- Introduction to the Supply Chain Analyst Role
- Key Responsibilities of a Supply Chain Analyst
- Essential Skills and Qualifications
- Tools and Technologies Used by Supply Chain Analysts
- The Importance of Data Analysis in Supply Chain Management
- How Supply Chain Analysts Improve Business Performance
- Career Path and Growth Opportunities
- Conclusion
Introduction to the Supply Chain Analyst Role
The role of a Supply Chain Analyst is pivotal in ensuring that the movement of goods and services within an organization is both efficient and cost-effective. This position involves deep analysis of supply chain data to identify trends, forecast demand, and recommend improvements across procurement, inventory, logistics, and distribution. Among the core supply chain analyst skills are strong analytical thinking, proficiency in tools like Excel, SQL, and ERP systems, and the ability to communicate insights effectively to cross-functional teams. Pursuing PMP Training can further enhance project management capabilities, making analysts more effective in coordinating supply chain initiatives. The supply chain analyst roles and responsibilities typically include monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), optimizing supply chain operations, and collaborating with vendors and internal departments to streamline processes. An important aspect of the job is managing analyst supply chain replenishment strategies ensuring stock levels meet customer demand without overburdening the inventory. Analysts must be able to evaluate supplier performance, reduce lead times, and contribute to strategic sourcing decisions. In industries where timely delivery and inventory accuracy are crucial, a skilled supply chain analyst can make a significant impact on reducing costs and increasing operational agility. Overall, the role demands a blend of technical ability, business acumen, and strategic foresight to support end-to-end supply chain excellence.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Key Responsibilities of a Supply Chain Analyst
- Data Analysis & Reporting: Analyze large volumes of supply chain data to uncover trends, bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement using tools such as Oracle Supply Chain and advanced Excel functions.
- Demand Forecasting & Inventory Management: Develop accurate forecasts and maintain optimal inventory levels, including the management of cold chain logistics for temperature-sensitive goods by applying Managerial Economics Concepts to make informed, cost-effective decisions.
- Process Optimization: Identify inefficiencies and recommend improvements to streamline supply chain workflows, reduce costs, and improve delivery performance.
A Supply Chain Analyst plays a vital role in enhancing the efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability of supply chain operations. By leveraging data and technology, analysts support strategic decisions that impact everything from procurement to final delivery. Their responsibilities span across planning, execution, and continuous improvement, often involving platforms like Oracle SCM and contributing to a more sustainable supply chain. Below are the key responsibilities of a Supply Chain Analyst:
