- Introduction to Supply Chain Management
- Why Choose a Career in Supply Chain Management
- Core Functions in Supply Chain
- Essential Skills for Supply Chain Professionals
- Career Paths and Roles in Supply Chain
- Education and Certifications
- Industry Trends and Future Outlook
- Tips for Building a Successful Career in SCM
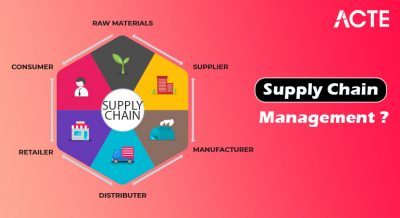
Introduction to Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the backbone of modern commerce, encompassing the coordination of materials, information, and finances as they move through the supply network from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer. In today’s globalized market, an efficient logistics management system is critical for businesses to stay competitive and responsive to customer demands. SCM not only involves transportation and warehousing but also strategic planning, inventory control, procurement, and customer service. With digital transformation reshaping industries, companies are investing heavily in advanced tools and technologies to optimize their supply chains. Professionals equipped with project management skills, including those who have undergone PMP Training, are increasingly in demand to lead complex supply chain initiatives and ensure smooth execution across global networks. This evolution has opened up a wide range of opportunities for professionals seeking a career in Supply Chain Management, offering roles that span across industries like manufacturing, e-commerce, healthcare, and retail. Logistics and supply chain management jobs are in high demand, requiring analytical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and proficiency in digital systems. From entry-level logistics coordinators to senior supply chain strategists, the field offers continuous growth and the chance to impact global operations directly. As businesses seek greater efficiency, sustainability, and resilience, the need for skilled professionals with knowledge in SCM and the ability to manage complex logistics processes continues to grow, making it a dynamic and rewarding career path.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Why Choose a Career in Supply Chain Management
- High Demand Across Industries: From manufacturing and retail to pharmaceuticals and food services, the demand for supply chain professionals spans multiple sectors, including niche areas like cold chain logistics.
- Strong Career Growth and Stability: As global trade expands and supply networks become more complex, roles in supply chain planning and supplier risk management offer long-term career stability and advancement. Understanding Managerial Economics Concepts also plays a vital role in making data-driven decisions that align with organizational goals and market dynamics.
- Opportunities for Innovation and Technology: The field is rapidly adopting technologies like AI, blockchain, and IoT, giving professionals the chance to work on cutting-edge logistics management systems.
A career in Supply Chain Management offers diverse opportunities in a rapidly evolving global business environment. As companies increasingly focus on efficiency, sustainability, and customer satisfaction, professionals skilled in logistics management, supply chain planning, and supplier management are in high demand. Here are six compelling reasons to choose a career in this dynamic field:
- Global Exposure and Cross-Functional Roles: Supply chain careers often involve collaboration across countries, cultures, and departments broadening your skills and global perspective.
- Critical Role in Business Success: Effective supplier management and planning directly impact a company’s bottom line, making these roles crucial to organizational performance.
- Focus on Sustainability and Impact: With growing emphasis on eco-friendly practices, especially in cold chain logistics, the field supports meaningful contributions toward global sustainability goals.
Core Functions in Supply Chain
The core functions in supply chain management are essential to ensuring the smooth flow of goods, information, and finances from origin to end consumer. At the heart of this system lies logistics management, which oversees transportation, warehousing, and distribution processes to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery. A specialized area within this is cold chain logistics, which deals with the storage and transport of temperature-sensitive products, vital for industries like pharmaceuticals and food. Another critical function is supply chain planning, which involves forecasting demand, managing inventory, and aligning supply with customer needs to optimize operations. Leveraging Financial Management Skills for Growth enables professionals to allocate resources efficiently, reduce costs, and enhance overall supply chain profitability. Effective supplier management plays a key role in maintaining strong relationships with vendors, ensuring quality, timely deliveries, and competitive pricing. Meanwhile, supplier risk management focuses on identifying and mitigating potential disruptions from suppliers, whether due to financial instability, geopolitical issues, or natural disasters. Together, these functions form the backbone of a resilient and agile supply chain, enabling businesses to respond quickly to market changes, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. As global supply networks grow increasingly complex, mastering these core functions becomes vital for operational success and long-term sustainability in any industry.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Essential Skills for Supply Chain Professionals
- Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to interpret data, forecast demand, and optimize operations is key to making informed decisions and improving efficiency.
- Technological Proficiency: Familiarity with modern tools and platforms, especially a robust Logistics Management System, is crucial for tracking inventory, managing transportation, and streamlining workflows. Professionals with PMP Training can effectively integrate these technologies into project plans, ensuring smoother implementation and better cross-functional coordination.
- Effective Communication: Clear communication across departments, with suppliers and customers, ensures smoother coordination and timely issue resolution.
A successful career in Supply Chain Management requires more than just technical knowledge it demands a diverse skill set that blends analytical thinking, communication, and adaptability. As the industry evolves with new technologies and global challenges, professionals must stay equipped with the right capabilities to thrive in various logistics and supply chain management jobs. Here are six essential skills every supply chain professional should have:
- Strategic Thinking: Professionals must align logistics strategies with broader business goals, contributing to long-term growth and customer satisfaction.
