
- How to Become a Software Architect?
- Role of a Software Architect
- Required Technical Skills
- Design Patterns and Principles
- System Design and Scalability
- Software Development Life Cycle
- Coding Standards
- Mentoring and Leadership
- Conclusion
How to Become a Software Architect?
Becoming a software architect is a significant milestone in a software professional’s career. It requires not just technical expertise but also strategic thinking, communication skills, and a deep understanding of business requirements. A software architect is responsible for designing high-level software frameworks, defining system architecture, and ensuring the development team adheres to the architectural vision. The journey to becoming a software architect often begins with experience in software development and evolves through consistent learning, hands-on practice, and mentorship. Becoming a software architect is a rewarding career goal for experienced software developers who want to take on a leadership role in designing complex systems Full Stack Training. A software architect is responsible for planning, structuring, and overseeing the development of software solutions to meet business needs.To become a software architect, start by gaining strong programming skills and deep knowledge of software development principles. Most architects have several years of experience as software engineers or developers, allowing them to understand coding challenges and best practices thoroughly.Next, focus on learning system design, software architecture patterns, and design principles such as SOLID and DRY. Understanding how different components interact, ensuring scalability, reliability, and maintainability is crucial.Communication and leadership skills are equally important. Architects work closely with developers, project managers, and stakeholders to translate requirements into technical solutions. Mentoring junior developers and guiding teams is part of the role.Familiarize yourself with the full software development life cycle (SDLC) and get hands-on experience with tools and technologies relevant to your industry. Continuous learning is key.keep up with emerging technologies, C++ Vectors frameworks, and architectural trends. Certifications in architecture or cloud platforms can also boost your credentials.
Interested in Obtaining Your Full stack Certificate? View The Full Stack Developer Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Role of a Software Architect
- Designing Software Architecture: Define the overall structure and high-level design of software systems.
- Technical Leadership: Guide development teams on architectural best practices and standards.
- Requirement Analysis: Collaborate with stakeholders to understand business needs and translate them into technical solutions.
- Ensuring Scalability and Performance: Design systems that can grow and perform efficiently under load.
- Technology Selection: Evaluate and choose appropriate technologies, Backtracking Programming frameworks, and tools.
- Code Review and Quality Assurance: Oversee code quality, maintainability, and adherence to coding standards.
- Risk Management: Identify and mitigate technical risks early in the development process.
- Mentoring Developers: Support and mentor junior developers and engineers.
- Documentation: Create and maintain architecture documentation for current and future reference.
- Stakeholder Communication: Act as a bridge between technical teams and non-technical stakeholders.
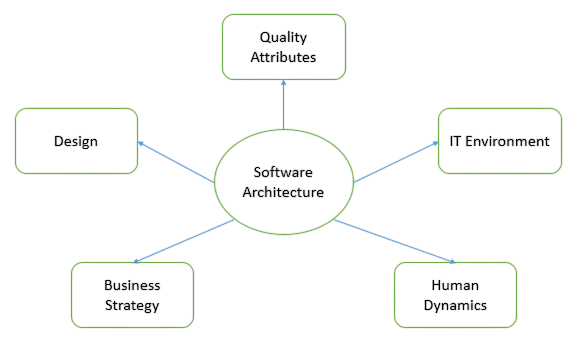
Required Technical Skills
To become a software architect, one must have a solid foundation in programming languages such as Java, Python, C#, or JavaScript. In addition, knowledge of databases (SQL and NoSQL), APIs, cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP), and DevOps practices are crucial. Architects are also expected to understand different architectural styles and patterns, such as microservices, serverless, Height of a Tree and monolithic designs. Proficiency in system integration, performance tuning, and application security is also essential. Hands-on experience with frameworks and libraries, coupled with the ability to choose the right tool for the job, differentiates great architects from good developers.
Design Patterns and Principles
- Reuse Proven Solutions: Design patterns provide reusable templates to solve common software design problems efficiently.
- Enhance Code Maintainability: Applying principles like SOLID helps create flexible and easy-to-maintain codebases.
- Promote Separation of Concerns: C Programming Examples Design principles encourage dividing software into distinct sections, improving modularity and readability.
- Facilitate Scalability: Patterns like Observer, Factory, and Singleton help build scalable and extensible systems.