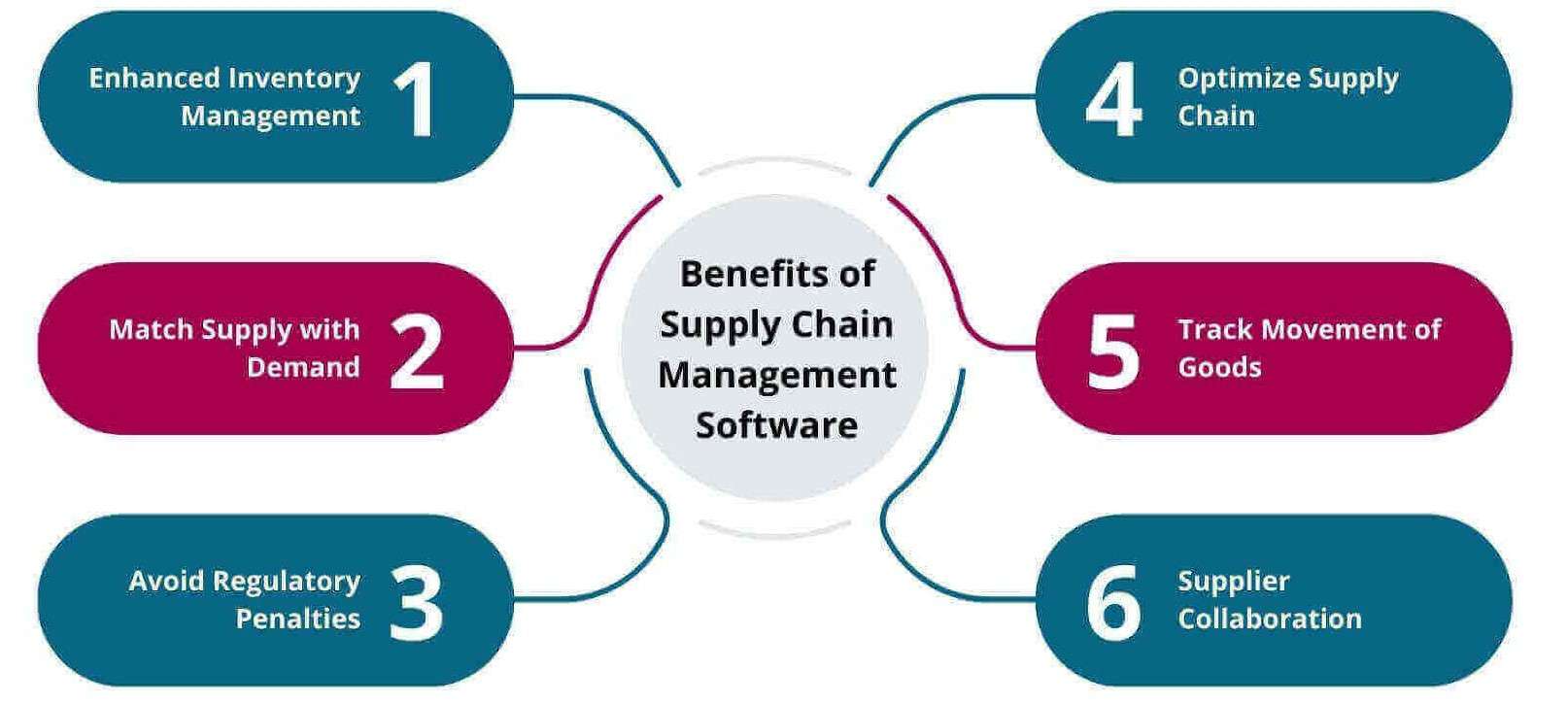
- Sustainability Tracking: Support initiatives aimed at building a sustainable supply chain by tracking environmental metrics and aligning practices with corporate responsibility goals.
- System Implementation & Support: Assist in the implementation and maintenance of ERP systems like Oracle SCM, ensuring data integrity and user training.
- Strategic Planning: Collaborate with cross-functional teams to align supply operations with overall supply chain strategy, helping to drive long-term business success.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
To succeed as a Supply Chain Analyst, possessing the right blend of skills and qualifications is essential for navigating the complexities of modern logistics and operations. Among the most critical supply chain analyst skills are analytical thinking, problem-solving, and proficiency in data tools such as Excel, SQL, and ERP systems. Strong communication abilities and attention to detail are also vital, as analysts must interpret complex data and translate insights into actionable recommendations. Educationally, a bachelor’s degree in supply chain management, business, or a related field is typically required, with many employers preferring candidates who also have experience with forecasting and procurement systems. Understanding What Is The Training Process And Its Stages can further prepare individuals to adapt quickly to organizational practices and tools used in modern supply chains. Understanding the end-to-end flow of supply chains, including analyst supply chain replenishment processes, is particularly important in maintaining optimal inventory levels and reducing waste. A firm grasp of key supply chain analyst roles and responsibilities such as demand planning, vendor performance evaluation, and logistics coordination ensures that the analyst can support both tactical and strategic decision-making. Certifications like APICS CPIM or Six Sigma can further enhance a candidate’s credibility. Altogether, these competencies empower analysts to contribute significantly to supply chain efficiency, cost reduction, and overall organizational performance in today’s highly competitive market.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Tools and Technologies Used by Supply Chain Analysts
- Oracle SCM Cloud: A comprehensive suite that supports procurement, inventory, logistics, and order management central to optimizing operations and executing a long-term supply chain strategy.
- ERP Systems: Enables integration of core business functions, allowing analysts to track and manage data from sourcing to delivery with high visibility and control. PMP Training enhances their ability to manage such end-to-end processes efficiently through structured project planning and execution.
