
- Proficiency in Core Python
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts
- Working with Python Libraries and Frameworks
- Understanding of Web Development (Flask/Django)
- Database Knowledge (SQL and NoSQL)
- Experience with APIs and RESTful Services
- Version Control Systems (e.g., Git)
- Conclusion
Proficiency in Core Python
A strong foundation in core Python Developer Skills is essential for any developer. This includes a deep understanding of Python’s syntax, semantics, and programming constructs such as data types (integers, floats, strings, booleans), variables, control structures (if-else, loops), functions, exception handling, and file operations. Developers should also be comfortable with Pythonic conventions and best practices, including list comprehensions, lambda functions, and context managers (with statement). Mastering these fundamentals allows a developer to write efficient, readable, and error-free code that aligns with Python Training philosophy of simplicity and clarity. Understanding how Python handles memory management, scoping rules (LEGB – Local, Enclosing, Global, Built-in), and dynamic typing also helps developers write optimized code and avoid common bugs. Familiarity with the Python standard library, which provides built-in modules for file I/O, math, date/time operations, and regular expressions, is indispensable. Proficiency in Core Python is fundamental for any Python developer. It involves a solid understanding of Python’s syntax, data types, control structures (like loops and conditionals), functions, and error handling. A proficient developer can write clean, efficient, and readable code using Python’s built-in features. Mastery of core concepts such as lists, dictionaries, sets, and tuples, along with file handling and modules, is essential. This foundation enables developers to build complex applications, automate tasks, and work effectively with libraries and frameworks. Strong Core Python skills also facilitate learning advanced topics and adapting to new tools in the Python ecosystem.
Do You Want to Learn More About Python? Get Info From Our Python Online Training Today!
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts
Object-oriented programming (OOP) in Python allows developers to write modular and reusable code using classes and objects. A proficient Python developer must have a firm grasp of key OOP concepts like:
- Encapsulation: Binding data and methods that operate on that data within a single unit (class).
- Inheritance: Creating new classes that inherit attributes and methods from existing classes Python Developer Skills .
- Polymorphism: Using a unified interface to operate on different data types or class hierarchies.
- Abstraction: Hiding the internal implementation details and exposing only the necessary parts.
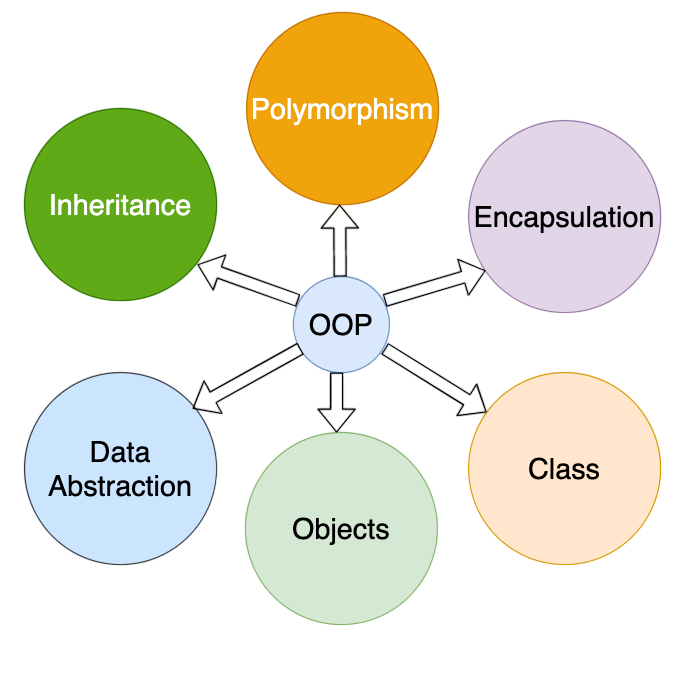
OOP enables code reusability, better organization, and easier debugging. Developers should be able to design class hierarchies, override methods using inheritance, and use access modifiers (public, protected, and private conventions) effectively. Additionally, understanding the use of super() and method resolution order (MRO) helps in managing complex inheritance structures.
