
- Introduction to Google Analytics
- History and Evolution
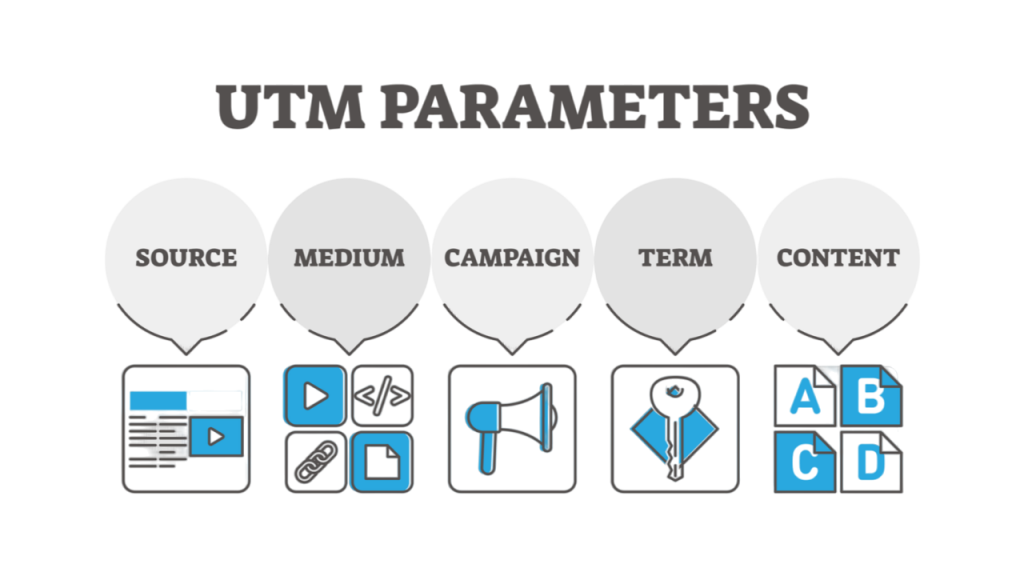
- Key Terminologies
- Setting Up an Account
- Tracking Code Overview
- Understanding Metrics and Dimensions
- Traffic Source Analysis
- Behavior and Conversion Reports
- Setting Goals and Funnels
- Real-Time Reporting
- Benefits and Limitations
- Conclusion
Introduction to Google Analytics
In today’s digital age, understanding how users interact with websites and digital assets is critical for businesses seeking growth, visibility, and success. Google Analytics, a powerful and widely used web analytics tool, empowers website owners, marketers, and businesses by providing deep insights into their digital performance, user behavior, and traffic sources core capabilities explored in Digital Marketing Training, where learners master audience segmentation, acquisition channels, behavioral flow, and conversion tracking to optimize campaigns, improve UX, and make data-driven decisions across the marketing funnel. It enables data-driven decision-making, giving users the tools necessary to optimize marketing efforts, enhance user experiences, and ultimately drive conversions. Whether you’re running an e-commerce site, blog, or enterprise platform, Google Analytics puts you in control, providing essential information to fine-tune strategies and measure success.
Ready to Get Certified in Digital Marketing? Explore the Program Now Digital Marketing Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
History and Evolution
Google Analytics was first launched in November 2005, following Google’s acquisition of Urchin Software Corporation. The original platform, known as “Urchin on Demand,” evolved over the years into a sophisticated analytics tool. The introduction of Universal Analytics in 2012 brought increased flexibility, including custom dimensions and enhanced tracking features capabilities widely adopted by Digital Marketing Experts, who leveraged session-based models, multi-channel attribution, and goal tracking to refine audience insights and optimize campaign performance. These tools laid the foundation for data-driven strategy before the shift to GA4’s event-based framework. However, the digital landscape continued to evolve, and so did the need for more advanced data measurement. This led to the launch of Google Analytics 4 (GA4) in 2020, a version that provides a comprehensive view of the user journey across websites and mobile apps. It leverages machine learning, cross-platform tracking, and event-based data models, preparing marketers for a future without cookies. This comprehensive view ensures that you are always informed and knowledgeable about your digital performance.