- Advanced Excel and Power BI: Widely used for data analysis, visualization, and dashboard creation to monitor KPIs and identify patterns across the supply chain.
Supply Chain Analysts rely on a range of tools and technologies to collect, process, and interpret data that drive key operational decisions. These tools are essential in supporting real-time visibility, improving forecasting accuracy, and enhancing supply chain performance. Whether working on optimizing cold chain logistics, contributing to a sustainable supply chain, or implementing a broader supply chain strategy, the right technology stack is vital. Below are six commonly used tools and platforms:
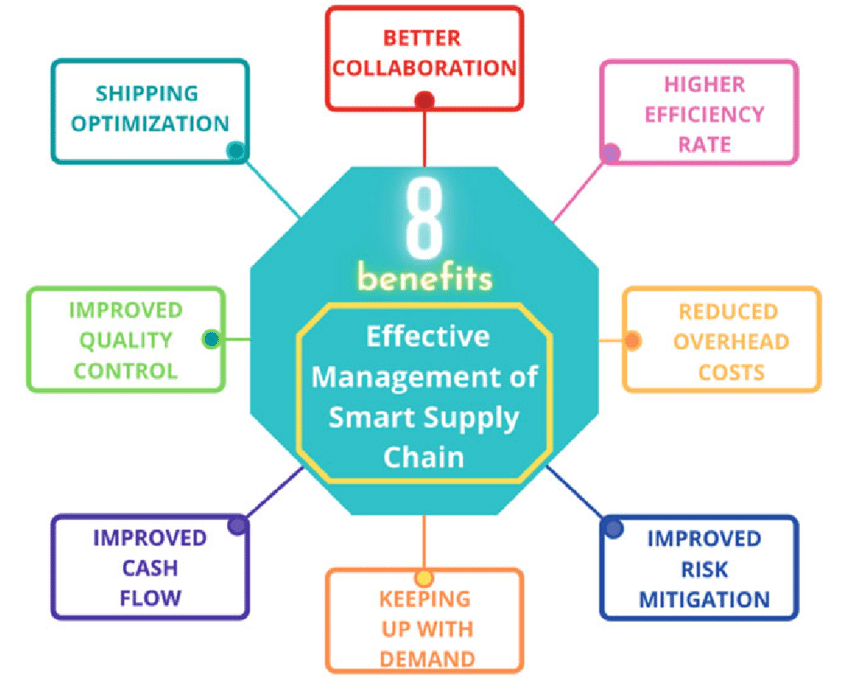
- Forecasting & Demand Planning Tools: Help predict future demand and align production schedules critical for planning cold chain logistics and perishable inventories.
- Sustainability Reporting Platforms: Track carbon emissions, energy usage, and waste to build a sustainable supply chain aligned with environmental goals.
- Transportation Management Systems (TMS): Optimize shipping routes, reduce freight costs, and improve delivery efficiency vital for analysts involved in global logistics coordination.
- Optimizing Inventory and Replenishment: Analysts ensure the right products are available at the right time, reducing excess stock and avoiding shortages especially critical in cold chain logistics where product quality is time-sensitive.
- Enhancing Supply Chain Strategy:Using historical data and market trends, they support the development and execution of an effective supply chain strategy that aligns with business goals and customer demands. A solid understanding of financial principles, such as those found when you Learn Objectives of Management Accounting, helps ensure decisions are both operationally efficient and cost-effective.
- Improving Supplier and Vendor Performance: Through data analysis and performance tracking, analysts evaluate vendors and streamline sourcing processes, leveraging systems like Oracle Supply Chain for accuracy.
- Promoting Sustainability: Analysts contribute to a sustainable supply chain by identifying waste, reducing carbon footprints, and recommending eco-friendly logistics practices.
- Implementing Advanced Technologies: By integrating tools like Oracle SCM, analysts enhance automation, forecasting, and reporting for smarter decision-making.
- Boosting Operational Efficiency: Analysts identify inefficiencies across logistics, procurement, and production delivering continuous improvements that positively impact profitability and agility.
