
- Introduction to C++ and Java
- History and Background of Both Languages
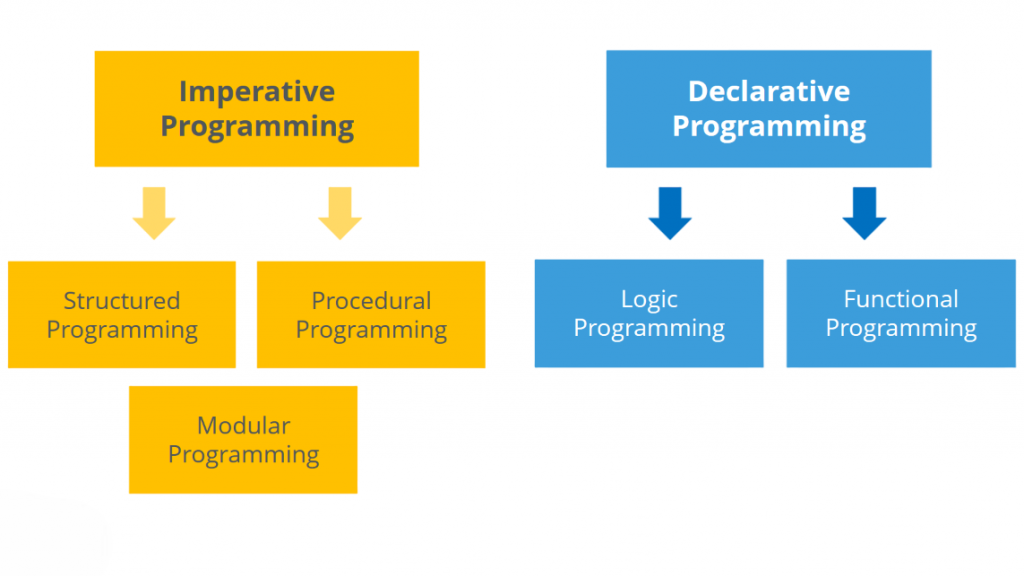
- Language Paradigm and Design Principles
- Syntax and Code Structure Comparison
- Object-Oriented Programming Support
- Memory Management and Garbage Collection
- Performance and Execution Speed
- Platform Independence and Portability
- Exception Handling Mechanisms
- Use Cases and Industry Applications
- Conclusion
Introduction to C++ and Java
C++ vs Java are two of the most popular programming languages in the software industry, each strong in different areas. C++ is known for its high performance and direct memory management, making it a great option for system programming and applications that require fast processing. In contrast, Java focuses on usability and flexibility, as it runs well on different platforms. Its emphasis on security and ease of development makes it especially popular for enterprise applications and web development. To build expertise in these areas, exploring Java Training reveals how structured learning in Java equips developers to design secure, scalable, and cross-platform solutions while understanding the nuanced differences between C++ and Java. Although both languages share similarities due to their C language roots, mastering the differences in C++ vs Java enables developers to choose the right tool for their specific project needs.
To Earn Your Java Training Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Java Training Today!
History and Background of Both Languages
C++ was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup in the early 1980s as an extension of the C programming language. It introduced object-oriented features to C and was initially called “C with Classes.” Over time, it evolved into a fully-featured programming language suitable for system/software development. Java was created by James Gosling and his team at Sun Microsystems in 1995. It was developed with the idea of “Write Once, Run Anywhere,” offering platform independence through the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). To understand how other languages approach data handling and scripting, exploring SQL and Python Comparison reveals how SQL excels in structured data queries while Python offers flexibility for automation, analytics, and application development. Java’s popularity surged with the rise of internet-based applications and enterprise software.
Language Paradigm and Design Principles
- C++ supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented, and generic programming. It allows developers to write both low-level system code and high-level application logic. This flexibility comes at the cost of complexity, as developers must manage memory and other resources manually.
- To optimize data access and retrieval within such systems, exploring Hashing in Data Structures reveals how hash functions and tables enable constant-time lookups, efficient storage, and collision resolution strategies crucial for high-performance applications.
- Java is strictly object-oriented (except for primitive types) and emphasizes simplicity and consistency. It abstracts many low-level details such as memory management, making it easier to use and maintain. Java enforces a cleaner object-oriented approach with features like interfaces and abstraction.
- Both C++ and Java have C-like syntax, using curly braces for code blocks, semicolons for line termination, and similar control structures. However, they differ in their standard libraries, header inclusion, and syntax for features like exception handling, inheritance, and generics.
- To understand how these language-level choices impact system design, exploring Software Architect reveals how mastering architectural principles, design patterns, and technology stacks enables professionals to make informed decisions across diverse programming environments.
- For instance, C++ uses #include for headers and supports both function overloading and operator overloading. Java uses import statements and doesn’t support operator overloading. In Java, everything resides in a class, whereas C++ allows global functions and variables.
- C++ provides manual memory management through new and delete operators. Developers have direct control over memory allocation and deallocation, which allows for optimization but also introduces risks like memory leaks and dangling pointers.
- To explore how modern languages handle scope and memory differently, JavaScript Closure Example reveals how closures preserve access to variables even after outer functions have executed enabling safer, more flexible memory handling in asynchronous environments.
