
High-performance database appliances like Oracle Exadata are made for the best possible data processing and management. With the help of specialised software and strong hardware, Exadata provides outstanding performance for workloads involving Oracle databases. Fast data access and query processing are ensured by its massively parallel design, flash storage, and InfiniBand networking. Exadata is designed to efficiently manage complicated transactions, analytics, and large-scale data processing. By shifting database operations to storage servers, its Smart Scan technology lowers data transfer costs and improves query performance.
1. What is Exadata?
Ans:
Exadata is a preconfigured hardware and software package that offers the Oracle Database running platform.
2. What environment is a good fit for Exadata?
Ans:
Exadata was originally designed for a warehouse environment. Later it was enhanced for use in OLTP databases as well.
3.What are Key components of Exadata?
Ans:
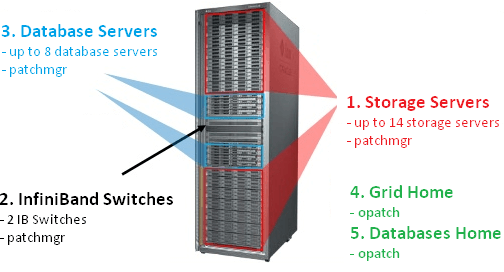
- DB Server
- Cell Storage
- Infiniband Switch
- Cisco Switch
- PDU
4.What are Features of Exadata?
Ans:
- Smart Scan
- Smart Flash Cache
- IORM
- Storage Index
- EHCC (Exadata Hybrid Columnar Compression)
5.What are the advantages of Exadata?
Ans:
The Exadata cluster allows for a consistent performance while allowing for an increased throughput. By using both intra- and inter-instance parallelism, the performance of the cluster is maintained even as the load increases.
6.What are Exadata Sizing configurations?
Ans:
Exadata comes in the following configuration
- Full Rack
- Half Rack
- Quarter Rack
- 1/8th Rack
7. What is hybrid columnar compression?
Ans:
Exadata has a feature called Hybrid Columnar compression, or HCC, which is used to compress data for tables at the column level.It produces compression data units, which are logical groupings of column values that usually contain multiple data blocks.
8.What is the Parallelism instance parameter used in Exadata?
Ans:
The PARALLEL_MAX_SERVERS parameter in the Oracle Database determines the maximum number of the parallel execution processes (parallel query slaves) that can be started by a single instance.
9. How do test performance of Exadata?
Ans:
Testing the performance of the Oracle Exadata system is a crucial task to ensure it meets expected performance requirements for specific workloads.
10. What are ways to migrate onto Exadata?
Ans:
Depending on downtime allowed there are several options:
- Oracle DataGuard
- Traditional Export/Import
- Tablespace transportation
- Goldengate Replication after data restores onto Exadata.
11. What are different Exadata configurations?
Ans:
There are four different configurations for the Exadata Appliance: Full Rack, Half Rack, Quarter Rack, or 1/8th Rack.
12. What is the secret behind Exadata’s higher throughput?
Ans:
Between a storage node, the database nodes, and the other nodes in the RAC cluster, Exadata transfers less data via pipes.Its capacity for massive parallelism, which enables it to run parallel processes on every cluster node, also gives it a far higher throughput.
13. What is a storage index ?
Ans:
Storage Indexes consist of minimum and a maximum value for up to eight columns. This structure is maintained for the 1MB chunks of storage (storage regions).
14. How does Exadata support high availability and disaster recovery?
Ans:
Exadata supports the high availability through features are Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) for load balancing and failover, as well as Oracle Data Guard for disaster recovery.
15. What is InfiniBand networking in Oracle Exadata?
Ans:
InfiniBand is high-speed, low-latency networking technology used in Oracle Exadata. It connects the database servers, storage servers, and other components within the system, facilitating fast and efficient communication.
16. What is cellcli?
Ans:
cellcli is the command-line interface provided by the Oracle Exadata Storage Server software. It allows administrators to manage and monitor Oracle Exadata storage cells.
17. How does one monitor and manage an Oracle Exadata system?
Ans:
Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) is commonly used to be monitor and manage Oracle Exadata systems. OEM provides the centralized platform for monitoring performance metrics, managing configurations, setting up alerts, and performing diagnostics.
18. What is the difference between cellcli and dcli?
Ans:
| Feature | Cellcli (Cell Command-Line Interface) | dcli (Distributed Command-Line Interface) | |
| Scope |
Management of a single cell |
Cluster-wide oversight | |
| Purpose | Configuration and administration of cells | Cluster setup and administration | |
| Application | local within a certain Exadata cell | Throughout several Exadata cells within a cluster | |
| Commands |
directives particular to a cell |
Cluster-wide directives |
19. What are the benefits of Exadata Storage Expansion Racks?
Ans:
Exadata Storage Expansion Racks allow an organization to scale storage capacity without adding the additional database servers.
