
What Is Big Data?
Big Data is a term used for a collection of data sets that are large and complex, which is difficult to store and process using available database management tools or traditional data processing applications. The challenge includes capturing, curating, storing, searching, sharing, transferring, analyzing and visualization of this data.
Role Of Big Data:
The primary goal of big data analytics is to help companies make more informed business decisions by enabling data scientists, predictive modelers, and other analytics professionals to analyze large volumes of transactional data, as well as other forms of data that may be untapped by more conventional Business Intelligence(BI) programs. That could include web server logs and Internet click-stream data, social media content and social network activity reports, text from customer emails and survey responses, mobile phone call detail records and machine data captured by sensors and connected to the Internet of Things.
Big Data Applications:

Big data has found many applications in various fields today. The major fields where big data is being used are as follows.
Sports: Most elite sports have now embraced data analytics. In Premier League football games, cameras installed around the stadiums track the movement of every player with the help of pattern recognition software generating over 25 data points per player every second. What more? NFL players have installed sensors on their shoulder pads to gather intelligent insights on their performance using data mining. It was analytics which helped British rowers row their way to the Olympic gold.
Hospitality: Hotel and the luxury industry have turned to advanced analytics solutions to understand the secret behind customer satisfaction initiatives. Yield management in the hotel industry is one common use of analytics which is an important means to tackle the recurring peaks in demand throughout the year in consideration with other factors which include weather and local events, that can influence the number and nationalities of guests checking in.Big Data in Healthcare
Big Data and healthcare are an ideal match. It complements the healthcare industry better than anything ever will. The amount of data the healthcare industry has to deal with is unimaginable.Gone are the days when healthcare practitioners were incapable of harnessing this data. From finding a cure to cancer to detecting Ebola and much more, Big Data has got it all under its belt and researchers have seen some life-saving outcomes through it.
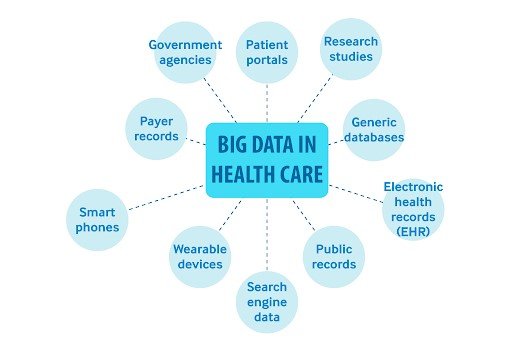
Big Data and analytics have given them the license to build more personalized medications. Data analysts are harnessing this data to develop more and more effective treatments. Identifying unusual patterns of certain medicines to discover ways for developing more economical solutions is a common practice these days.
Government And Public Sector Services : Analytics, data science, and big data have helped a number of cities to pilot the smart cities initiative where data collection, analytics and the IoT combine to create joined-up public services and utilities spanning the entire city. For example, a sensor network has been rolled out across all 80 of the council’s neighborhood recycling centres to help streamline collection services, so wagons can prioritize the fullest recycling centres and skip those with almost nothing in them.
Big data analytics has proven to be very useful in the government sector. Big data analysis played a large role in Barack Obama’s successful 2012 re-election campaign. Also most recently, Big data analysis was majorly responsible for the BJP and its allies to win a highly successful Indian General Election 2014. The Indian Government utilizes numerous techniques to ascertain how the Indian electorate is responding to government action, as well as ideas for policy augmentation.
Energy : The costs of extracting oil and gas are rising, and the turbulent state of international politics adds to the difficulties of exploration and drilling for new reserves. The energy industry Royal Dutch Shell, for example, has been developing the “data-driven oilfield” in an attempt to bring down the cost of drilling for oil.And on a smaller but no less important scale, data and the Internet of Things (IoT) is disrupting the way we use energy in our homes. The rise of “smart homes” includes technology like Google’s Nest thermostat, which helps make homes more comfortable and cut down on energy wastage.
Agriculture And Farming : The power of AI has embraced even traditional industries like Agriculture and Farming. Big data practices have been adopted by the US agricultural manufacturer John Deere which has launched several data-enabled services that have led farmers to benefit from the real-time monitoring of data collected from its thousands of users worldwide.
Education : Education sector generates massive data through courseware and learning methodologies. Important insights can identify better teaching strategies, highlight areas where students may not be learning efficiently, and transform how the education is delivered. Increasingly educational establishments have been putting data into use for everything from planning school bus routes to improving classroom cleanliness.
Banking And Securities : Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) has deployed big data to track and monitor the movements in the financial market. Big data and analytics with network analytics and natural language processors is used by the stock exchanges to catch illegal trade practices in the stock market.
Retail traders, Big banks, hedge funds and other so-called ‘big boys’ in the financial markets use big data for trade analytics used in high-frequency trading, pre-trade decision-support analytics, sentiment measurement, predictive analytics, etc. This industry also heavily relies on big data for risk analytics including; anti-money laundering, demand enterprise risk management, “Know Your Customer”, and fraud mitigation.
