
- Harnessing the Power of Open Source in Software Testing
- Importance of Open Source in QA
- Types of Testing Tools
- Functional Testing Tools
- Performance Testing Tools
- Security Testing Tools
- Challenges in Using Open Source Tools
- Installation and Setup Basics
- Use Cases and Industry Adoption
- Future of Open Source Testing Tools
- Conclusion
Harnessing the Power of Open Source in Software Testing
Software testing is a critical part of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). It ensures that applications work as expected, meet business needs, and provide a smooth experience for users. Among the various tools used for Software Testing, open source options have become very popular due to their flexibility, community support, and low cost. Open source testing means using tools with publicly available source code that developers and testers can modify, share, and improve. These tools are widely used in software quality assurance (QA) processes for tasks like functional testing, performance testing, and security testing. Unlike proprietary tools that often have high licensing fees and strict limits, open source tools let organizations customize solutions for their specific project requirements. The open source approach values teamwork and honesty, making it suitable for the fast and ever-changing Open Source Software Testing Tools for QA testing tools Teams landscape. By enabling testers to modify and contribute to tool development, open source testing helps organizations increase efficiency and innovation while lowering costs.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Software Testing? Sign Up For Our Software Testing Training Course Today!
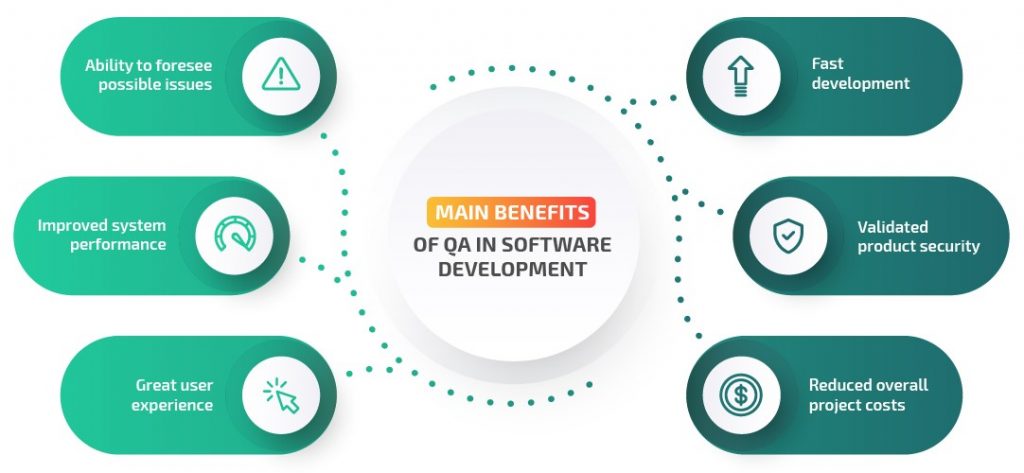
Importance of Open Source in QA
The role of open source testing tools in quality assurance is crucial. As businesses embrace digital change, their applications are becoming more complex, spread out, and user-focused. Ensuring the quality of such applications requires testing strategies that are flexible, scalable, and able to adjust to changing needs. Open source tools provide exactly that. A key benefit is cost savings. Proprietary tools can be expensive, making them hard for startups and small businesses to afford. Open source tools remove this financial hurdle and give everyone access to high-quality testing solutions. Additionally, open source tools promote community-driven innovation.
Types of Testing Tools
Open source testing tools come in various categories, depending on the application type and QA testing tools goals. Main types include:
- Functional Testing Tools These tools check if an application works correctly by testing its features, user interface, APIs, and workflows.
- Performance Testing Tools These assess the stability, scalability, and responsiveness of Open Source Software Testing Tools for QA Teams under different loads.
- Security Testing Tools These ensure applications are secure against vulnerabilities, data leaks, and attacks.
- Automation Testing Tools These automate repetitive test cases and integrate testing into continuous integration pipelines.
- Unit Testing Tools These test individual modules or code units to ensure they function correctly.
- Regression Testing Tools These check if changes or new features disrupt existing functionality.
Each type plays a unique role in delivering reliable, user-friendly, and secure software solutions. By combining different open source testing tools, QA teams can achieve thorough test coverage.
To Explore Software Testing in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Software Testing Training Course To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Functional Testing Tools
Functional testing ensures that a software application performs its intended tasks. Open source functional Software Testing tools are popular because they help testers create automated test cases for web, mobile, and desktop applications. Selenium is the most well-known functional testing tool. It offers tools like Selenium WebDriver, Selenium IDE, and Selenium Grid.