Working with Python Libraries and Frameworks
- Familiarity with popular Python libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Requests
- Ability to use frameworks such as Flask and Django for web development
- Understanding how to install and manage libraries using pip and virtual environments
- Experience integrating third-party libraries to extend application functionality Building a Career as a Python Developer
- Knowledge of how to read and utilize library documentation effectively
- Ability to troubleshoot and resolve compatibility or dependency issues
- Using frameworks to build scalable, maintainable, and secure applications
- Keeping up-to-date with new libraries and tools to enhance productivity
Understanding of Web Development (Flask/Django)
- Knowledge of web fundamentals: HTTP, request/response cycle, and REST principles
- Experience building web applications using Flask, a lightweight and flexible Python framework
- Familiarity with Django, a full-featured Python framework for rapid development
- Ability to create and manage routes, Best Python IDEs and Code Editors views, and templates in both Flask and Django
- Understanding of database integration and ORM (SQLAlchemy for Flask, Django ORM)
- Implementing user authentication, authorization, and session management
- Working with forms, validation, and handling user input securely
- Deploying Flask/Django applications to production environments
Want to Pursue a Python Master’s Degree? Enroll For Python Master Program Training Course Today!
Database Knowledge (SQL and NoSQL)
SQL Database Knowledge:
- Understanding of relational database concepts and structures
- Proficiency in writing SQL queries for data retrieval, insertion, updating, Python Training and deletion
- Experience with popular SQL databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQLite
- Knowledge of database normalization, indexing, and transactions
- Ability to design and optimize database schemas for performance and scalability
- Familiarity with NoSQL database types: document, key-value, column-family, and graph databases
- Experience working with databases like MongoDB, Redis, or Cassandra
- Understanding of schema-less data models and flexible data storage
- Ability to choose between SQL and NoSQL based on application needs
- Knowledge of data replication, sharding, and eventual consistency concepts
NoSQL Database Knowledge:
Experience with APIs and RESTful Services
Experience with APIs and RESTful services is essential for Python Developer Skills building modern, interconnected applications. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) allow different software systems to communicate and share data seamlessly, making them a cornerstone of web development, mobile apps, and cloud services. RESTful services, based on Representational State Transfer principles, provide a standardized way to design APIs that are scalable, stateless, and easy to maintain. A skilled Python developer understands how Python Serialization to design RESTful endpoints that use HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE to perform operations on resources represented by URLs. In Python, developers often use libraries such as Requests to interact with external APIs by sending HTTP requests and handling responses in formats like JSON or XML. On the server side, frameworks like Flask and Django REST Framework make it straightforward to build APIs that expose data and functionality to other applications. Handling authentication methods such as OAuth, API keys, or JWT tokens ensures secure access to resources. Additionally, managing error handling, rate limiting, and data serialization/deserialization improves API reliability and user experience. Overall, hands-on experience with APIs and RESTful services enables Python developers to create powerful, flexible, and secure applications that can easily integrate with other platforms and services.
Version Control Systems (e.g., Git)
Version Control Systems (VCS) are essential tools for Python developers to manage and track changes in their codebases efficiently. Git is the most widely used VCS, allowing developers to collaborate seamlessly by maintaining a history of code modifications, branching for new features or experiments, and merging changes from multiple contributors. Using version control helps prevent code conflicts and makes it easier to revert to previous versions if bugs or errors occur. Python developers integrate Git What is pip with platforms like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket for remote repository hosting, issue tracking, and continuous integration workflows. Mastery of version control involves understanding key concepts such as commits, branches, merges, pull requests, and resolving merge conflicts. It also promotes best practices like writing meaningful commit messages and organizing code changes logically. Overall, proficiency with version control systems enhances team collaboration, code quality, and project maintainability, making it a fundamental skill for any developer working in professional environments.
Preparing for a Python Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Python Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Becoming a proficientPython Developer Skills requires a blend of technical skills, hands-on experience, and continuous learning. From mastering core syntax and OOP principles to deploying cloud-based applications and writing clean, testable code, the journey is both challenging and rewarding. Python’s versatility makes it a valuable tool across web development, data science, automation, AI, and more. As the demand for Python expertise grows, developers who invest in building and refining these skills will find Python Training abundant opportunities and rewarding career paths. Mastering these core skills proficiency in Core Python, working with libraries and frameworks, web development expertise, and solid database knowledge is essential for any Python developer aiming to build robust, efficient, and scalable applications. Continuously improving your understanding of these areas, along with testing, debugging, and version control, will help you stay competitive in the fast-evolving tech landscape. Whether you’re building web apps, APIs, or data-driven solutions, a strong foundation in these skills empowers you to tackle diverse challenges and grow your career successfully.


