
- Understanding Functions and Their Role
- Function Declaration vs Definition
- Function Calling Mechanisms
- Return Type and void Functions
- Parameter Passing by Value
- Using Multiple Parameters
- Recursion in C Functions
- Variable Scope and Lifetime
- Static vs Global Variables
- Conclusion
Understanding Functions and Their Role
One of the most important building blocks in the function in C Programming. A function is a block of code that performs a specific task, and it can be reused multiple times within a program. Functions improve program modularity, reduce code redundancy, and make programs easier to maintain and debug. To extend these principles into scalable infrastructure, exploring Cloud Computing Training reveals how modular design supports cloud-native development enabling efficient resource allocation, seamless deployment, and maintainable architectures across distributed environments. In C, functions allow programmers to break large programs into smaller, manageable modules, where each module handles a specific functionality. For example, instead of writing the same piece of code multiple times for mathematical calculations, we can define a function once and call it wherever required.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Course Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Course Today!
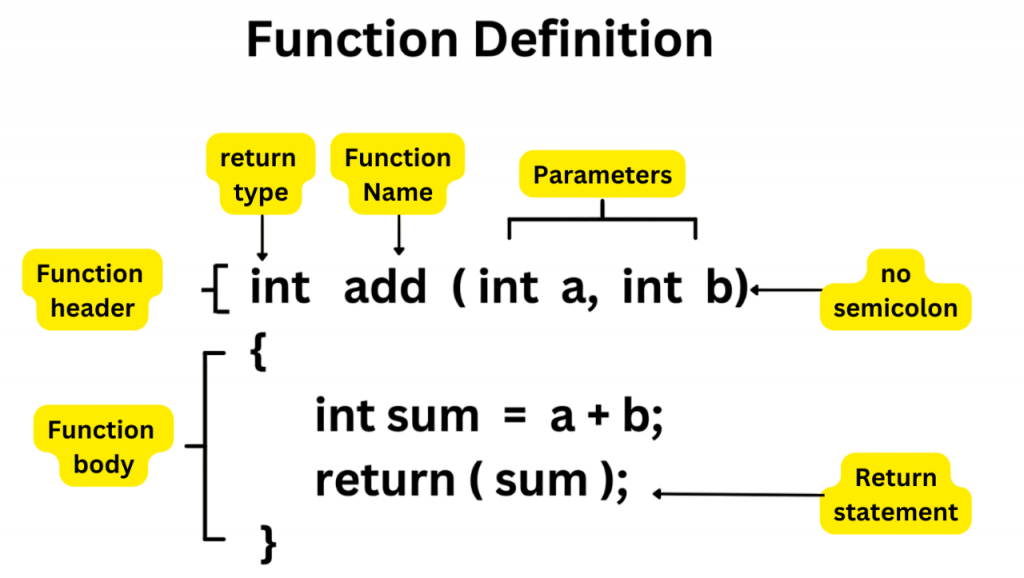
Function Declaration vs Definition
Function in C Programming, it’s important to declare functions before using them. A function declaration, or prototype, gives the compiler key details about the function, like its name, return type, and parameters. This allows the compiler to handle function calls, even if the actual function definition appears later in the code. To streamline such development workflows across languages, exploring Python IDEs and Code Editors reveals how modern tools offer syntax highlighting, auto-completion, and debugging support making it easier to manage declarations, definitions, and code structure efficiently.
- int add(int a, int b);
- return_type function_name(parameter_list);
- int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; }
The function definition, on the other hand, includes the full code that runs when the function is called. It follows the declaration but has a block of code enclosed in curly braces. Here’s an example of the function definition, Function declarations can be in header files, while definitions are usually in .c files. This clear organization helps keep the code clear and manageable.
Function Calling Mechanisms
A function can be called from the main() function or from other functions. When a function is called, the control of the program transfers to that function’s body, executes its statements, and then returns control back to the calling function. The syntax for calling a function is straightforward: To explore how modern languages handle function calls and concurrency, Go Programming Language reveals how Go’s lightweight goroutines, strict typing, and clean syntax make it ideal for building scalable, efficient systems.
- int sum = add(5, 10);
The values passed during the function call are called arguments, and the variables that receive these values in the function definition are called parameters. In C, arguments are passed by value by default, meaning that a copy of the variable is passed to the function, and changes to it do not affect the original variable outside the function.
Would You Like to Know More About Cloud Computing Course? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Course Now!
Return Type and void Functions
Every function in C Programming has a return type that specifies the kind of value it returns to the caller. For instance, a function returning an integer will have the return type int, and a function returning a floating-point value will have a float. If a function doesn’t return any value, it has the return type void. Example of a function returning an integer:
- int multiply(int x, int y) {
- return x * y;
- }
- // Example of a void function:
- void greet() {
- printf(“Hello, World!\n”);
- }
While return values are useful for sending results back to the calling function, void functions are used for tasks like displaying output or performing actions that do not require a return value. To understand how function behavior varies across contexts, exploring Python Scopes and Their Built-in Functions reveals how local, global, and nonlocal scopes interact with built-in methods empowering developers to write cleaner, more predictable code in Python.
Parameter Passing by Value
In pass-by-value, which is the default in C, the arguments provided to a function are copied into the parameters. The function works with these copies, so any modification inside the function does not affect the original variables in the caller. To explore how output and data representation differ across languages, Python String Formatting reveals how f-strings, format(), and interpolation techniques allow developers to present values cleanly and dynamically enhancing readability and control in Python applications.