Performance Testing Tools
Performance testing is vital to ensure that applications can manage expected user loads without failure. Open source performance testing tools have become the preferred choice for many organizations due to their strength and flexibility. Apache JMeter is a leading tool in this area. It is used for load testing, stress testing, and performance analysis of web applications, APIs, and databases. JMeter can simulate thousands of users at once, allowing testers to analyze system behavior under varying loads. Another popular tool is Gatling, which specializes in high-performance load testing using a Scala-based scripting language. It provides real-time metrics and detailed reports that help organizations find performance issues. Locust is another open source tool that allows performance load testing with scenarios written in Python. It is known for its ease of use, scalability, and ability to run load tests across multiple machines. By using these performance testing tools, QA teams can ensure that their software performs reliably under high traffic and offers a smooth user experience.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Software Testing by Enrolling in Our Software Testing Master Program Training Course.
Security Testing Tools
As cyber threats and data breaches increase, security testing has become crucial in QA. Open source security automation testing tools give organizations strong ways to identify vulnerabilities and enhance application security. OWASP ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy) is one of the most widely used open source security tools. It helps find vulnerabilities in web applications by simulating various attack scenarios. Burp Suite Community Edition also offers tools for scanning and analyzing application security, though its advanced features are in the paid version. For static code analysis, SonarQube is a helpful open source tool that assists developers in identifying code vulnerabilities, maintainability issues, and bugs during development. Nikto is another popular security tool that scans web servers for known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and outdated software. By using these open source security testing tools, organizations can strengthen their software security, protect user data, and build trust with customers.
Challenges in Using Open Source Tools
Despite their many advantages, open source testing tools come with challenges. One major issue is the steep learning curve. Unlike proprietary tools that often provide in-depth training and user-friendly interfaces, open source tools may need technical knowledge to install, configure, and use effectively. Limited official support is another challenge. While communities can be active, organizations may find it hard to get immediate help for critical issues or bugs. Some open source tools might lack advanced features available in proprietary solutions, especially in large or enterprise settings. Integration with other enterprise systems and scalability can also be complex. Additionally, maintenance and updates rely on community support. If a tool is not actively maintained, it can quickly become outdated, creating risks for organizations depending on it.
Installation and Setup Basics
Most open source testing tools are built to be platform-independent and relatively easy to install. For example, setting up Selenium involves downloading the WebDriver for a specific browser and integrating it with a programming language framework. Appium needs Node.js to be installed before setting up the Appium server and configuring mobile SDKs. JMeter, which is a Java-based application, only requires installing the Java Development Kit (JDK) before downloading and extracting the JMeter package. OWASP ZAP is available as a simple installer for various operating systems. Although installation might be straightforward, proper configuration, environment testing tool setup, and integration into testing pipelines usually require technical skills. Documentation and community forums are valuable resources that help guide users through the testing tool setup process.
Use Cases and Industry Adoption
Open source testing tools are widely used across different industries. In software development, tools like Selenium and JMeter are part of almost every QA team’s toolkit. E-commerce companies rely on open source performance testing tools to ensure their websites can handle high traffic during sales. Banks and financial institutions use security testing tools like OWASP ZAP to protect applications and prevent data breaches. Startups turn to open source tools to minimize costs while maintaining quality standards. Even large organizations like Google, Microsoft, and IBM integrate open source testing tools into their DevOps pipelines to enhance testing efficiency and speed up time-to-market. The versatility, affordability, and community-driven development of open source testing tools make them suitable for businesses of all sizes and sectors.
Future of Open Source Testing Tools
The future for open source testing tools is promising, with more organizations adopting DevOps, Agile, and Continuous Testing practices. As the demand for faster software delivery grows, so does the need for automation, scalability, and integration. AI and machine learning will significantly influence the development of open source testing tools. Smart test automation, self-healing test scripts, and predictive analytics will improve QA processes. Open source communities are already looking into AI-driven features to enhance accuracy and reduce human effort. Furthermore, as cloud computing becomes more widespread, open source testing tool setup will continue to grow with cloud-based capabilities, creating distributed and scalable testing environments. With strong global communities pushing innovation, open source testing tools will stay at the forefront of Open Source Software Testing Tools for QA Teams quality assurance for years ahead.
Conclusion
Open source testing tools have changed the landscape of Open Source Software Testing Tools for QA Teams quality assurance by providing powerful, flexible, and affordable solutions to organizations. From functional and performance load testing to security and API testing, open source tools like Selenium, JMeter, Appium, and OWASP ZAP have become key parts of modern QA practices. While they present challenges such as steep learning curves and limited official support, their benefits in cost savings, transparency, and community-driven innovation greatly outweigh the drawbacks. As industries continue to adopt Agile and DevOps methodologies, the importance of open source Software Testing tools will only grow, influencing the future of software quality assurance.




