
- Introduction to Business Process Management (BPM)
- What is JBPM?
- Architecture and Core Components of JBPM
- Installation and Setup Guide
- Understanding Business Processes and Workflows
- Creating a Simple JBPM Process
- JBPM Designer and Workflow Modeling
- Human Tasks and Service Tasks
- Conclusion
Introduction to Business Process Management (BPM)
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic approach to improving an organization’s processes to enhance efficiency, effectiveness, and adaptability. It involves analyzing, designing, implementing, monitoring, and optimizing business processes to meet organizational goals and customer needs. BPM focuses on processes rather than individual tasks, enabling organizations to streamline workflows, reduce costs, and improve service quality. By mapping out processes, businesses can identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies, allowing for continuous improvement. Modern BPM often integrates technology, such as workflow automation tools and software, to facilitate real-time process management and data-driven decision-making Java Training. This enables organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions, regulatory requirements, and customer expectations. Moreover, BPM fosters collaboration across departments by clearly defining roles and responsibilities within processes. This alignment helps ensure that everyone in the organization works towards common objectives. Ultimately, BPM is not just about automation but about creating a culture of ongoing process optimization and innovation. By embracing BPM, organizations can enhance agility, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve sustainable business growth.
To Earn Your Java Training Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Java Training Today!
What is JBPM?
JBPM (Java Business Process Management) is a flexible, open-source workflow engine written in Java. It allows you to model, execute, and monitor business processes written in BPMN 2.0 (Business Process Model and Notation). JBPM supports both developers and business analysts in creating process-driven applications. It’s maintained by the KIE (Knowledge Is Everything) group under Red Hat and is a part of the Drools rule engine ecosystem Socket Programming in Java. Its integration with rules, events, and business logic makes it powerful for dynamic workflow execution.
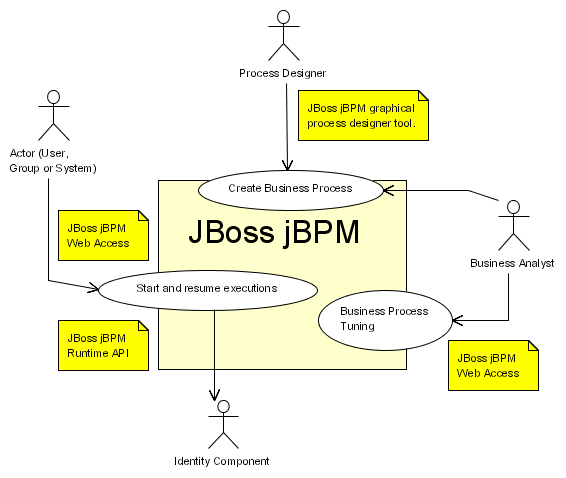
jBPM (Java Business Process Management) is an open-source workflow and business process management engine written in Java. It allows organizations to model, execute, and monitor business processes using a flexible and scalable platform. jBPM supports BPMN 2.0 (Business Process Model and Notation) standards, enabling easy design and automation of complex workflows. It integrates well with Java applications and provides tools for process modeling, execution, and analytics. jBPM helps businesses automate routine tasks, improve process efficiency, and gain better visibility into operations, making it a popular choice for enterprise process management.
Architecture and Core Components of JBPM
The JBPM architecture is modular and scalable. The key components are:
- JBPM Engine: The core of the system responsible for interpreting and executing business processes.
- BPMN2 Modeler: A graphical editor for designing workflows.
- Human Task Service: Handles user interactions like approvals and reviews Purpose Of Abstract Class .
- Persistence Layer: Integrates with JPA/Hibernate to store process state.
- Task Service: Provides REST and Java APIs for managing user tasks.
- Process Designer (Web or Eclipse-based): Used for creating and editing BPMN 2.0 diagrams.
JBPM can run in standalone mode, embedded within a Java application, or as part of a web-based business suite (e.g., KIE Workbench).
Would You Like to Know More About Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Now!
Installation and Setup Guide
Getting started with JBPM can be done in multiple ways:
Using JBPM Workbench:
- Download the full JBPM Business Suite or KIE Workbench from the official JBPM site.
- Extract the archive and run standalone.sh or standalone.bat.
- Open your browser at http://localhost:8080/business-central.
- Add JBPM dependencies in your Maven pom.xml Reverse a String in Java .
- Include core modules like jbpm-flow, jbpm-human-task-core, and kie-api.
- Install the BPMN2 Modeler and Drools plugin to model and execute processes from Eclipse.
- Once installed, ensure that your JDK (Java Development Kit) is correctly configured and that you have access to a database (e.g., H2, MySQL, PostgreSQL) for persistence.
Using Maven or Java Project:
JBPM Eclipse Plugin:
Understanding Business Processes and Workflows
- Business Processes: A series of structured activities or tasks performed to achieve a specific organizational goal or outcome.
- Workflows: The sequence and automation of these tasks or activities, often involving multiple people or systems.
- Purpose: To improve efficiency, consistency, and quality in delivering products or services.
- Components: Includes inputs, tasks, decision points, roles, and outputs Java Serialization .