- Adaptability and Resilience: In a constantly changing environment, the ability to adapt quickly to disruptions like supply shortages or global crises is critical.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: Strong interpersonal skills help build relationships across supply networks and foster teamwork in high-pressure, deadline-driven environments.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Supply Chain or Related Fields: Degrees in supply chain management, logistics, business, or industrial engineering provide a solid foundation for understanding core concepts and industry practices.
- Master’s in Supply Chain or MBA with SCM Focus: Advanced degrees help professionals qualify for strategic roles and offer in-depth knowledge of planning, procurement, and logistics management systems. Additionally, understanding What is Human Resource Management equips them to effectively lead teams, manage talent, and foster a collaborative work environment within the supply chain function.
- APICS Certified in Planning and Inventory Management (CPIM): A globally recognized certification that enhances skills in production and inventory management valuable for manufacturing and operations.
- Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP): This certification covers the entire supply chain, from planning to delivery, and is ideal for those seeking cross-functional roles.
- Six Sigma Certification: Focuses on process improvement and quality control, which are essential in optimizing supply chain efficiency.
- Online Courses and ERP Training: Learning platforms and ERP tools like SAP or Oracle SCM help professionals stay updated with current logistics management systems and technologies.
Career Paths and Roles in Supply Chain
A career in supply chain offers a wide range of paths and roles that cater to different skills and interests, making it one of the most versatile and in-demand fields today. Professionals can begin in entry-level positions like procurement assistants or logistics coordinators and gradually move into specialized or leadership roles. Logistics management remains a foundational function, ensuring the efficient movement of goods across the network. Those with a focus on temperature-sensitive goods can explore cold chain logistics, which is crucial for sectors like food and pharmaceuticals. Strategic roles in supply chain planning involve forecasting demand, optimizing inventory, and aligning supply with business goals. Understanding What is Leadership And Its Important helps professionals drive collaboration across departments, make informed decisions, and lead supply chain teams effectively toward organizational success. As businesses grow globally, managing vendors effectively becomes essential, giving rise to careers in supplier management, where professionals maintain strong relationships and ensure consistent quality and service. Another critical area is supplier risk management, which involves identifying potential disruptions, assessing vulnerabilities, and implementing strategies to mitigate risks from the supplier base. With opportunities ranging from operations to strategy, and from local to global levels, supply chain roles provide not only career stability and growth but also the chance to directly impact a company’s success and resilience in today’s fast-changing market.
Want to Pursue a PMP Master’s Degree? Enroll For PMP Master Program Training Course Today!
Education and Certifications
Pursuing the right education and certifications is a crucial step toward building a successful career in Supply Chain Management. As the industry becomes more data-driven and technology-oriented, employers increasingly seek candidates with formal training and recognized credentials that demonstrate both technical knowledge and practical expertise. Whether you’re aiming for entry-level logistics and supply chain management jobs or leadership roles, the following educational paths and certifications can give you a strong competitive edge:
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The supply chain industry is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by digitalization, globalization, and changing consumer expectations. One of the most prominent trends is the integration of advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain into logistics management, enabling real-time tracking, predictive analytics, and smarter decision-making. With the rise in demand for pharmaceuticals and perishable goods, cold chain logistics has become increasingly critical, pushing companies to invest in temperature-controlled transportation and storage solutions. In parallel, the growing complexity of global supply networks has intensified the need for robust supplier risk management, helping organizations proactively identify and mitigate potential disruptions from geopolitical instability, natural disasters, or supplier insolvency. Additionally, supply chain planning is becoming more data-centric, with companies using machine learning to forecast demand and optimize inventory levels. A solid understanding of the Scope of Management Accounting enables professionals to analyze cost behavior, evaluate performance metrics, and support data-driven decision-making in these advanced planning processes. Effective supplier management is also a key focus, as businesses seek to build resilient, ethical, and sustainable supply chains. Looking ahead, sustainability, transparency, and resilience will remain top priorities, prompting organizations to reevaluate sourcing strategies and invest in agile systems. As these trends continue to evolve, professionals with the right skills and adaptability will find ample opportunities to grow and lead in this dynamic, future-ready industry.
Preparing for a PMP Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on PMP Interview Questions and Answers
Tips for Building a Successful Career in SCM
Building a successful career in Supply Chain Management (SCM) requires a combination of technical skills, strategic thinking, and a proactive learning mindset. To begin with, gaining a strong foundation in logistics management is essential, as it forms the operational core of SCM, dealing with the movement, storage, and distribution of goods. Specializing in high-demand areas like cold chain logistics can open doors to niche industries such as pharmaceuticals and food supply, where temperature-sensitive handling is critical. Developing expertise in supply chain planning helps professionals anticipate demand, manage inventory effectively, and align operations with business objectives. Equally important is building strong supplier management skills, which involve negotiating contracts, maintaining relationships, and ensuring timely procurement of quality materials. Professionals with PMP Training are better equipped to manage these processes efficiently through structured project planning and execution. As global supply chains face increased volatility, understanding supplier risk management is vital to foresee potential disruptions and build resilience into systems. Staying updated with industry trends, pursuing certifications, and gaining hands-on experience with digital tools like ERP systems will enhance your profile. Networking with industry professionals and participating in cross-functional projects can further broaden your perspective. Ultimately, success in SCM comes from being detail-oriented yet strategic, technologically adept, and capable of adapting quickly in a fast-evolving, globally interconnected landscape.