Anaconda is the world’s most popular Data Science platform for Data Scientists and IT professionals. In this Python Anaconda tutorial, you will learn about Anaconda and its benefits, the installation process and how you can work with Anaconda, and in the end, we will peek over the companies that are using Anaconda in their workflow.
What is Anaconda?
Some tutorials install packages with conda instead of pip. So what is conda?

Anaconda is a distribution of Python (and R). It is free and open-source and makes package management and deployment simpler. Keep reading to see how. It is the standard platform for Python data science and open-source machine learning. Anaconda is used by data scientists, IT professionals and business leaders.
Benefits of Using Python Anaconda
Why should you use Anaconda for your project? Well, it does have the following benefits:
- It is free and open-source
- It has more than 1500 Python/R data science packages
- Anaconda simplifies package management and deployment
- It has tools to easily collect data from sources using machine learning and AI
- It creates an environment that is easily manageable for deploying any project
- Anaconda is the industry standard for developing, testing and training on a single machine
- It has good community support- you can ask your questions there.
What you get
- Download more than 1500 Python/R data science packages
- Manage libraries, dependencies, and environments with conda
- Build and train ML and deep learning models with scikit-learn, TensorFlow and Theano
- Use Dask, NumPy, Pandas and Numpy to analyze data scalably and fast
- Perform visualization with Matplotlib, Bokeh, Datashader, and Holoviews
Python Anaconda Installation
Next in the Python anaconda tutorial is its installation. The latest version of Anaconda at the time of writing is 2019.07. Follow these steps to download and install Anaconda on your machine:
1. Go to this link and download Anaconda for Windows, Mac, or Linux: – Download anaconda
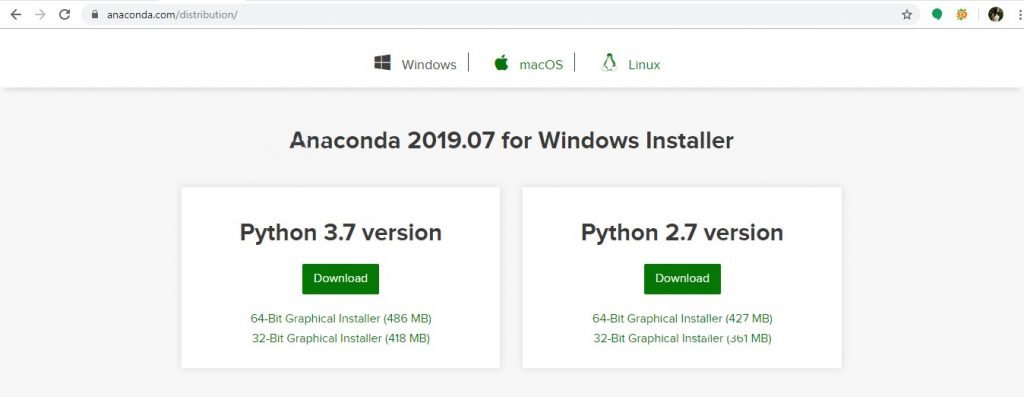
You can download the installer for Python 3.7 or for Python 2.7 (at the time of writing). And you can download it for a 32-bit or 64-bit machine.
2. Click on the downloaded .exe to open it. This is the Anaconda setup. Click next.
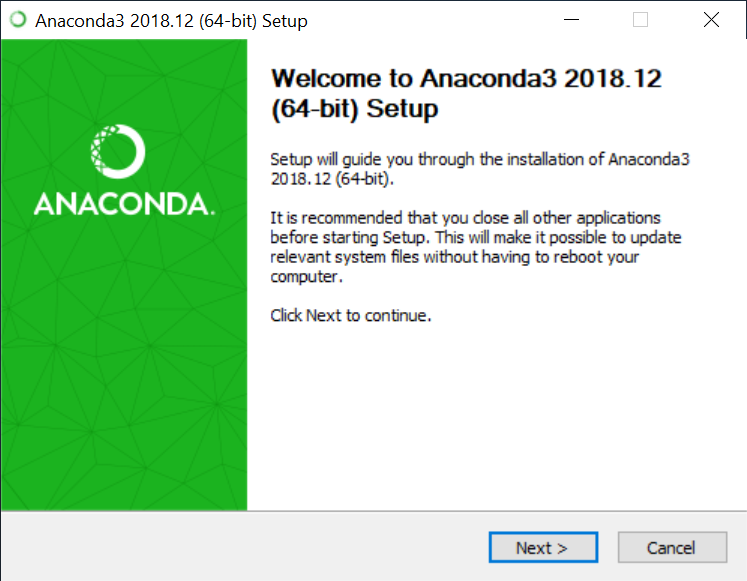
3. Now, you’ll see the license agreement. Click on ‘I Agree’.
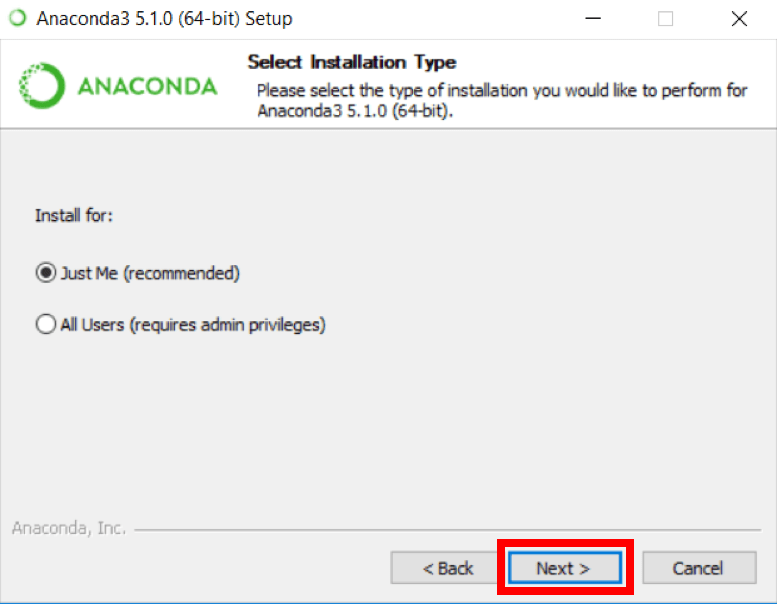
4. You can install it for all users or just for yourself. If you want to install it for all users, you need administrator privileges.
