- What is Encapsulation?
- Benefits of Encapsulation
- Importance in OOP
- Access Modifiers in Java
- Creating Getters and Setters
- Example of Encapsulation
- Real-world Applications
- Encapsulation vs Abstraction
- Data Hiding Principle
- Common Mistakes
- Code Maintenance Benefits
- Quiz or Interview Practice
What is Encapsulation?
Encapsulation in Java is one of the four fundamental principles of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), alongside inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction. It refers to the concept of wrapping data (variables) and methods (functions) together into a single unit, typically a class, and restricting direct access to some of the object’s components.
- The idea is to prevent external code from directly modifying internal object states, which ensures better control over how data is accessed or modified. This concept is a key part of Java Training where learners gain an understanding of object-oriented principles like encapsulation, which helps in designing secure and maintainable Java applications.
- This is achieved by making the fields of a class private and providing public getter and setter methods to read and modify the values indirectly.
In essence, encapsulation is a form of data protection and security for object properties.A key idea in Java is data encapsulation in java, which limits direct access to an object’s fields in order to safeguard its internal state. Data encapsulation in java guarantees improved security, maintainability, and control over how data is accessed and altered within a program by utilizing private variables and public getter and setter methods.
To Earn Your Java Training Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Game Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Java Training
Benefits of Encapsulation
The benefits of encapsulation extend beyond simple data hiding. It improves maintainability because internal code changes do not impact external code that uses the class. It makes debugging easier since each class’s data is managed in a controlled manner. Encapsulation also improves flexibility by allowing you to modify the underlying data structure without changing the interface that other code relies on. This concept is thoroughly explored in an MTech Course in CSE where students dive deep into object-oriented design principles and learn how to apply them to create scalable and maintainable software systems. This leads to a clean separation of concerns and supports modular design, which is a hallmark of well-structured software.Encapsulation code in java protects data inside a class by utilizing private variables in conjunction with public getter and setter methods. Proper encapsulation code in Java guarantees restricted data access, boosts security, and makes object-oriented programming easier to maintain.
Importance in OOP
The importance of encapsulation in OOP lies in its ability to safeguard an object’s internal state. Without encapsulation, any part of the code could modify an object’s data directly, which could lead to inconsistent states, bugs, and maintenance nightmares. Encapsulation promotes modularity, as each class can manage its own internal data without interference from other parts of the program. It also allows changes to the internal implementation without affecting the external interface, thus supporting flexibility and code reusability. Encapsulation makes it easier to apply validation rules before changing a variable’s value, ensuring only valid data is stored in the object.
The programming paradigm known as object-oriented programming, or OOP, centers code around objects, which are instances of classes. A class acts as a blueprint that specifies the characteristics and methods (behaviors) that its objects will possess. This fundamental concept is a core part of Java Basics where beginners learn how to define and use classes to structure their code, creating objects with specific properties and behaviors in Java applications. The fundamental ideas of OOP include polymorphism, which allows different classes to react differently to the same method call, inheritance, which permits new classes to inherit features from existing ones, abstraction, which conceals intricate implementation details and only displays what is required, and encapsulation, which safeguards data by limiting direct access. OOP is particularly helpful when creating large and sophisticated software systems since it encourages modular, reusable, and maintainable code by applying these concepts.
Access Modifiers in Java:
Access modifiers in Java play a crucial role in encapsulation. They define the level of access other classes or packages have to a particular variable or method. Java provides four main access modifiers: private, default (package-private), protected, and public.
- Private members are accessible only within the same class, which is the most restrictive level of access and is often used for encapsulating data.
- Public members are accessible from anywhere, while protected members are accessible within the same package and by subclasses. This concept ties directly into Java Encapsulation where access control mechanisms like public and protected access modifiers are used to enforce data hiding and protect the internal state of objects, ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible in controlled ways.
Default access allows access only within the same package. For encapsulation, fields are generally declared as private, and controlled access is provided via public getters and setters.
Creating Getters and Setters
When creating getters and setters, the process involves declaring class variables as private and then creating public methods to access and update their values. A getter method returns the current value of the variable, while a setter method allows modification of the variable’s value. This concept is part of Polymorphism in OOPS where different classes can implement getter and setter methods in various ways, allowing for flexible behavior and interaction with object properties through method overloading or overriding, ensuring code that can handle different types of objects seamlessly. The setter can include validation logic to ensure only valid data is stored. For example, if you have a private field age, the setter can check if the provided age is non-negative before setting the value. This pattern not only controls access but also ensures data integrity.
Would You Like to Know More About Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Now!
Real-world Applications
In real-world applications, encapsulation is everywhere. For example, in a banking application, the balance of a bank account is typically stored as a private field. Access to it is controlled through methods like deposit() and withdraw(), which apply business rules such as checking for sufficient funds before processing a withdrawal. This is a key concept taught in Java Training where students learn to implement encapsulation and enforce business logic through methods, ensuring the integrity and security of object states in Java applications. This prevents unauthorized or invalid operations on the account’s balance. Similarly, in e-commerce systems, product prices might be encapsulated to ensure they are only changed through authorized pricing rules and calculations.
Example of Encapsulation
Let’s look at a simple example of encapsulation in Java:
- public class Student {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- // Getter for name
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- // Setter for name
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- // Getter for age
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- // Setter for age with validation
- public void setAge(int age) {
- if(age > 0) {
- this.age = age;
- } else {
- System.out.println(“Age must be positive!”);
- }
- }
- }
An encapsulation example in Java , the name and age fields are private and cannot be accessed directly outside the Student class. The public getter and setter methods allow controlled access, with the setter for age including validation to ensure the value is valid. Developers can learn how to safeguard data, enforce regulations, and create cleaner, more maintainable code by studying a encapsulation example in Java.
