- Introduction to SAP security
- About SAP security
- History
- Methods of SAP security
- Policies of SAP security
- Importance of SAP security
- Tools of SAP security
- Functions of SAP security
- Features of SAP security
- Scope of SAP security
- Uses of SAP security
- Conclusion
- Database users are not properly maintained and security measures are not taken.
- Single sign- on is not properly configured and maintained in the SAP environment. To overcome all the above reasons, you need to define a security policy SAP environment. You need to define security parameters and password policies.
- If an unauthorized user can access SAP system under a known authorized user and can Authentication mechanism defines the way you access your SAP system.
- Most common method of authentication in a SAP system is by using the username and The SAP administrator creates a login user ID. There is a need for a secure authentication mechanism with username and password Defines a password policy that prevents users from setting passwords that are easily predictable.
- SAP provides various default parameters that need to be set to define password policies, password lengths, password complexity, default password changes, and more. SAP system user management tool The SAP NetWeaver system provides a variety of user management tools that you can use Some of the most common user management tools are: ABAP application server user management (transaction code: SU01). You can update users in ABAP using transaction code SU01 in User Management.
- User management engine UME You can open the UME management console using the SAP NetWeaver Administrator option. Password policies are defined as a set of instructions that users must follow to improve. organizations, password policy is shared as a part of security awareness training and it is mandatory for users to maintain the policy for security of critical systems and information Using password policy in a SAP system, an administrator can setup system users to deploy
- To change the parameter value, run transaction RZ10 and select the profile as shown. Multiple application servers: Use the DEFAULT profile.
- Information security is our top priority For your business. With cyber attackers More sophisticated We SAP who are relentlessly working on their approach Strive to continually innovate software to ensure Data is always safe – Both on-premises and in the cloud. we Prioritize safety so that you can stay Focus on running your business, Customer relationship management Effective and secure with SAP® solutions Your data It is completely protected.
- Why SAP software must be secure SAP software stores and processes a wide range Of highly confidential and valuable information such as Personal data, prices, product processes. To protect this data and ensure it is guaranteed Information cannot be intercepted or tampered with. We recommend that you follow security requirements. In this guide Measures and methods to be implemented It works, maintains, and works properly and safely.
- login / min_password_diff
- login / min_password_digits
- login / min_password_letters
- login / min_password_specials
- login / min_password_lowercase
- login / min_password_uppercase
- login / password_compliance_to_current_policy
- Security compliance
- Safe operation
- Safe setup
- security code
- Infrastructure Security
- Lack of established patching process
- Unencrypted communication between SAP solution
- Poorly protected interface
- There is no established backup process
- There is no urgent process
- Missing or incorrect security configuration From the system Infrastructure security You need to start by protecting your network Database and front end settings.
- They are Protect key components when in use Started implementation of security measures Your system. Network security Network security includes management Network topology, network isolation, Network service and protocol restrictions, Domain concept development. your Network security should match our security Requirements.
- You may need to evolve to do this Process and configure system settings. Given the ever-increasing number of mobiles Devices and their Internet accessibility It is recommended to configure the network to enable it Internal network segments within an infrastructure internal zone similar to Scheme require very different levels of approval to reflect different levels of access.
- Security between management network and servers Network and office network. Detail is It is described in the white paper “Secure Configuration of SAP NetWeaver® Application Servers”. Use ABAP®. ” You need to set up the backend system, Individual internal network segments With the upstream demilitarized zone (DMZ) Internet in the “inner zone”.
- Inside the inner zone
- Between the three layers of the DMZ: security, Presentation and integration
- Internet, DMZ, and internal zone Only important connections need to be able to pass Through these firewalls. Attempts should be blocked Access the database and SAP HANA® Studio.
- You also need to authenticate and verify yourself All access via the internet in the DMZ Before being transferred inside With a network using a web application firewall Identity provider authentication.
- Configuration, settings Firewall between network segments according to.
- Administrators also need to be restricted Access and make sure it is easy to use Authentication and encrypted connection of Internal encryption is generally recommended Communication via Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Network communication (SNC).
