- Searching in Data Structures
- Importance of Searching
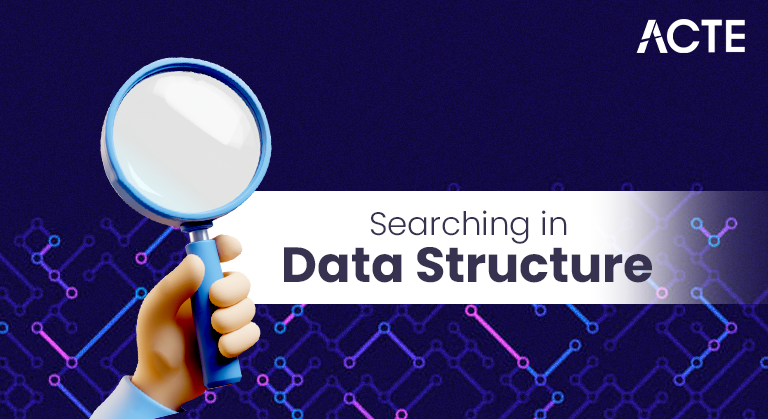
- Linear Search
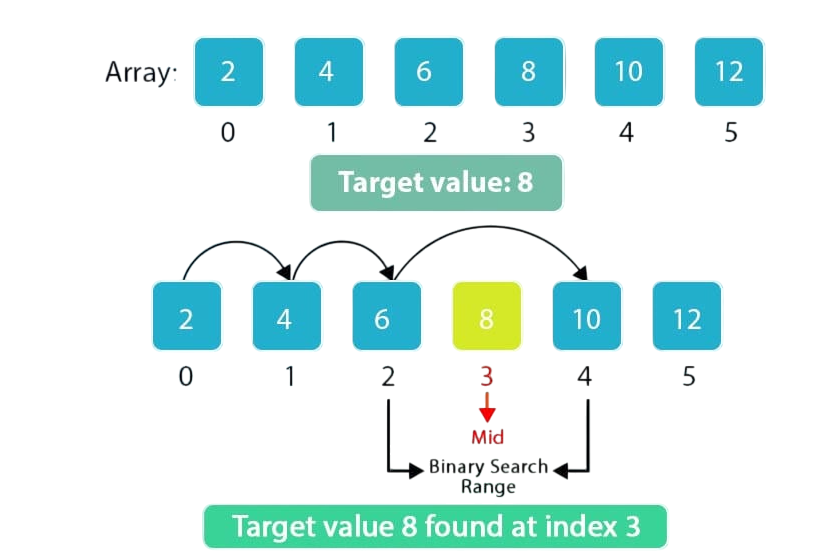
- Binary Search
- Interpolation Search
- Jump Search
- Exponential Search
- Search in Linked Lists
- Searching in Trees
- Performance Comparison
- Searching in Data Structures Use Cases
- Optimizations
- Summary
Searching in Data Structures
Searching in Data Structures is one of the fundamental operations in computer science. It involves locating a specific element in a data structure or verifying its existence. The efficiency of a search operation can significantly impact the overall performance of an application, particularly when dealing with large datasets. To master such performance-critical techniques and implement them effectively, exploring Python Training reveals how structured learning in Python equips developers to optimize search algorithms, manage data intelligently, and build scalable solutions for real-world challenges. The choice of a suitable searching algorithm depends on the nature of the data, its size, and how the data is organized. In this article, we will explore various searching techniques, understand their importance, and evaluate their performance.
Interested in Obtaining Your Python Certificate? View The Python Developer Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Importance of Searching
Searching in Data Structures is vital because it underpins many operations in computing, from accessing records in a database to retrieving information from memory. In real-world applications, effective searching can lead to performance improvements and better user experiences. To maintain and iterate on such performance-critical codebases efficiently, exploring Git and Version Control reveals how developers track changes, collaborate seamlessly, and manage multiple versions of their projects ensuring stability and scalability throughout the development lifecycle. For example, search functionality in search engines, databases, and file systems relies heavily on optimized search algorithms. Moreover, many algorithms and data structures are designed to improve search efficiency, emphasizing the critical nature of searching in computing.
Linear Search
- Linear search, also known as sequential search, is the simplest search algorithm. It checks each element in the data structure sequentially until the target element is found or the list ends. This algorithm does not require the data to be sorted and is suitable for small or unsorted datasets.
- For example, in an array of 10 integers, linear search will begin at the first index and check each element until it either finds the desired value or reaches the end. Though simple to implement, linear search has a time complexity of O(n), making it inefficient for large datasets.
- Binary search is a more efficient algorithm but requires the data to be sorted. It works by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half. If the value of the target element is less than the element in the middle of the interval, the algorithm continues in the lower half. Otherwise, it continues in the upper half.
- Binary search has a time complexity of O(log n), which is significantly faster than linear search for large datasets. It is commonly used in applications where data is static and frequently searched, such as dictionaries or databases with sorted entries. However, the limitation is the need for a sorted dataset.
- position = low + ((target – array[low]) * (high – low)) / (array[high] – array[low])
- Jump search is designed for sorted arrays. It reduces the number of comparisons by jumping ahead by fixed steps and then performing a linear search within a block. The optimal step size is usually the square root of the array length.
- For example, in an array of 100 elements, the algorithm would jump in steps of 10. Once it finds a block where the target could reside, it performs a linear search in that block. The time complexity is O(\sqrt{n}), which is more efficient than linear search but less efficient than binary search.