The Importance of Data Analysis in Supply Chain Management
Data analysis plays a critical role in modern supply chain management, enabling organizations to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and respond quickly to market fluctuations. For professionals in this field, particularly those in supply chain analyst roles, the ability to interpret complex datasets is foundational to success. Strong supply chain analyst skills include data mining, trend forecasting, and statistical modeling all essential for uncovering inefficiencies, reducing costs, and improving service levels. Among the key supply chain analyst roles and responsibilities is using data to support demand forecasting, supplier performance evaluation, and logistics optimization tasks that often overlap with Operations Manager Responsibilities, highlighting the need for strong cross-functional coordination. Through detailed analysis, analysts can fine-tune analyst supply chain replenishment strategies, ensuring that inventory levels are accurate and aligned with actual demand while minimizing excess stock and shortages. Data analysis also allows for scenario planning and risk assessment, empowering businesses to anticipate disruptions and adjust their strategies accordingly. Furthermore, in today’s competitive and data-driven environment, insights derived from analytics support the creation of agile and responsive supply chains that can adapt to customer needs in real time. Ultimately, data analysis is not just a technical skill but a strategic asset that drives efficiency, innovation, and long-term success in supply chain management.
Want to Pursue a PMP Master’s Degree? Enroll For PMP Master Program Training Course Today!
How Supply Chain Analysts Improve Business Performance
Supply Chain Analysts play a pivotal role in driving operational efficiency and improving overall business performance. By turning raw data into actionable insights, they help organizations streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance service delivery. Their work supports strategic decision-making and ensures the supply chain aligns with both short-term goals and long-term visions. Below are six key ways Supply Chain Analysts contribute to better business outcomes:
Career Path and Growth Opportunities
A career as a Supply Chain Analyst offers strong growth potential and a clear path toward leadership roles in operations, logistics, and strategic planning. Professionals who develop core supply chain analyst skills such as data analysis, problem-solving, and proficiency in tools like ERP systems are well-positioned to advance within the supply chain field. At the entry level, analysts are typically involved in demand forecasting, vendor evaluation, and analyst supply chain replenishment activities, where they help maintain optimal inventory levels and streamline procurement. As they gain experience, analysts may take on broader supply chain analyst roles and responsibilities, including cross-functional project management, supply chain optimization, and strategic sourcing. Gaining Understanding Scope of Management Accounting further equips them to align operational strategies with financial objectives across the supply chain. With time and continued skill development, many move into roles like Supply Chain Manager, Operations Manager, or Procurement Lead. Earning certifications such as APICS CPIM, CSCP, or Six Sigma can further accelerate career advancement and open doors to executive positions like Director of Supply Chain or VP of Operations. Additionally, the global nature of supply chains allows professionals to work across industries such as manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and tech. With supply chains becoming more data-driven and complex, skilled analysts are increasingly vital, making this a rewarding and future-proof career choice.
Preparing for a PMP Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on PMP Interview Questions and Answers
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of a Supply Chain Analyst is becoming increasingly vital in today’s data-driven and globally connected business environment. By leveraging tools such as Oracle SCM and Oracle Supply Chain, analysts provide critical insights that support end-to-end visibility, operational efficiency, and strategic decision-making. Their ability to analyze trends, manage inventory, and improve logistics processes directly influences the success of any supply chain strategy, whether it’s focused on reducing costs, enhancing delivery speed, or increasing customer satisfaction. In sectors where precision and timeliness are essential such as cold chain logistics, analysts play a crucial role in maintaining product integrity and compliance. PMP Training can further equip these professionals with structured project management skills to handle time-sensitive operations effectively. Moreover, as companies prioritize environmental and social governance, Supply Chain Analysts also contribute to building a sustainable supply chain by identifying areas to reduce waste, optimize routes, and lower emissions. Their work not only improves short-term performance but also drives long-term growth and resilience. As technology continues to evolve, the value of skilled analysts will only grow, making this career path both impactful and future-ready. Overall, the Supply Chain Analyst is no longer just a behind-the-scenes data handler but a strategic contributor to business success across industries.