
- Introduction to NoSQL Databases
- Why Cassandra?
- Key Features of Cassandra
- CAP Theorem and Cassandra
- Data Modeling in Cassandra
- Querying with CQL
- Performance Optimization
- Conclusion
Introduction to NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases arose to address limitations of traditional relational systems. They offer flexible schema models such as document, key-value, wide-column, or graph and support horizontal scaling across commodity servers. NoSQL solutions allow for rapid development cycles and handle semi-structured or unstructured data much more naturally. Use cases like tracking user sessions, managing IoT telemetry, catalog data, or large-scale logging require systems that support high write throughput Database Training, distribute data across nodes, and remain always available. Cassandra, a wide-column store, is one of the most robust NoSQL engines, designed specifically for these needs. NoSQL databases are non-relational data storage systems designed for flexibility, scalability, and performance. Unlike traditional relational databases, NoSQL allows the storage of unstructured or semi-structured data without a fixed schema. Common types include key-value stores, document databases, column-family stores, and graph databases. NoSQL is ideal for big data, real-time web apps, and scenarios requiring horizontal scaling. These databases often follow the BASE model (Basically Available, Soft state, Eventually consistent) over ACID guarantees.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Why Cassandra?
Apache Cassandra stands out due to several compelling attributes. First, its masterless, peer-to-peer architecture ensures no single point of failure; every node can handle reads and writes. Second, its linear scalability means that as you add nodes, both read and write throughput increase proportionally. Cassandra also supports tunable consistency, where applications can configure strong or eventual consistency on a per-query basis. Combined with multi-datacenter replication, Entity in DBMS fault tolerance via hinted handoff and replica synchronization, and flexible schema-on-read data modeling, Cassandra meets the requirements of modern distributed systems.
Apache Cassandra is a highly scalable, distributed NoSQL database designed for handling large volumes of data across many servers without a single point of failure. It offers high availability, fault tolerance, and excellent write performance, Querying with CQL making it ideal for real-time applications. Cassandra’s peer-to-peer architecture ensures no master node, allowing horizontal scaling and automatic data replication.
Key Features of Cassandra
Cassandra’s architecture is rich with enterprise-grade features:
- Peer-to-peer design: Each node is identical; communication happens via a gossip protocol and failure detection (Phi accrual).
- Replication and partitioning: Data is evenly distributed using consistent hashing, with configurable replication across nodes and data centers.
- Commit log + memtable + SSTable storage model: Writes are durable and fast; data is flushed in sorted structures for efficient reads.
- Flexible schema: Tables allow optional and dynamic columns; clustering and partition keys define both distribution and ordering Firebase Realtime Database.
- Tunable consistency: Options like ONE, QUORUM, ALL let applications adjust consistency vs. latency per operation.
- Lightweight transactions (LWT): Paxos-based support for conditional updates enabling linearizable consistency for critical operations.
- High availability: Continuous operation during node or data center outages, with eventual synchronization of replicas.
These features make Cassandra ideal for globally distributed systems that require high ingestion rates and continuous uptime.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
CAP Theorem and Cassandra
According to the CAP Theorem, a distributed system can guarantee at most two of the following: Consistency, Availability, and Partition tolerance (DataStax Documentation, Apache Cassandra). Cassandra is designed as a highly available, partition-tolerant (AP) system, meaning it sacrifices strict immediate consistency in exchange for always-on service (DataStax Documentation). In other words, during a network partition, Cassandra continues to accept reads and writes, potentially returning slightly Database Training stale data that is reconciled later via eventual consistency. However, Cassandra offers tunable consistency by adjusting replication factors and consistency levels; users can configure stronger consistency (closer to CP models) if strictly needed (Stack Overflow).