Key Terminologies
Understanding the key terminologies in Google Analytics is crucial for its effective use. These terms include ‘users’ (individual visitors who have initiated at least one session on your site), ‘sessions’ (a group of interactions that occur within a specified time frame), ‘pageviews’ (the total number of times a page is viewed), ‘bounce rate’ (the percentage of sessions where users leave after viewing only one page), ‘conversions’ (the completion of desired actions such as purchases, sign-ups, or downloads), and ‘events’ (user interactions tracked independently of web page loading) core metrics explored in Become a Digital Marketing Specialist, where learners master Google Analytics terminology, interpret behavioral data, and apply insights to optimize campaigns, improve UX, and drive measurable results across digital channels. These metrics provide a comprehensive view of user behavior and website performance.
To Explore Digital Marketing in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Digital Marketing Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Setting Up an Account
- The first step in using Google Analytics is setting up an account. This involves creating a Google Analytics account through your Google account, setting up the account and property (which represents a website or app), and creating a data stream (web or app).
- The data stream is what Google uses to collect and analyze data. GA4 streamlines this process by allowing for both app and web data in one property. Proper configuration at this stage ensures the accuracy of the insights you gather. Key settings include enabling enhanced measurement, linking with Google Ads for campaign tracking, and configuring user permissions.
Tracking Code Overview
- One of the fundamental components of Google Analytics is the tracking code, also known as the Global Site Tag (gtag.js). This snippet of JavaScript code needs to be installed on every page of your website, ideally in the section. The code collects data, including page views, user interactions, and session duration, and sends it to your Google Analytics account.
- For more complex tracking, such as button clicks or video views, you can customize the code or use Google Tag Manager, which enables centralized tag management without requiring modifications to the site’s code. In GA4, events are more flexible, and the tracking is not solely reliant on predefined categories, making you adaptable and resourceful in tracking unique actions.
- Google Analytics offers deep insights into user behavior through its Behavior Reports. These reports show how users interact with your site, which pages they visit, how long they stay, what path they follow, and where they drop off. You can identify top-performing content and pinpoint underperforming pages that need optimization.
- The Conversion Reports, especially in GA4, allow you to define custom conversion events that are critical to your business goals. Whether it’s completing a purchase, filling out a lead form, or subscribing to a newsletter, you can track and optimize each of these actions to improve your results.
- Goals in Google Analytics help track specific actions you want users to take. Setting up goals allows you to measure how well your site fulfills your target objectives. In Universal Analytics, goals can be based on destination URLs, duration, pages per session, or events. In GA4, conversions are more event-based and flexible.
- Funnels allow you to visualize the steps users take before completing a goal. For example, an e-commerce funnel typically includes steps such as visiting a product page, adding a product to the cart, and completing the checkout process. Analyzing funnel data can help you identify where users drop off and optimize those stages to improve conversion rates.
- The benefits of using Google Analytics are extensive. It provides comprehensive insights into your audience and their engagement with your content. You can identify high-performing traffic sources, uncover behavioral trends, track conversions, and make informed decisions to enhance user experience and business performance. GA4’s machine learning capabilities even provide predictive metrics, such as churn probability and potential revenue.
- However, there are limitations as well. For instance, data sampling in Universal Analytics can lead to inaccurate reports for large datasets. There are also privacy concerns, especially with GDPR and cookie restrictions. GA4 aims to address some of these by offering better control over data retention and user anonymity.
Looking to Digital Marketing Training? Discover the Digital Marketing Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Understanding Metrics and Dimensions
In Google Analytics, data is categorized into metrics and dimensions. Metrics are quantitative measurements, such as the number of users, sessions, average session duration, and conversion rates.Dimensions, on the other hand, are descriptive attributes, such as device type, browser, geographic location, and traffic source core elements covered in Digital Marketing Training, where learners explore how dimensions categorize user behavior, segment traffic, and enrich performance analysis. Understanding these attributes is essential for building actionable reports, refining audience targeting, and optimizing cross-channel strategies. The interaction between metrics and dimensions allows for a multidimensional analysis of your data. For instance, by cross-referencing the dimension “City” with the metric “Sessions,” you can find out how many sessions originated from a specific city. This capability to dissect data in multiple ways is what makes Google Analytics an indispensable tool for digital marketers.