Data Hiding Principle
The data hiding principle is a core part of encapsulation. By making fields private, you hide the actual data from direct access, ensuring that any change to the data must go through well-defined and controlled methods. This allows for validation, logging, security checks, and other processes before data is altered. Similarly, Literals in Java are used to represent constant values directly in the code, such as numbers, strings, or boolean values, which can be validated or processed before being assigned to variables or passed to methods. Without data hiding, an external class could modify a field directly, bypassing important business rules.
Encapsulation vs Abstraction
It is also essential to distinguish between encapsulation and abstraction, as they are related but different concepts. Encapsulation is about bundling data and methods together and restricting access to the internal state, whereas abstraction focuses on exposing only the essential features of an object while hiding the implementation details. Encapsulation is implemented using access modifiers and class structures, while abstraction can be achieved using abstract classes and interfaces. In short, encapsulation is about how you hide the data, while abstraction is about what you hide from the user.
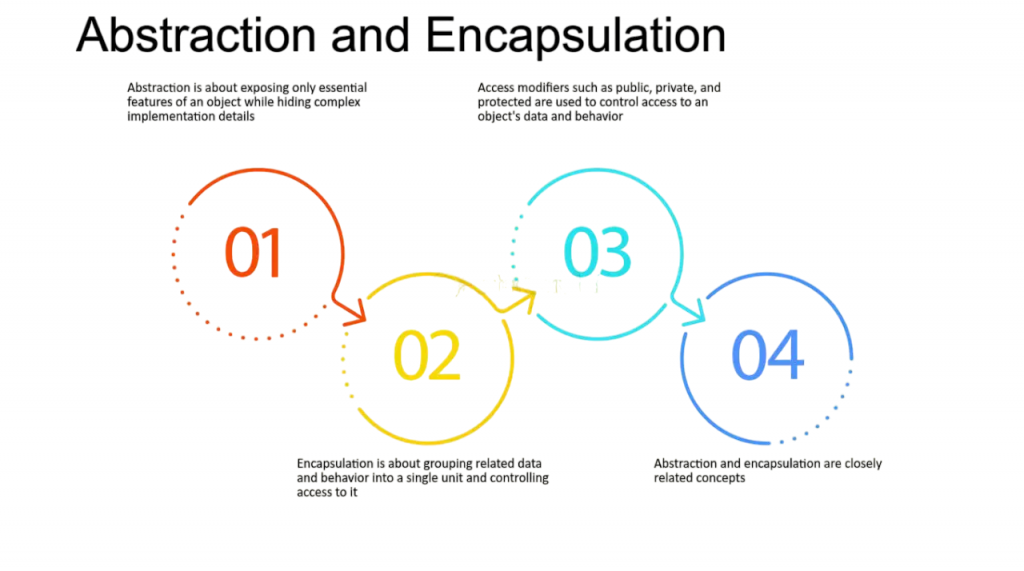
Although both abstraction and encapsulation are essential ideas in object-oriented programming, they have distinct functions. Bundling data (variables) and methods that manipulate that data into a single unit, usually a class, and limiting direct access to certain of the object’s components is known as encapsulation. Access modifiers like private, protected, and public are typically used to do this, controlling the visibility and accessibility of class members. Similarly, the Go To Statement though rarely used in modern programming, allows for an unconditional jump to another part of the code, often bypassing structured control flow, which can lead to less maintainable code. These assist safeguard the data’s integrity by prohibiting unauthorized changes from external programs. Conversely, abstraction is the practice of displaying only an object’s key characteristics while concealing intricate implementation details. To put it briefly, abstraction is about concealing complexity by offering a simplified interface, but encapsulation is about concealing the underlying state and requiring all interaction to be carried out through an object’s methods.
Preparing for Java Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Java Training Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Common Mistakes
However, there are common mistakes to avoid when implementing encapsulation. One mistake is providing public getters and setters for every private field without adding any validation or logic, which defeats the purpose of encapsulation and makes the data effectively public. Another mistake is using package-private or protected access for fields that should be strictly private, which can expose them to unintended modifications. Additionally, poor naming conventions for getters and setters can reduce code readability and cause confusion.
Code Maintenance Benefits
One of the underrated aspects of encapsulation is its code maintenance benefits. As projects grow in complexity, maintaining code without encapsulation can become extremely difficult, as you need to track down every place where a variable is directly accessed or modified. Encapsulation reduces this problem by centralizing access to data in specific methods. If the data structure changes, you only need to update the getter and setter methods, rather than every line of code that previously accessed the field directly.
Quiz or Interview Practice
Finally, for quiz or interview practice, encapsulation is a favorite topic among interviewers, as it tests a candidate’s understanding of OOP principles, coding best practices, and design patterns. Common interview questions include:
- What is encapsulation in Java?
- How is it implemented?
- What is the difference between encapsulation and abstraction?
- Why do we use private fields and public getters/setters?
- Can you provide a real-world example of encapsulation?
Preparing answers to these questions with examples will help you demonstrate a solid grasp of the concept.In summary, Java encapsulation is a powerful concept that enhances data security, maintainability, and flexibility in object-oriented applications. By wrapping data and methods into a class and controlling access via getters and setters, you can enforce business rules, validate data, and protect the integrity of your application. This approach is a fundamental concept covered in Java Training where learners understand how to design secure, maintainable software by applying principles like encapsulation and data validation within Java classes. It is not just a coding pattern but a design principle that underpins clean, modular, and robust software systems. Mastering encapsulation will not only improve your Java skills but also strengthen your overall programming and software design expertise.