Example:
- void changeValue(int x) {
- x = 20;
- }
- int main() {
- int a = 10;
- changeValue(a);
- printf(“%d”, a); // Output: 10
- }
Since only a copy of a was changed inside the function, the original value remains unaffected. This behavior ensures data integrity but can be inefficient for large data structures, in which case pointers are used to simulate pass-by-reference.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course Now!
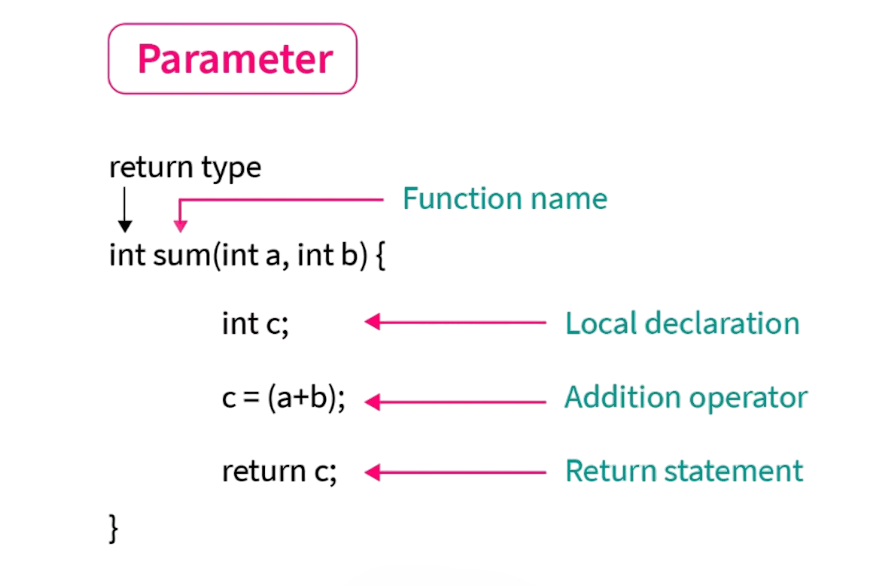
Using Multiple Parameters
Functions can take multiple parameters, separated by commas in the declaration and definition. This allows for greater flexibility, enabling functions to work with multiple inputs at once. For example: To extend this flexibility into scalable systems, exploring Cloud Computing Training reveals how cloud platforms handle multi-parameter APIs, distributed workloads, and modular services empowering developers to build dynamic, input-driven architectures across virtual environments.
- int calculateArea(int length, int width) {
- return length * width;
- }
- // When calling such a function:
- int area = calculateArea(5, 10);
Each argument is matched with the corresponding parameter in order. The number, type, and order of arguments passed during a call must match the parameters defined in the function prototype.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing Course? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Course Today!
Recursion in C Functions
Recursion is a programming technique where a function calls itself to solve problems. It works well for tasks that can be broken down into smaller, similar tasks. For example, calculating a factorial or generating the Fibonacci series are classic examples of recursive functions. Each recursive function has two key parts. The first is the base case, which defines when the recursion should stop and prevents infinite loops. The second part is the recursive case, where the function calls itself with adjusted parameters to get closer to the base case. By breaking complex problems into smaller steps, recursion allows for elegant and efficient solutions. Understanding these elements is essential for anyone who wants to master this powerful method in programming.
- int factorial(int n) {
- if (n == 0)
- return 1; // Base case
- return n * factorial(n – 1); // Recursive case
- }
While recursion can make code cleaner, it can also lead to stack overflow if not handled carefully, so an appropriate base case is crucial. To preserve recursive data structures or transmit them across systems, exploring Python Serialization reveals how modules like `pickle` and `json` convert complex objects into storable formats enabling safe data exchange, persistence, and recovery in Python applications.
Preparing for Cloud Computing Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Variable Scope and Lifetime
The scope of a variable refers to where it can be accessed within a program, and lifetime refers to how long the variable exists in memory. In C, function parameters and variables declared inside a function are local variables, accessible only within that function. They have automatic storage duration, meaning they are created when the function is called and destroyed when it ends. Variables declared outside all functions are global variables and can be accessed from any function in C Programming.
- int globalVar = 5;
- void display() {
- int localVar = 10;
- printf(“%d %d”, globalVar, localVar);
- }
Local variables in different functions are independent of each other, even if they share the same name. To understand how such scope isolation contributes to robust application design, exploring What is .Net FrameWork reveals how the .NET runtime manages memory, enforces type safety, and supports modular development across desktop, web, and cloud-based environments.
Static vs Global Variables
Global variables are declared outside all functions and maintain their value throughout the program execution. Static variables can be local or global, but when used inside a function, they retain their value between function calls. This makes them useful for counting function calls or preserving state. To ensure such behavior aligns with expected outcomes, exploring What is Quality Assurance reveals how systematic testing, validation, and process control help maintain reliability, detect anomalies, and uphold coding standards throughout the software lifecycle.
- void counter() {
- static int count = 0;
- count++;
- printf(“%d\n”, count);
- }
Every time counter() is called, count keeps incrementing instead of resetting to 0.
Conclusion
Function in C Programming are important in structured programming because they promote modularity and allow for code reuse. They enable developers to break complex problems into smaller, manageable parts. By understanding key concepts like declarations, definitions, parameter passing, and recursion, programmers can create clear and efficient code. To scale these principles into distributed environments, exploring Cloud Computing Training reveals how modular thinking supports cloud-native architectures enabling seamless deployment, resource optimization, and resilient system design across virtualized platforms. Knowing variable scope helps manage data access, which leads to fewer errors and greater clarity. Whether you are writing simple utility functions or dealing with complex recursive algorithms, functions help you organize programs logically. This organization improves development, makes testing easier, and ensures simpler maintenance.