- This is an update Software testing, running antivirus scans, Verify the integrity of important system files And composition.
- In general, you need to be able to track all administrator access to your operating system.
- Use only Personalized account.
- If you switch to an admin account, you need to be transparent Log the activity performed.
- Due to restrictions Using databases, proprietary database applications, and database-specific features B.
- To manage privilege management, you can: Helps ensure optimal database security.
- Make sure you can save the data to the database Access is only done through SAP tools or by implementing special security measures.
- Set up encryption for authentication and Communication at the database level By driver or appropriate mechanism At the operating system or application level
- Installation of individually protected network segments For databases and application servers
- Set up a dedicated security mechanism Depends on different details Databases and database providers ( SAP HANA or SAP MaxDB® database Front-end security Front-end security settings must be in place Made for both client workstations and mobile devices Device.
- Corporate mobile phone security settings Device
- Definition of secure software processes Distribution, management, and configuration These endpoints
- Implementation of secure communication Between the endpoint and the backend system
- Encryption of company data on the device
- Mobile password complexity rules Equipment equivalent to that for the workplace computer
- Ability to centrally delete sensitive data Mobile devices and mobile devices Management Solution Security Code Network, database,
- Failure of an individual server
- Failure of an individual database
- Compromise of an SAP solution
- Failure of the transport system (ABAP) or the software distribution (Java)
- Outage of network connections
- Outage of an entire data center When planning your emergency procedure, you must be careful to:
- Define the processes and people responsible
- Conduct regular emergency drills and adjust the processes accordingly
- Create and modify emergency users
- Collect required logs and data
- Define the rules and triggers for identification and classification of incidents
- Define “incident response” processes – that is, the occurrence of a vulnerability in the respective system environment – including the implementation of corrections and recovery measures
- Prepare technical and nontechnical (for example, legal) followon activities and improvements A material aspect of emergency planning is the data backup of the SAP software systems.
- Time of backup of components and data
- Authorizations required for this purpose
- Authorizations required for data recovery
- Access authorizations for archived backup data
- Physical storage of backup data, which should be separated from production data When conducting your risk assessment, remember to also check whether the availability requirements for individual application areas, business processes, or organizational areas are high enough to warrant making a backup system available.
- SAP Security Optimization Services Media Library
- Security Baseline Template
- Secure Operations Map
- Security White Papers
- SAP Security Optimization
- Security guides for SAP Solutions
- SAP HANA Security Checklists and Recommendations
- SAP EarlyWatch Alert
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance Management No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or for any purpose without the express permission of SAP SE or an SAP affi liate company. The information contained herein may be changed without prior notice. Some software products marketed by SAP SE and its distributors contain proprietary software components of other software vendors. Country product specifications may vary.
- These materials are provided by SAP SE or SAP subsidiaries for informational purposes only. SAP or its affiliates shall not be liable without any representation or warranty of any kind. About mistakes or omissions in the materials. SAP or SAP Affiliate’s Only Guarantee Company products and services are as stated in the express warranty.
- With such products and services. What is described here should not be construed as constructive. Additional warranty. In particular, SAP SE or its affiliates are not obligated to do business.
- Develop or release features described or featured in this document or related presentations. It is mentioned in it. This document or related presentations and presentations of SAP SE or its affiliates With corporate strategy and possible future development, product and / or platform direction All features are subject to change and are subject to change by SAP SE or its affiliates. Anytime without explaining the reason.
- The information in this document is not a commitment. A promise or legal obligation to provide material, code, or functionality. All positive Statements carry various risks and uncertainties and actual results may vary. Substantially from expectations. Readers should be careful not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements and should not rely on them when making purchasing decisions.
- SAP has made great strides in recent years. Providing functions It has been enhanced with the implementation of new technologies, applications, and systems. An important step in this jump is the movement from the previous jump New delimiter architecture based on the programming language ABAP / 4 SAP NetWeaver architecture with components such as SAP Enterprise Portal and SAP Exchange infrastructure, J2EE, and mobile infrastructure. on the one hand, New technologies and enhancements increase the potential for integration Partner companies and customers.