- Improve Communication: Using well-known design patterns creates a common language among developers, easing collaboration and understanding.
- Requirement Gathering: Collect and analyze business and user needs.
- System Design: Plan the architecture and design specifications.
- Implementation: Write and compile the actual code.
- Testing: Verify and validate the software to find and fix defects Minimum Spanning Tree.
- Deployment: Release the software to the production environment.
- Maintenance: Provide ongoing support, bug fixes, and updates post-deployment.
- Guiding Team Members: Provide technical guidance and support to developers and engineers.
- Sharing Knowledge: Mentor junior staff to help them grow their skills and careers.
- Promoting Best Practices: Encourage adherence to coding standards, Reverse C++ Vector design principles, and quality assurance.
- Facilitating Collaboration: Foster effective communication and teamwork across cross-functional teams.
- Decision Making: Lead architectural decisions and resolve technical conflicts.
- Inspiring Innovation: Motivate teams to adopt new technologies and improve processes.
- Stakeholder Management: Bridge the gap between technical teams and business stakeholders.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Full Stack Developer by Enrolling in Our Full Stack Master Program Training Course Now!
System Design and Scalability
Software architects must master system design and scalability concepts to build applications that can handle growth. This includes designing systems that support horizontal scaling, load balancing, distributed computing, and high availability. Architects often work on high-level components like message queues, databases, caching layers, and microservices orchestration. They are also expected to make decisions about data partitioning, consistency models, Full Stack Training and eventual consistency to ensure that systems remain efficient under increased loads. System design involves planning and structuring software components to meet functional and non-functional requirements. A well-designed system ensures reliability, maintainability, and performance. Scalability is a critical aspect, focusing on the system’s ability to handle increased load by efficiently utilizing resources. This can be achieved through techniques like load balancing, caching, database sharding, and horizontal scaling. Architects must design systems that can grow seamlessly without performance degradation. Understanding user demand, choosing appropriate architectures (e.g., microservices or monoliths), and anticipating future growth are essential for building scalable, robust software solutions.
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
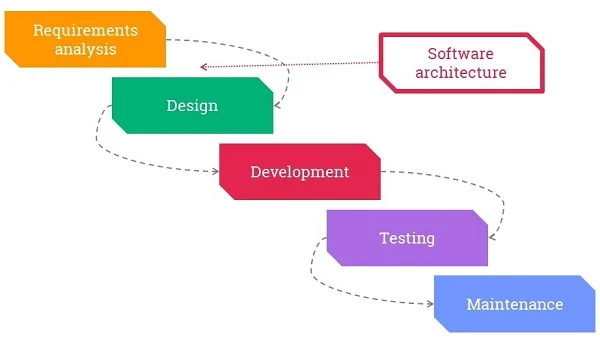
Are You Preparing for Full Stack Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Full stack Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Coding Standards
Though architects may not write code daily, they are responsible for defining and enforcing coding standards across the development team. This ensures consistency, readability, and maintainability of the codebase. They may introduce tools such as linters, code formatters, and CI/CD pipelines to automate quality checks. Coding standards also extend to practices such as version control, commenting, and modular programming, which collectively contribute GUI Tkinter Module to the efficiency and quality of the software product. Coding standards are a set of guidelines and best practices that developers follow to write clean, consistent, and maintainable code. They help improve code readability, reduce errors, and facilitate collaboration among team members. Standards typically cover naming conventions, indentation, comment styles, and file organization. Adhering to coding standards ensures uniformity across the codebase, making it easier to review, debug, and extend. Many organizations adopt industry-recognized standards like Google’s or Microsoft’s coding guidelines, and use automated tools to enforce them. Consistent coding practices are essential for long-term project success and effective teamwork.
Mentoring and Leadership
Conclusion
To become a successful software architect, focus on building a broad and deep understanding of technology. Practice designing systems, seek mentorship, contribute to open-source projects, and write about your experiences. Stay curious, learn from failures, and always consider the business impact Full Stack Training of your technical decisions. Being a software architect is as much about leadership and communication as it is about technical proficiency. By blending these skills, you can build solutions that are not only functional and scalable but also aligned with long-term organizational goals.





