
- What is Inheritance in C++?
- Purpose and Benefits of Inheritance in C++
- Parent and Child Classes in C++
- Basic Syntax of Inheritance in C++
- Types of Inheritance
- Constructors and Destructors in Inherited Classes
- Composition Vs. Inheritance
- Conclusion
What is Inheritance in C++?
Inheritance is an important concept in object-oriented programming. It allows you to create a new class by inheriting properties and behaviors from an existing class. The class that is inherited from is called the “base” or “parent” class, and the new class is referred to as the “derived” or “child” class. To understand how inheritance principles apply to distributed systems and virtualized environments, explore Cloud Computing Training a hands-on program that connects object-oriented concepts with scalable infrastructure, enabling learners to design, deploy, and manage cloud-native applications across platforms. Inheritance promotes code reuse, making it easier to create and maintain a codebase. It helps you model relationships between classes in a clear and hierarchical way.
Purpose and Benefits of Inheritance in C++
Purpose of Inheritance:
Inheritance in C++ is a useful way to build modern code. It improves code structure and supports flexible and extensible software. It is a key concept in object-oriented programming. This idea helps developers write cleaner, more maintainable, and scalable code. To ensure such code remains robust and fault-tolerant, explore Exception Handling in C++ a critical concept that teaches how to gracefully manage runtime errors using try-catch blocks, ensuring stability and reliability in object-oriented applications.
Benefits of Inheritance:
Inheritance in C++ aims to promote code reuse and create a hierarchical relationship among classes. It allows a new class (called the derived or child class) to inherit properties and behaviors from an existing class (called the base or parent class).
- Code Reusability: Reduces redundancy by reusing code from existing classes.
- Maintenance and Updates: Updating the base class automatically reflects in all derived classes.
- Polymorphism: Enables flexible and extensible code by treating different class objects as base class objects.
- Structuring Code: Organizes code logically and hierarchically for better readability and maintenance.
- Enhancement of Existing Classes: Extends functionality without modifying original class code.
- Encapsulation: Supports modular and encapsulated code when combined with other object-oriented principles.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Course Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Course Today!
Parent and Child Classes in C++
Classes explain how to create gadgets in object-oriented programming (OOP). You can think of a class as a plan or template. Objects are copies of that template. Some classes are more general or abstract than others. This is known as a parent-child relationship. One class is called the parent or base class, and the other is called the child or derived class. Inheritance describes this type of connection. To understand how object creation is initialized and managed within this structure, explore What Is a Constructors in C++ a foundational concept that defines how objects are instantiated, initialized, and cleaned up using constructors and destructors in class hierarchies.
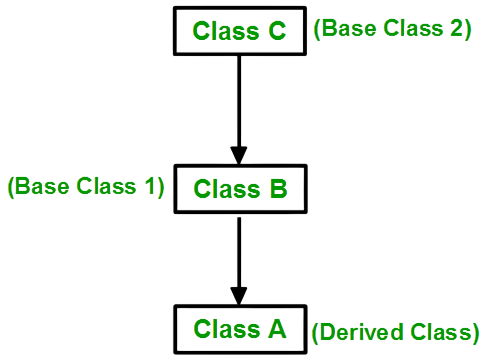
Parent Class
A parent class is a category that has common attributes and behaviors that other classes can use. It is sometimes called a base or super class.
Child Class:A child class is a category that inherits from another class, gaining its attributes and behaviors. It is also known as a derived class.
Would You Like to Know More About Cloud Computing Course? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Course Now!
Basic Syntax of Inheritance in C++
Let’s look at how we can claim base and derived training in C++. This includes access specifiers and the creation of objects from the derived class. Finally, we will examine the concept of constructors and destructors. To understand how these object-oriented principles extend into virtualized environments and distributed systems, explore Cloud Computing Training a practical program that connects core programming concepts with scalable infrastructure, enabling learners to build and manage cloud-native applications across platforms.
- Declaring Base and Derived Classes: In C++, inheritance is indicated using a colon (:) followed by an access specifier. The derived class inherits attributes and methods from the base class.