- On the other hand, you need to be careful Reduce the risks associated with new development. Financial collapse of large companies like Enron and management activities Accounting office at the beginning of the new millennium In particular, the trust of investors and shareholders in listed companies has been shaken.
- These developments have led to new legislation and strengthened state control. Standards such as the US Servens Oxley Act on Listed Securities Companies and Basel II for the financial industry. The purpose of such a law is Establishing stronger management and improved security measures in the enterprise, An organization that protects investors, businesses, employees and consumers. 1 The way to enforce state control legislation, including fines for responsible managers, is to use consistent protection of IT-supported processes. Commercial and financial data extracted from IT security measures.
- In addition, many existing organizations implement SAP. Products need to keep up with measures to establish effective approval and secure and optimized management processes. Because there is virtually no Companies with systematic standards for approval and role structure Use almost an infinite variety of solutions for everything related to technical IT security. Approval managers are a bit overwhelmed, but the process is often not Meet current requirements for secure user management and management. This book is based on international consulting and educational experience Close collaboration between the author and SAP and partners in this area Of risk and security. Provides an overview of SAP NetWeaver security and the components of a secure SAP implementation. Product.
- The author does not claim to have written everything about security You need to know, but they follow consulting methodologies Explanation of concepts, problems, procedures, and examples. Information in this This book will be useful to company management, accountants and in-house staff. Accountant, Sarbanes Oxley Team, Information Owner, Data Protection Officer, Authorization administrator, SAP implementation project leader, security Security officers and employees, service providers and consultants. Readers will be provided with a beginner’s guide to risk assessment and creation Control options, design security measures, and the appropriate process for setting them Supports practices and processes.
- Like SAP Web AS, the SAP Enterprise Portal (SAP EP) plays an important role in SAP. NetWeaver product strategy. SAP EP makes important applications and information (such as documents) available to individual employees through a central access point. In internet scenarios, you can also transfer your business partner to another partner Corporate internet applications through this central access point. To get them started Employees and business partners only need a web browser to access the application SAPEP. You no longer have to launch each application individually.
- Use SAP GUI. SAP EP controls all access to these applications. That is Called human integration SAP EP is based on SAP Web ASJ2EE. This is the SAP application server that forms the SAP Enterprise Portal with other knowledge management software components, Union Server and Connector Framework. Architecture. The SAPEP architecture is shown in Figure 19.2. Its main components are: portal server
- The portal server contains the portal runtime, which is the portal runtime environment. (PRT), including application information partially returned by With backend applications (such as XML) or other portal content It is appropriately prepared for the front end of the page (web browser). builder. A variety of content is provided to users in iView. iView The smallest unit for splitting and structuring a portal page. Portal services include services for managing iView content. User management through the user management engine (definition of permissions and roles) (UME) is also important. Another service manages the connection Individual iViews to backend applications via the connector framework.
- For other important services, Overall portal content, caching services, portal content processing services, URL generation services (eg via SAP Internet transactions) Server) and web services. The portal can be accessed via the latter Internet service. You can also access web services. Portal content A directory (PCD) is content, that is, all objects (eg, all objects). iView, roles, content, applications, backend applications).
- PCD sets up the portal Define roles and access to individual objects, and services You can call it, i.e. H. Portal content management using management tools (To create iViews, layouts, documents, etc.) and search and classification engine TREX. TREX is an SAP search engine that indexes on. It is the entire portal content and can be used to search for keywords or logically related search terms in the portal content. Users can save the documents and information found in the portal for personal knowledge management.
- These programming interfaces are: User API The portal application can call the authentication service using the user API. It also validates existing users and their approvals. User account API The User Account API allows you to create new users in your portal application Especially to maintain master data and assign portal roles.
- Therefore, the User Account API is implemented for management services. Unlike the user API, it is not used at runtime. Group API You can use the Groups API to create group definitions. Also, at run time You can inquire whether a user belongs to a particular group. Role API The Role API is used to manage the role of the portal. Can also be used to assign The role of the portal to the user. Persistence Manager regulates access to user data through programming The above interface. Persistence Manager takes on the task of managing the available storage systems. Portal database, You can implement an external LDAP directory or SAP Web ASABAP.