- Exponential search combines the benefits of binary search and an initial range-finding step. It is used for unbounded or infinite-sized arrays. The algorithm starts by checking the first element, then the next 2, 4, 8, and so on, until the range is found where the target might reside.
- Then, it performs a binary search within that range. This search method is useful in scenarios where the size of the dataset is unknown or infinite. The time complexity is O(log i), where i is the position of the element to be found, making it highly efficient for large and growing datasets.
- Searching in linked lists is generally less efficient than in arrays due to the sequential nature of access. Linear search is commonly used for linked lists, resulting in a time complexity of O(n). Since linked lists do not support random access, advanced search algorithms like binary search are not applicable unless the list is converted to another data structure.
- However, certain enhancements like skip lists or self-organizing lists can improve search efficiency in linked lists. Skip lists, for instance, use additional pointers to jump across elements, reducing the number of steps needed to find an item. To understand how such data structure optimizations fit into broader programming concepts, exploring What is Python Programming reveals how Python’s simplicity and versatility make it ideal for implementing advanced algorithms and building efficient, scalable applications.
- Linear Search: Simple, works on unsorted data, but slow (O(n)).
- Binary Search: Fast (O(log n)), requires sorted data.
- Interpolation Search: Very fast for uniformly distributed data (average O(log log n)), not suitable for skewed data.
- Jump Search: Better than linear, ideal for sorted data (O(√n)).
- Exponential Search: Ideal for unbounded arrays, fast (O(log i)).
- Linked List Search: Slow (O(n)), unless enhanced with skip lists.
- Tree Search: Efficient in balanced trees (O(log n)).
- Databases: SQL queries rely on search algorithms to retrieve records.
- Search Engines: Keywords are searched using trie trees and hash-based methods.
- E-commerce: Product search and filtering depend on efficient searching.
- Network Routing: Searching helps in finding paths and routes.
- Artificial Intelligence: Search techniques are used in game playing and decision making.
- Indexing: Creating indexes on fields improves search speed.
- Hashing: Provides constant-time access in ideal conditions.
- Caching: Frequently searched items can be stored for quicker access.
- Balancing: Maintaining balanced trees prevents performance degradation.
- Data Distribution Awareness: Knowing how data is distributed can help select the most suitable algorithm.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Python Developer by Enrolling in Our Python Master Program Training Course Now!
Binary Search
Interpolation Search
Interpolation search is an improved variant of binary search that works best on uniformly distributed data. Instead of dividing the list into equal halves, interpolation search estimates the position of the target value based on the distribution of data values. It uses the formula: to understand how such estimation and modular logic apply to scalable system design, exploring What are Microservices reveals how breaking applications into loosely coupled services improves maintainability, performance, and deployment flexibility across distributed architectures.
If the distribution is uniform, interpolation search can be faster than binary search, with an average time complexity of O(log log n). However, in the worst case, it still degrades to O(n), especially for skewed distributions.
Jump Search
Are You Preparing for Python Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Python Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Exponential Search
Search in Linked Lists
Searching in Trees
Tree data structures offer efficient searching capabilities. In a Binary Search Tree (BST), searching starts from the root and moves left or right depending on the comparison result. The average time complexity is O(log n), though in the worst case (unbalanced tree), it becomes O(n). Balanced trees like AVL trees or Red-Black trees maintain height balance, ensuring that the time complexity stays close to O(log n) even in the worst-case scenarios. To implement such advanced data structures with confidence and clarity, exploring Python Training reveals how mastering Python equips developers to build efficient algorithms, manage memory effectively, and solve complex problems with scalable solutions. Trie trees are another type, especially useful for prefix-based searches in strings or dictionaries, with a time complexity proportional to the length of the word being searched.
Performance Comparison
Each searching algorithm offers trade-offs between simplicity, speed, and data structure compatibility. To understand how these algorithms interact with one of Python’s most versatile data types, exploring All You Need To Know About Python List reveals how lists support dynamic resizing, indexing, and iteration making them a foundational structure for implementing search logic in real-world applications.
The best choice depends on the nature of the data and the performance requirements of the application.
Searching in Data Structures Use Cases
Searching algorithms are widely used in various fields: from databases and operating systems to artificial intelligence and cybersecurity. To understand how these algorithms fit into broader development responsibilities, exploring What Is a Software Developer reveals how professionals design, implement, and optimize such logic to build efficient, scalable, and user-centric applications across industries.
Optimizations
Several strategies can optimize search operations: from refining algorithmic logic to choosing the right data structures for the task. To understand how language choice influences implementation style and performance, exploring Kotlin vs Java reveals how both languages approach functional constructs, null safety, and syntax helping developers decide which tool best suits their application needs.
Summary
Searching in Data Structures is a cornerstone of data handling in computer science. With a variety of search algorithms available, choosing the right one depends on data structure, size, and use case. While linear search is simple, algorithms like binary, interpolation, and exponential search offer greater efficiency for sorted or large datasets. To master these techniques and apply them effectively across diverse problem sets, exploring Python Training reveals how structured learning in Python equips developers to implement search algorithms, optimize performance, and solve real-world challenges with precision. Tree-based searches and enhancements like skip lists and hashing further expand the toolkit available for developers. As data continues to grow, efficient searching will remain a key focus in building responsive and high-performance systems.