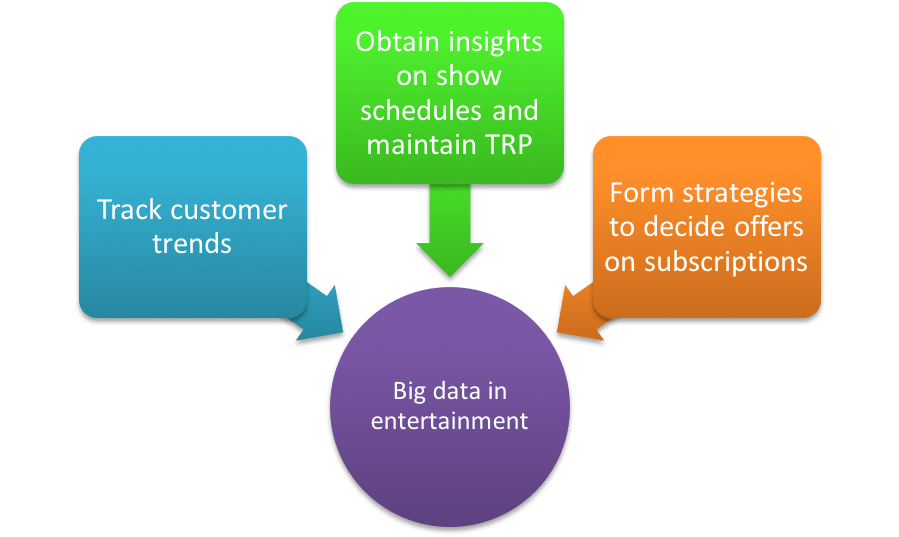
Entertainment, Communications And The Media : The on-demand music service, Spotify uses Hadoop big data analytics to collate data from its millions of users across the world. This data is used and analyzed to give customized music recommendations to its individual users. Over the top media, services have relied big on big data to offer customized content offerings to its users. An important move in the growing competitive market.
Retail And Wholesale Trade : Big data has in a big way impacted the traditional brick and mortar retailers and wholesalers to current day e-commerce traders. The retail and whole industry has gathered a lot of data over time which is derived from POS scanners, RFID, customer loyalty cards, store inventory, local demographics, etc. Big data is applicable to the retail and wholesale industry to mitigate fraud, offer customized products to the end user thereby improving the user experience.
Transportation : Big data analytics finds huge application to the transportation industry. Governments of different countries use big data to control the traffic, optimize route planning and intelligent transport systems and congestion management.Moreover, the private sector uses big data in revenue management, technological enhancements, logistics and to gain a competitive advantage.
Big data is improving user experiences, and the massive adoption change has just begun.
Social Media Analytics : The advent of social media has led to an outburst of big data. Various solutions have been built in order to analyze social media activity like IBM’s Cognos Consumer Insights, a point solution running on IBM’s BigInsights Big Data platform, can make sense of the chatter. Social media can provide valuable real-time insights into how the market is responding to products and campaigns. With the help of these insights, the companies can adjust their pricing, promotion, and campaign placements accordingly. Before utilizing the big data there needs to be some preprocessing to be done on the big data in order to derive some intelligent and valuable results. Thus to know the consumer mindset the application of intelligent decisions derived from big data is necessary.
Technology : The technological applications of big data comprise of the following companies which deal with huge amounts of data every day and put them to use for business decisions as well. For example, eBay.com uses two data warehouses at 7.5 petabytes and 40PB as well as a 40PB Hadoop cluster for search, consumer recommendations, and merchandising. Inside eBay‟s 90PB data warehouse. Amazon.com handles millions of back-end operations every day, as well as queries from more than half a million third-party sellers. The core technology that keeps Amazon running is Linux-based and as of 2005, they had the world’s three largest Linux databases, with capacities of 7.8 TB, 18.5 TB, and 24.7 TB. Facebook handles 50 billion photos from its user base. Windermere Real Estate uses anonymous GPS signals from nearly 100 million drivers to help new home buyers determine their typical drive times to and from work throughout various times of the day.
Fraud Detection : For businesses whose operations involve any type of claims or transaction processing, fraud detection is one of the most compelling Big Data application examples. Historically, fraud detection on the fly has proven an elusive goal. In most cases, fraud is discovered long after the fact, at which point the damage has been done and all that’s left is to minimize the harm and adjust policies to prevent it from happening again. Big Data platforms that can analyze claims and transactions in real time, identifying large-scale patterns across many transactions or detecting anomalous behavior from an individual user, can change the fraud detection game.
Challenges With Big Data
Let me tell you few challenges which come along with Big Data:
- Data Quality : The problem here is the 4th V i.e. Veracity. The data here is very messy, inconsistent and incomplete. Dirty data cost $600 billion to the companies every year in the United States.
- Discovery : Finding insights on Big Data is like finding a needle in a haystack. Analyzing petabytes of data using extremely powerful algorithms to find patterns and insights are very difficult.
- Storage : The more data an organization has, the more complex the problems of managing it can become. The question that arises here is “Where to store it?”. We need a storage system which can easily scale up or down on-demand.
- Analytics : In the case of Big Data, most of the time we are unaware of the kind of data we are dealing with, so analyzing that data is even more difficult.
- Security : Since the data is huge in size, keeping it secure is another challenge. It includes user authentication, restricting access based on a user, recording data access histories, proper use of data encryption etc.
- Lack of Talent : There are a lot of Big Data projects in major organizations, but a sophisticated team of developers, data scientists and analysts who also have sufficient amount of domain knowledge is still a challenge.