- You can use the following formats for your database: Oracle 9.2 or later Microsoft SQL Server 2000 or later IBM DB2 / UDP The possible LDAP directories are: NovelleDirectory Sun ONE Directory Server Microsoft Active Directory Server Siemens DirX You need the following SAP system: SAPWebAS 6.20 or later Persistence Manager can manage multiple LDAP directories at the same time. she Therefore, users can be distributed across different storage systems.
- Connection to UME. This is especially important when implementing SAPEP. Internet scenario. For example, you can make external users persistent in the portal database and internal users in the LDAP directory. that is It is also possible to do this classification according to user attributes. for example, You can save the portal role assignments to users in the portal database. The corresponding master data can be stored in LDAP directory
Introduction to SAP security :-
SAP Security is required to protect SAP Systems and Critical Information from Communication Security and protecting standard users and other best practices that should be followed in maintaining your SAP Environment.
About SAP security :-
In a SAP Distributed Environment, there is always a need that you protect your critical Provisioning shouldn`t allow unauthorized access to system and there is a need to maintain and review the profile policies and system security policies in your SAP environment. Understand the basics of security terminology for Windows and UNIX environments. In a distributed SAP environment, you always need to protect your critical data Information and data from unauthorized access.
History :-
Maintain and review SAP profile and system security policies To make your system safe, you need to be familiar with user access profiles. Password policies, data encryption, and approval methods used by the system. The default superuser is well protected and requires user profile parameters and values It can be important to access information in a distributed environment Information and data are leaked due to unauthorized access, ensuring system security
Either – lack of password policy, default superuser is not properly maintained, or The main reasons for access violations in the SAP system are:
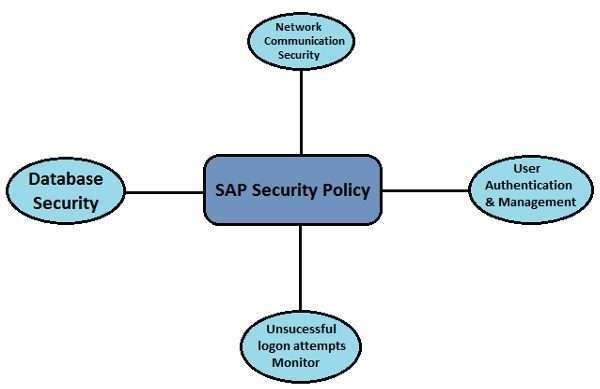
Methods of SAP security :-
Policies of SAP security :-
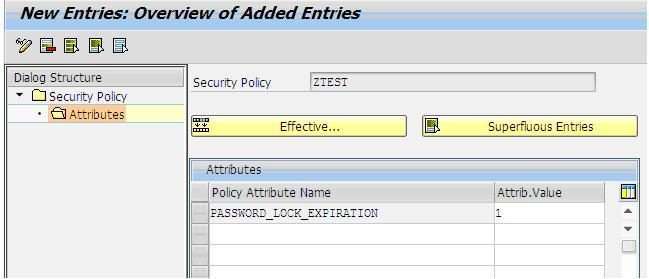
The following password policies are commonly used in a SAP System: This allows the users to change the initial password immediately when used for the first The value can be changed using profile parameters and the maximum allowed length is 8 This policy allows users to change their password almost once a day, The administrator can reset the user`s password as many times as needed.
There are various profile parameters that can be defined for users of the SAP system Management and password policy. In the SAP system, you can view the document for each profile parameter by performing the following steps: The SAP system has various password parameters.