20. What operating systems does Exadata support?
Ans:
Oracle Exadata Database Machine supports the specific versions of Oracle Linux and Oracle Solaris operating systems.
- Oracle Linux
- Oracle Solaris
21. What are options to update cell_flashcache for any object?
Ans:
- KEEP
- DEFAULT
- NONE
22. What is the default size of a smart flash log?
Ans:
- 512MB per module.
- Every storage cell has 4 modules so its 4X512 MB per CELL
23. Explain flash cache and how it works?
Ans:
The flash cache is a hardware component configured in an Exadata storage cell server which delivers high performance in reading and writing operations.
24. What is cellcli?
Ans:
cellcli – It is a cell command-line utility. Manage cell storage with use of cellcli utility. It is a utility to administer cell storage.
25. What are all Types of EHCC?
Ans:
- Query Low
- Query High
- Archive High
- Archive Low
26. Explain the role of InfiniBand networking in Exadata Clusters.
Ans:
InfiniBand networking in Exadata Clusters provides high-speed, low-latency communication between the database servers, storage servers, and other components within the cluster.
27. What are Background services of Cell Server?
Ans:
- MS- Management Server
- cellsrv – Cell Server
- RS – Restart Server
28. What is Exadata sizing configuration?
Ans:
- Full Rack
- Half Rack
- Quarter Rack
- 1/8th Rack
29. How does one replace a faulty HDD in Exadata Storage?
Ans:
- All HDDs are hot-swappable so if using proper redundancy then can directly remove and replace a new HDD.
- Storage software will take care of all stuff in the background after replacing the HDD.
30. How to migrate a database from normal setup to Exadata?
Ans:
- Export/Import
- Physical Standby
- Logical Standby
- Transportable Tablespace
- Transportable Database
- Golden gate
31. What is Exadata shutdown and start-up procedure?
Ans:
Shutdown Procedure:
- Stop Database and Listener
- Stop Cluster
- Shutdown Database Servers
- Shutdown Cell Storage
- Shutdown all the switches
- Remove powers from PDUs
32. What is ASR?
Ans:
Oracle hardware is managed via ASR. ASR automatically raises an SR with Oracle Support and notifies the relevant customer whenever a hardware malfunction occurs.
33. How to integrate Exadata with OEM 12c?
Ans:
- Install the OEM agent on DB server
- Launch auto-discovery with use of One Command XML file
- Specify required credentials for all components
- Review Configuration
- Complete the setup
34. What Exadata Smart Fusion Block Transfer (FBT)?
Ans:
Smart Fusion Block Transfer (FBT) is the feature that enhances I/O performance by allowing the multiple database blocks to be sent or received in a single I/O operation.
35. How does Exadata handle High Availability?
Ans:
Exadata ensures the high availability through features such as Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) for load balancing and failover, Oracle Data Guard for data replication and disaster recovery, and ability to perform rolling upgrades and patching without downtime.
36. What are Exadata Health check tools?
Ans:
- Exacheck
- sundiagtest
- oswatcher
- OEM 12c
37. What is EHCC?
Ans:
EHCC stands for Exadata Hybrid Columnar Compression. It is unique compression feature in Oracle Exadata that allows for a highly efficient storage of data in a columnar format.
38. What is offloading and how does it work?
Ans:
It refers to a fact that part of the traditional SQL processing done by database can be offloaded from the database layer to a storage layer.
39.What is the Storage Index in Oracle Exadata?
Ans:
Storage Index is the feature in Oracle Exadata that helps improve the query performance by reducing I/O.
40. What is Cell RAM cache?
Ans:
Cell RAM cache is an extension of the database cache that sits in front of Flash Cache on storage servers.
41. What is adaptive scrubbing?
Ans:
An Oracle Exadata System Software automatically inspects and repairs the hard disks periodically when the hard disks are idle.
42. How many networks are required in Exadata?
Ans:
- Public/Client Network — For Application Connectivity
- Management Network — For an Exadata H/W management
- Private Network — For the cluster inter connectivity and Storage connectivity
43. How to take cell storage software backup?
Ans:
It is not required to take backup as it happens automatically. Exadata uses an internal USB drive called Cellboot Flash Drive to take backup of a software.
44. How does Exadata improve database consolidation efforts?
Ans:
Exadata improves the database consolidation by providing a highly scalable and efficient platform for running the multiple databases on a single system.