- BaseClass: The parent class containing common attributes or methods.
- DerivedClass: Inherits from BaseClass and gains access to its members.
- Public Inheritance: Base class members become public in the derived class and are accessible externally.
- Protected Inheritance: Base class members become protected in the derived class, accessible within the class and its subclasses.
- Private Inheritance: Base class members become private in the derived class, accessible only within the derived class itself.
- Object Creation: After defining the class, you can instantiate it. For example, creating myDog from the Dog class gives access to both eat (from base) and bark (from derived).
Constructors and Destructors in Inherited Classes
A constructor is a special function that is called when an object is created. A destructor is called when an object is about to be destroyed, usually when the program ends. Inherited classes can use both the base class’s constructor and destructor. To understand how these lifecycle behaviors differ across programming languages, explore Python vs C++: Key Differences a comparative guide that highlights syntax contrasts, memory management strategies, and object-oriented design patterns unique to each language.
- Constructor (Animal(), Dog()): Special functions that run when objects of the respective classes are created. They set initial values or perform setup tasks.
- Destructor (~Animal(), ~Dog()): Special functions that run when objects are about to be destroyed. They clean up resources or perform final tasks.
When you create an object of the derived class, both the base class’s and the derived class’s constructors are called. When the program ends, both the derived class’s and the base class’s destructors are called.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course Now!
Types of Inheritance
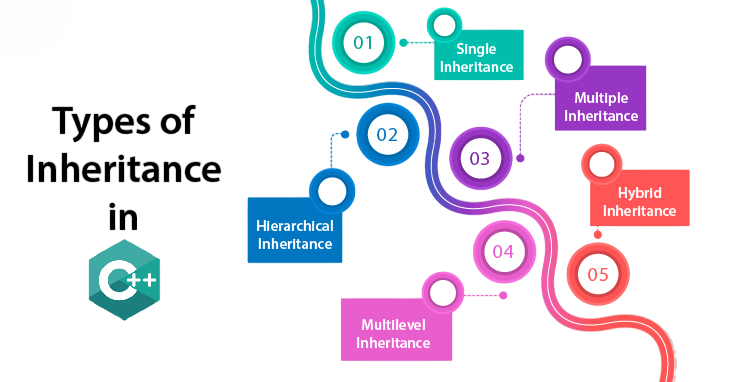
Types of Inheritance in Object-Oriented Programming
- Single Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
Now, let’s discuss each of them in detail below. To understand how syntax, memory management, and runtime behavior vary across languages, explore Differences Between C++ and Java a comparative guide that highlights key distinctions in object-oriented principles, platform dependency, and application performance across both programming ecosystems.
- Single Inheritance: A class inherits properties and behaviors from only one other class, like a child inheriting traits from one parent.
- Multiple Inheritance: A class inherits from more than one class, similar to a child inheriting traits from both parents.
- Multilevel Inheritance: A derived class is created from another derived class, forming a chain of inheritance across multiple levels.
- Hierarchical Inheritance: Multiple derived classes inherit from a single base class, forming a tree-like structure.
Preparing for Cloud Computing Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Composition Vs. Inheritance
Composition and inheritance in C++ are methods for achieving code reuse. Inheritance involves creating a new class by inheriting the properties of an existing one. To explore how these principles form the backbone of modular software design, dive into C++ Object-Oriented Programming a structured course that covers class hierarchies, encapsulation, polymorphism, and real-world implementation strategies for building scalable applications. Composition, on the other hand, involves creating objects within a class for flexibility and modularity.
Conclusion
Inheritance in C++ is an effective way to create flexible and reusable code. It allows a new class to inherit properties from an existing one, which helps with code organization and modularity. The significance of inheritance is in its ability to reduce redundancy and support a maintainable codebase. Instead of duplicating code in multiple places, common attributes and methods can be centralized in the base class. To see how these principles scale in distributed environments and virtualized systems, explore Cloud Computing Training a hands-on program that connects object-oriented design with cloud-native architecture, enabling learners to build scalable, modular applications across platforms. This provides a strong foundation for building scalable, well-structured, and modular software systems.