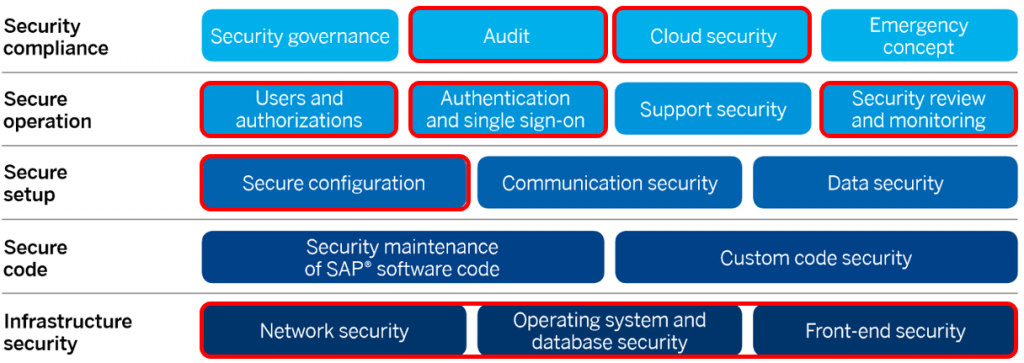
Configure the SAP solution. Safety recommendations Figure 1 shows a secure operational map. Form the basis of our security structure Recommendations. Consists of 16 safety related Software system topics in five areas:
The most common problems that can occur Encountered in our security implementation The recommendations are:
Importance of SAP security :-
You should too Set up firewalls in all of the following locations:
Exceptionally accessible SAP HANA database via terminal server.
Database security needs to be implemented Requirements for all SAP solutions And according to your system provider’s Recommendations.
Tools of SAP security ;-
Because the use of Personal mobile devices, it’s important to be clear Define different security strategies Between corporate and personal devices Mobile device. Bring your device or BYOD. Is becoming more and more important to you accompaniment. Front-end security for mobile devices include:
The front end should start an ongoing process to ensure that the code is always complete Safe and up to date. SAP software code Our solution needs to be reviewed and updated Regular intervals. Installation is recommended Update the latest support package regularly, at least once 1 year. We publish the latest security fixes and security advisories on the second Tuesday of every month. Recommendations as security advice as part of “SAP Security Patch Day” Attention should be paid to evaluation and implementation Regular. Don’t just implement Modify or replace the actual program Each code, but needs to be activated Implementation of configuration recommendations Contains safety precautions. recommendation Establish a dedicated process to implement these updates. In addition, we recommend a secure setup. And continuous maintenance, part of you Customer-defined SAP solution landscape using SAP Solution Manager and System Recommendations and Configuration Verification function. Summarize Check Plag Grammar
Ideally, these measures should be integrated What you need to do in a corporate audit plan Follow your risk management strategy Update at least once a year. When planning Specific test objectives to consider Company risk management, regulation, And legal requirements. Test management Various technical information should be included. Depending on their skills Specifications, our solution offers a variety of possibilities
Functions of SAP security :-
For monitoring and recording safety-related data event. Emergency and backup process To be able to do this, you need to prepare a disaster recovery and backup process. Use immediately in an emergency. It should address the following emergency scenarios:
Clear responsibilities and process flows for endtoend data backup and recovery must be defined in a data backup strategy. When creating this strategy, consider the following:
From here you You will be in a strong position to create your own organization’s action plan and security roadmap. It is also recommended to use the existing one External offers including developed guidelines, working groups and interest groups Through local user groups. Finally, we invite you to actively raise open security questions with us by sending us a message any time.
Features of SAP security :-
Recommendations for SAP solutions Our Compliance and Security Solutions For more information on the solutions that we offer in the area of compliance and security, please refer to the following sources:
Security Software
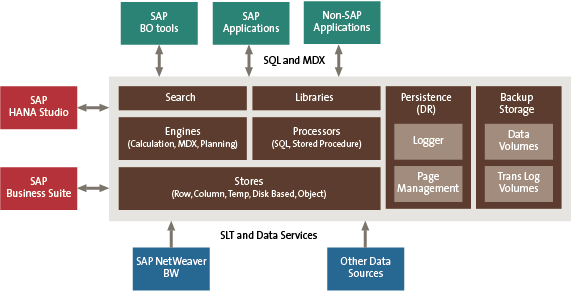
Scope of SAP security :-
Uses of SAP security :-