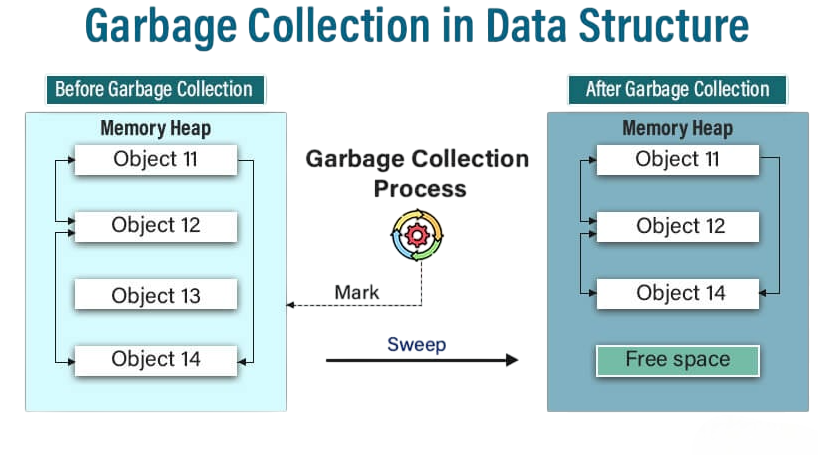
- Java automates memory management with its built-in garbage collector. Developers don’t have to explicitly manage memory, reducing the chances of memory-related bugs. However, garbage collection can introduce latency and performance overhead in certain situations.
- C++ generally outperforms Java in terms of execution speed, especially for applications that require high-performance computing, such as game engines or real-time systems. This is due to its compilation to native machine code and absence of runtime overhead.
- Java is slower in comparison because it runs on the JVM, which interprets or compiles bytecode at runtime. However, Java’s Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler and modern JVM optimizations have significantly improved its performance for most applications.
- When choosing between C++ and Java for your project, it’s essential to consider your specific needs. C++ excels when you need high performance and tight control over system resources. It’s a good fit for applications like video games, financial trading, and situations where every bit of efficiency matters. In contrast, Java is ideal if you want your application to work on multiple platforms easily.
- To understand how these languages interact with hardware and software environments, exploring Operating Systems reveals how memory management, process scheduling, and system calls influence application behavior across platforms.
- It supports fast development, strong security features, and excellent scalability, making it a popular option for enterprise apps, mobile projects, and cloud solutions. Both languages have unique benefits, so understanding their differences helps developers pick the right tool for the job. This ensures that the final product meets all requirements effectively.
Would You Like to Know More About Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Now!
Syntax and Code Structure Comparison
Object-Oriented Programming Support
Both languages support the core principles of OOP: inheritance, encapsulation, abstraction, and polymorphism. C++ offers more granular control with multiple inheritance and virtual functions, while Java simplifies these features by using single inheritance and interfaces to resolve ambiguity. To gain practical experience with these object-oriented principles, exploring Java Training reveals how structured learning in Java helps developers build scalable applications while mastering inheritance, abstraction, and interface-driven design. Java’s runtime type identification and reflection make it more flexible for dynamic operations. Meanwhile, C++ allows more direct manipulation of memory, providing features like object slicing and pointers to functions or objects.
Memory Management and Garbage Collection
Are You Interested in Learning More About FullStack With Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Today!
Performance and Execution Speed
Platform Independence and Portability
Java is designed to be platform independence. Its compiled bytecode can run on any system that has a JVM installed, fulfilling the promise of “Write Once, Run Anywhere.” This makes Java especially suitable for cross-platform applications. C++ is platform-dependent by default. The compiled code is specific to the target operating system and hardware. To understand how Java maintains modularity and security across platforms, exploring Java Encapsulation Explained reveals how encapsulation hides internal object states, enforces access control, and promotes clean, maintainable code in enterprise-grade applications. While it’s possible to write portable C++ code, developers must consider compiler differences, system calls, and libraries.
Preparing for Java Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Java Training Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Exception Handling Mechanisms
Both C++ and Java have ways to handle exceptions using try, catch, and throw, but they handle them differently. Java’s approach is stricter. It uses checked exceptions, meaning programmers must either handle or declare exceptions in their code. This rule makes Java programs more reliable by ensuring that possible errors are addressed. In contrast, C++ offers more flexibility since it does not use checked exceptions. To understand how data flows and errors are managed in sequence-based logic, exploring Linear Data Structure reveals how arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues operate in predictable order making them essential for building robust, error-aware applications. While this allows developers more freedom in coding, it can also result in uncaught runtime errors if exceptions are not properly managed. C++ also has a feature called exception specification, but it is rarely used in modern coding. The differences in how these two languages manage exceptions are important for developers when they choose tools for building strong applications.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Conclusion
C++ vs Java requires careful consideration of the specific needs of your project. C++ is often the best choice for applications where performance and direct control over the system are crucial. It works well in areas like gaming, high-frequency trading, and situations with limited system resources. In contrast, if your project needs to run on different platforms, requires quick development, offers strong security, and can easily scale, Java might be the better option. To build expertise in such platform-independent development, exploring Java Training reveals how mastering Java’s core libraries, frameworks, and deployment strategies prepares developers for enterprise-grade applications across diverse environments. Understanding C++ vs Java allows developers to weigh the trade-offs between speed, flexibility, and portability. Both languages have their unique strengths, making them valuable in software development. By analyzing C++ vs Java, developers can make informed decisions and choose the right tool for their project’s specific needs.