45. What is Exadata’s Storage Quality of Service (QoS) feature?
Ans:
Storage Quality of Service (QoS) in Exadata allows the administrators to define I/O performance objectives for different database workloads.
46. Which Exadata feature is used to get rid of disc input/output?
Ans:
Several features of Oracle Exadata work together to minimize disk I/O and improve the overall system performance. One of key features designed to eliminate unnecessary disk I/O is a Smart Scan.
47. What is the capacity of Infiniband port?
Ans:
The capacity of InfiniBand port is typically measured in the terms of data transfer rate, which is expressed in gigabits per second (Gbps) or terabits per second (Tbps) for high-speed InfiniBand technologies.
48. What is the difference between high capacity and high-performance disk?
Ans:
- High capacity disk comes with the more storage space and less rpm (7.5k)
- High-Performance disk comes with the less storage and high rpm (15k)
49. When should one execute Exacheck?
Ans:
Before and after any configuration change in the Database Machine. Exacheck is the diagnostic tool provided by Oracle specifically for the Oracle Exadata Database Machine.
50. What is a grid disk?
Ans:
Grid Disks are created on top of the Cell Disks and are presented to the Oracle ASM as ASM disks.
51. Which network is used for RAC inter-connectivity?
Ans:
Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) configurations, high-speed InfiniBand networking technology is used for inter-connectivity.
52. What are steps to create DBFS?
Ans:
- Create a Directory
- Create Tablespace on database which going to use for DBFS
- Create user for DBFS
- Grant required privileges to be created user
- Now connect to the database with created user
53. List some techniques for converting high-endian OS architecture to low-endian OS architecture.
Ans:
- Golden Gate
- Transportable Tablespace
- Incremental Transportable Tablespace
- Data Pump
54. What is a Cell and Grid Disk?
Ans:
The logical parts of physical Exadata storage are Cell and Grid Disc. A collection of disc drives assembled to store user data is called a cell, or Exadata Storage server cell.
55. What is Smart Scan?
Ans:
It is the feature of the Exadata Software which enhances database performance many times over. It processes the queries in an intelligent way, retrieving specific rows rather than a complete block
56. What are Parallelism instance parameters used in Exadata?
Ans:
Parallelism is the critical aspect of database performance optimization, especially for data-intensive workloads
57. What operating systems does Exadata support?
Ans:
Oracle Exadata Database Machine supports the specific versions of Oracle Linux and Oracle Solaris operating systems
Oracle Linux: Exadata supports the Oracle Linux 5, 6, and 7. Oracle recommends using Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel (UEK) for Oracle Linux installations on Exadata systems.
Oracle Solaris: Exadata supports the Oracle Solaris 11 on SPARC systems.
58. Which statistic used to check flash hit ration on database level?
Ans:
To check flash hit ratio at database level, can use the Oracle Database performance view V$SYSSTAT.
59. On which Exadata disc group are OCR files stored?
Ans:
Oracle Clusterware uses Automatic Storage Management (ASM) features to manage Oracle Cluster Registry (OCR) and Voting Disk (CRSVD) files.
60. What is Oracle Exadata used for?
Ans:
Oracle Exadata Database@Azure lets an organizations run workloads where they choose, modernize and innovate with the Oracle and Azure services, and simplify cloud purchasing and management using the Oracle
61. What is the difference between an Exadata X3-2 machine and Exadata X3-8 machine?
Ans:
Exadata X3-2: The X3-2 model is the smaller configuration designed for a mid-sized workload.
Exadata X3-8: The X3-8 model is larger, more scalable configuration intended for high-end and enterprise-level workloads.
62. What is the difference between DBRM and IORM?
Ans:
DBRM, or Database Resource Manager, is a feature within Oracle Database that allows it to manage database resources, including the CPU and parallel execution servers.
63. What are Advantages and disadvantages of rolling and non-rolling patching on Exadata Database Machine?
Ans:
Rolling Advantages:No downtime required
Disadvantages:It takes a more time to apply bundle patches
Non-Rolling Advantages:Less time required to do patching
Disadvantages:Downtime required while applying the bundle patch.
64. Which ASM parameters are used for Auto disk management in Exadata?
Ans:
_AUTO_MANAGE_EXADATA_DISKS — It control the auto disk management feature _AUTO_MANAGE_NUM_TRIES — It controls the maximum number of attempt to perform automatic operation
65. How to enable Flashcache compression?
Ans:
Enabling Flash Cache Compression on Oracle Exadata systems involves the configuring Hybrid Columnar Compression (HCC) for a specific database object.
66. How many Exadata Database Machine X4-8 Exadata Storage Server Nodes are there in the machine?
Ans:
The Oracle Exadata Database Machine X4-8 includes the 14 Exadata Storage Server Nodes.
