient, and error-free code by managing object creation systematically. A solid understanding of constructors and their behaviors is essential for mastering object-oriented programming in C++, leading to robust software design and easier maintenance over time.