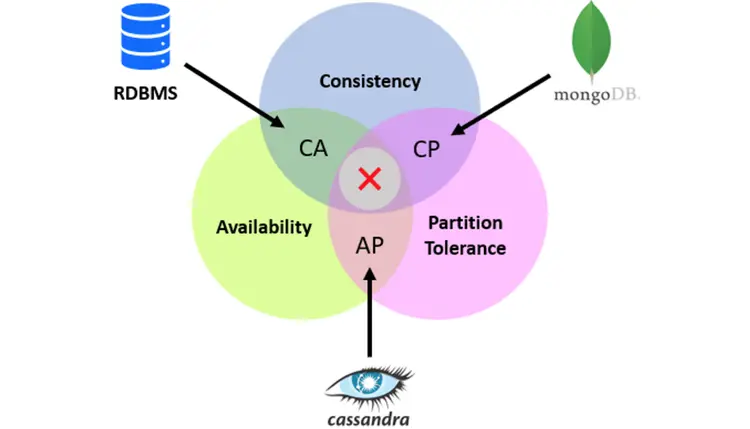
Moreover, modern interpretations extend CAP with the PACELC theorem, which states that even without partition events, systems face a trade-off between latency (L) and consistency (C) during normal operations (“Else”) (Wikipedia). Cassandra, under normal conditions, tends to favor low latency instead of strict consistency, aligning it with PA + EL classification What is Database Testing . Thus, while Cassandra defaults to AP behavior, it gives developers fine control over consistency-latency-availability trade-offs based on application priorities.
Data Modeling in Cassandra
Effective data modeling in Cassandra differs from relational database design. In Cassandra:
- Data is modeled around queries, not normalized tables.
- The primary key consists of a partition key (hash-distributed) and optional clustering columns to define sort order within partitions.
- Denormalization is encouraged; data is often duplicated across tables optimized for different query patterns.
- Schema design must anticipate query paths, as Cassandra lacks support for joins and multi-row transactions (except optional lightweight transactions).
For instance, if an application needs to retrieve user messages by timestamp, the partition key could be user_id, and clustering column could be timestamp DESC to enable efficient new-first reads. Cursors in SQL This query-driven modeling ensures tables are read-efficient and scalable. Online training programs focus extensively on designing tables for query access, choosing appropriate clustering, managing wide partitions, and setting replication strategies skills essential to Cassandra success.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Querying with CQL
Cassandra Query Language (CQL) is a NoSQL Databases -like syntax tailored for the wide-column model. It supports operations such as INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and SELECT, but does not support joins or complex aggregations natively. Key aspects include:
- CREATE TABLE with specified primary keys (partition and clustering).
- INSERT and UPDATE operations: fast append-only writes.
- SELECT queries that must align with the table’s primary key structure Attributes in DBMS .
- BATCH operations across tables use cautiously to avoid performance issues.
- Tunable consistency levels: LOCAL_QUORUM, ALL, ONE, etc., affect acknowledgements needed before success is returned.
- Support for lightweight transaction (LWT) using IF NOT EXISTS or compare-and-set semantics to enforce serial consistency for critical updates.
Training covers writing efficient Querying with CQL queries, designing conditional updates, understanding lightweight locks, handling pagination and paging state, and understanding limitations like no join support.
Performance Optimization
Optimizing Cassandra performance involves tuning several system and data aspects:
- Choosing an optimal replication factor across nodes/data-centers.
- Proper configuration of consistency levels to balance user tolerance vs. speed.
- Tuning compaction strategies like SizeTiered or Leveled compaction to manage SSTable growth and tombstone cleanup.
- Managing tombstone settings to avoid fresh deletes causing read latency spikes Serializability in DBMS .
- Distributing data evenly across nodes by setting appropriate token ranges or using vnodes.
- Tuning heap memory and cache settings, and monitoring metrics like read/write latency, pending compactions, and coordinator load.
- Understanding the impact of anti-entropy repair and hinted handoff on consistency and cluster health.
Hands-on labs in training courses help learners set up clusters, run performance benchmarks (e.g., using YCSB), tune read/write paths, detect hotspots, and perform cluster maintenance.
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Cassandra is a modern NoSQL database purpose-built for distributed, real-time, and globally available use cases. It offers unmatched reliability through its masterless architecture, scalable performance, optional strong consistency via lightweight transactions, and flexible query patterns using Querying with CQL. By embracing Cassandra through structured online training, including hands-on labs, performance tuning exercises, and certification preparation, learners gain the capability to design, deploy, Database Training and maintain enterprise-level databases. Whether serving streaming pipelines, feature stores for machine learning, time-series data, or operational catalogs, Cassandra powers the modern data stack. Mastering Cassandra positions you for high-value roles in data engineering, backend development, or system architecture where modern, scalable, and resilient infrastructure is central.