67. What is the use case of Exadata?
Ans:
Exadata uses the scale-out design with unique optimizations that include a persistent memory, SQL query offload, and built-in resource management.
68. Why is Exadata better?
Ans:
Oracle Exadata delivers greater database and application performance with less hardware—and fewer licenses.
69. What are Key Software Features?
Ans:
- Smart Scan
- Smart Flash Cache
- Storage Index
- Exadata Hybrid Columnar Compression (EHCC)
70. What is IORM?
Ans:
IORM stands for I/O Resource Manager. It manages I/O demand based on the configuration, with the amount of resources available. It ensures that none of I/O cells become oversubscribed with the I/O requests. This is achieved by managing incoming requests at consumer group level.
71. How do Test performance of Exadata?
Ans:
Can use the “calibrate” commands at cellcli command line. Testing the performance of Oracle Exadata system involves the various methods and tools to evaluate its capabilities under the different workloads.
72. What types of operations does Exadata “offload”?
Ans:
Several tasks are transferred from a database host to mobile servers, including:
- Predicate filtering
- Column project filtering
- Join processing
- Backups
73. What is the purpose of the spine switch?
Ans:
The spine switch plays the critical role in the overall networking architecture. The purpose of a spine switch is to provide high-speed, non-blocking connectivity between leaf switches.
74. How do you stop Exadata?
Ans:
Power Off Sequence for an Exadata Stack First stop the oracle cluster with the below command. #$GRID_HOME/grid/bin/crsctl stop cluster.
75. What are prerequisites to configure ASR?
Ans:
- Access to the My Oracle Support
- Internet connectivity using the HTTPS
- Network connectivity from a ASR server to Exadata components
76. Which MOS ID should refer for the latest patch update?
Ans:
When log in to MOS, can search for specific patches, patch sets, and critical patch updates using Patch Search feature. can also find information about patch availability, known issues, and patch installation instructions.
77. Which tool is used to generate initial configuration files based on customer’s data?
Ans:
The ExaChk utility is commonly used to generate initial configuration files based on the customer’s data. ExaChk is a diagnostic tool provided by Oracle specifically for Exadata systems.
78. Which are all networks available in Exadata?
Ans:
- Infiniband Network
- ILOM and Management Network
- Client/Public Network
79. What is client or public network in exadata?
Ans:
- The connection between the database and the application is established via a client or public network.
- The client network is a network that connects the Exadata database servers (compute nodes) to external clients, applications, and the other database servers outside Exadata machines.
80. What are steps involved for initial Exadata configuration?
Ans:
- Initial network preparation
- Configure an Exadata servers
- Configure an Exadata software
- Configure a database hosts to use Exadata
- Configure the ASM and database instances
- Configure the ASM disk group for Exadat
81. What is the iDB protocol?
Ans:
iDB stands for an intelligent database protocol. It is the network based protocol which is responsible to communicate between the storage cell and database server.
82. What is LIBCELL?
Ans:
Libcell stands for a Library Cell which is linked with the Oracle kernel. It allows the oracle kernel to talk with the storage server by network instead of operating system reads and writes.
83. What is the primary goal of the storage index?
Ans:
The exclusive feature of the Exadata Database Machine is storage indexes, whose main objective is to minimize the amount of input/output needed to process input/output requests for Exadata Smart Scan.
84. What is smart scan offloading?
Ans:
Offloading and Smart Scan are the two terms that are used somewhat interchangeably. Exadata Smart.Scan offloads the processing of queries from a database server to the storage server.
85. What is check Ip and what use of it?
Ans:
An Exadata will use the IP address and hostname contained in the OS level script Check Ip during the configuration phase.
86. What is a smart flash log?
Ans:
Smart Flash Log (SFL) is the feature introduced in Oracle Exadata Storage Servers to improve write performance of database redo log operations.
87. Which parameter is used to enable and disable smart scan?
Ans:
To enable or disable Smart Scan on Oracle Exadata, can use the CELL_OFFLOAD_PROCESSING parameter.
88. What is offload block filtering?
Ans:
Only the blocks needed for backup are sent to the database by the Exadata storage server, which filters out any blocks that are not needed for the incremental backup that is currently running.
89. What are types of EHCC?
Ans:
- Query Low
- Query Low
- Query High
- Archive High
90. What are the major steps involved for cell server patching?
Ans:
Check and note down an existing configuration of cell
- Clean up the any previous patchmgr utility
- Verify that cells meet prerequisite checks
- Patch cell server using the patchmgr
- Validation updated cell