- Types: Can be simple (linear) or complex (with parallel tasks and loops).
- Visualization: Often represented using flowcharts or BPMN diagrams for clarity.
- Automation: Workflows can be automated using BPM tools to reduce manual effort and errors.
- Benefits: Enhances collaboration, transparency, accountability, and process optimization.
Creating a Simple JBPM Process
- Set Up Environment: Install jBPM tools like jBPM Workbench or KIE Workbench, or set up the jBPM libraries in your Java project.
- Create a New Project: Start a new BPM project within the workbench or your IDE.
- Design the Process: Use the BPMN 2.0 graphical editor to design your workflow. Typically, start with a Start Event, add Tasks (user or automated), Installation and Setup Guide and end with an End Event.
- Add Tasks: Define task types (user tasks for manual input or service tasks for automation) and assign actors or services StringBuilder Methods in Java.
- Define Transitions: Connect the tasks with sequence flows that control the order of execution.
- Configure Process Variables: Set up variables to pass data between tasks.
- Deploy the Process: Build and deploy your process definition to the jBPM runtime environment.
- Execute and Monitor: Start process instances and monitor their progress via the workbench or API.
Are You Interested in Learning More About FullStack With Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Today!
JBPM Designer and Workflow Modeling
jBPM Designer is a powerful, user-friendly graphical tool integrated into the jBPM ecosystem that allows users to model business processes using the BPMN 2.0 standard. It simplifies the creation of workflows by providing a drag-and-drop interface where users can design, visualize, and edit process diagrams without needing extensive coding knowledge. Workflow modeling in jBPM involves defining a sequence of activities or tasks that represent business operations. Using the designer, What Is the Java API users can create start and end events, user tasks, service tasks, gateways (decision points), and other BPMN elements to map out complex business processes. This visual approach ensures clarity, making it easier to understand and communicate workflows across teams.
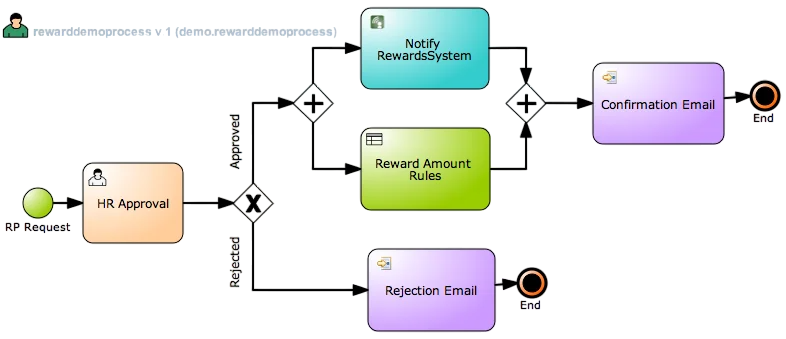
jBPM Designer also supports defining process variables, event listeners, timers, and subprocesses, enabling more dynamic and flexible process behaviors. Once a workflow is designed, it can be deployed to the jBPM engine, where it can be executed, monitored, Java Training and managed in real time. By combining intuitive design tools with powerful execution capabilities, jBPM Designer helps organizations automate their business processes efficiently, improve collaboration, and adapt quickly to changing business needs.
Preparing for Java Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Java Training Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Human Tasks and Service Tasks
In Business Process Management (BPM), tasks are fundamental building blocks that represent work to be done within a process. Two common types of tasks are Human Tasks and Service Tasks, each serving distinct purposes. Human Tasks require manual intervention by a person. These tasks are assigned to users or groups and often involve decision-making, approvals, data entry, or other activities that cannot be fully automated. In jBPM, human tasks can be managed via task lists or workbenches, allowing users to claim, complete, C++ and Java or delegate tasks. Human tasks help ensure that critical business processes incorporate necessary human judgment and oversight. Service Tasks, on the other hand, are automated tasks performed by systems or services without human intervention. These tasks execute predefined logic such as invoking web services, running scripts, or interacting with databases. Service tasks help streamline workflows by automating routine, repetitive, or integration-heavy operations. Together, human and service tasks enable hybrid workflows that combine automation with human expertise. This balance enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and maintains flexibility. In jBPM, both task types can be modeled using BPMN 2.0 elements, allowing seamless orchestration of complex business processes that involve people and technology working in harmony.
Conclusion
JBPM empowers organizations to automate, manage, and optimize their business workflows. With support for BPMN 2.0, seamless Java integration, and a powerful web-based designer, it bridges the gap between business users and developers. Whether you’re creating approval flows, service orchestration, or hybrid automation pipelines, JBPM offers a flexible and scalable solution. Business Process Management (BPM) and tools like jBPM play a vital role in helping organizations optimize their workflows Java Training by combining automation with human decision-making. By effectively modeling processes and leveraging both human and service tasks, Creating a Simple JBPM Process, businesses can increase efficiency, reduce errors, and improve collaboration across teams. With user-friendly tools like jBPM Designer, creating, executing, and monitoring complex workflows becomes accessible, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to changing needs and achieve sustainable growth. Embracing BPM fosters a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring processes remain aligned with strategic goals.