Traffic Source Analysis
One of the most valuable aspects of Google Analytics is its ability to identify the sources of your website traffic. The Acquisition Reports display traffic sources, including Organic Search (from search engines) a foundational insight covered in Create a Digital Marketing Report, where marketers learn to interpret source/medium data, evaluate campaign performance, and optimize channel strategies. Mastering these reports enables data-driven decisions that improve ROI, audience targeting, and overall digital visibility.
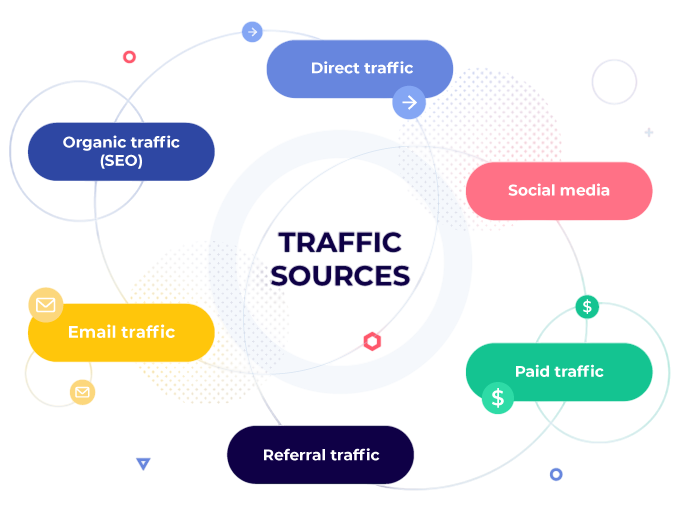
Direct (users typing the URL directly), Referral (users clicking on links from other websites), Social (traffic from social media platforms), and Paid Search (traffic from paid campaigns, such as Google Ads). Understanding which channels bring in the most valuable traffic can help allocate resources more efficiently. For instance, if organic search drives the most conversions, then it might make sense to invest more in SEO strategies.
Preparing for Digital Marketing Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Digital Marketing Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Behavior and Conversion Reports
Setting Goals and Funnels
Real-Time Reporting
The Real-Time Report in Google Analytics enables you to view current activity on your site as it occurs. You can monitor the number of users on your site, their geographic locations, the pages they’re viewing, the devices they’re using, and the traffic sources that brought them core analytics skills emphasized in Choose a Career in Digital Marketing, where aspiring professionals learn to interpret behavioral data, optimize user journeys, and apply insights to improve campaign performance. Mastery of these metrics is essential for building data-driven strategies and advancing in roles like marketing analyst, SEO specialist, or digital strategist. This feature is handy during campaign launches, product announcements, or live events, as it enables marketers to respond promptly to user behavior. Real-time data helps identify issues such as broken links, tracking failures, or unexpected traffic surges.
Benefits and Limitations
Conclusion
Google Analytics is an indispensable tool for anyone involved in digital marketing, web development, or business analytics. With the evolution of GA4, the platform has become even more robust, flexible, and future-ready. From setting up tracking codes to understanding complex user journeys, the platform offers unmatched capabilities to understand and optimize digital presence. Despite some learning curves and privacy limitations, the benefits far outweigh the challenges a perspective reinforced in Digital Marketing Training, where professionals learn to navigate evolving regulations like GDPR and CCPA, adapt to algorithmic shifts, and leverage data responsibly. With the right skills, marketers transform constraints into strategic advantages, driving growth through ethical, performance-driven campaigns. Businesses that effectively leverage Google Analytics are better positioned to meet customer needs, improve website performance, and grow sustainably in the competitive digital landscape. Whether you’re a small blogger or a large enterprise, mastering Google Analytics is a crucial step toward achieving more innovative marketing and driving business growth.