5. Choose where you want to install it. Here, you can see the available space and how much you need.
6. Now, you’ll get some advanced options. You can add Anaconda to your system’s PATH environment variable, and register it as the primary system Python 3.7. If you add it to PATH, it will be found before any other installation. Click on ‘Install’.
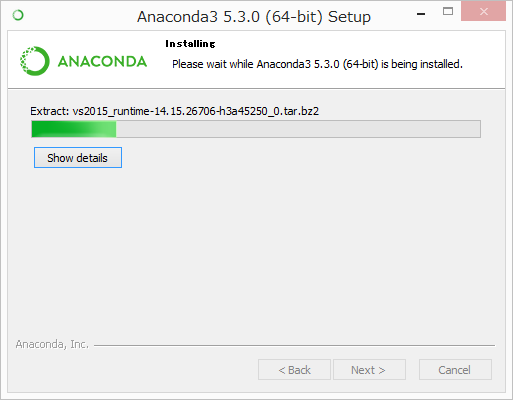
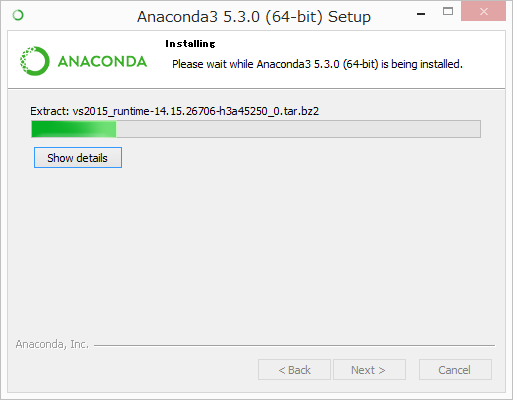
7. It will unpack some packages and extract some files on your machine. This will take a few minutes.
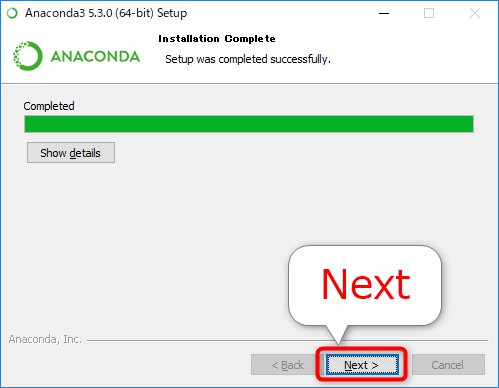
8. The installation is complete. Click Next.
9. This screen will inform you about PyCharm. Click continue.
10. The installation is complete. You can choose to get more information about Anaconda cloud and how to get started with Anaconda. Click Finish.
11. If you search for Anaconda now, you will see the following options:
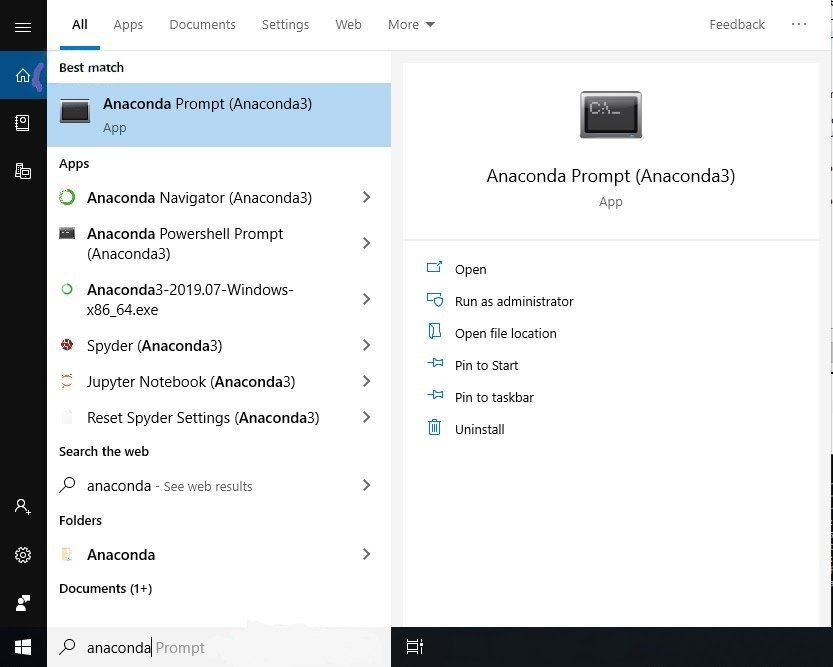
- The Anaconda prompt
- Anaconda Navigator
- Anaconda Powershell prompt
- Spyder IDE
- and Jupyter Notebook
If you go to your command prompt and type ‘jupyter notebook’, it will open the Jupyter dashboard for you.
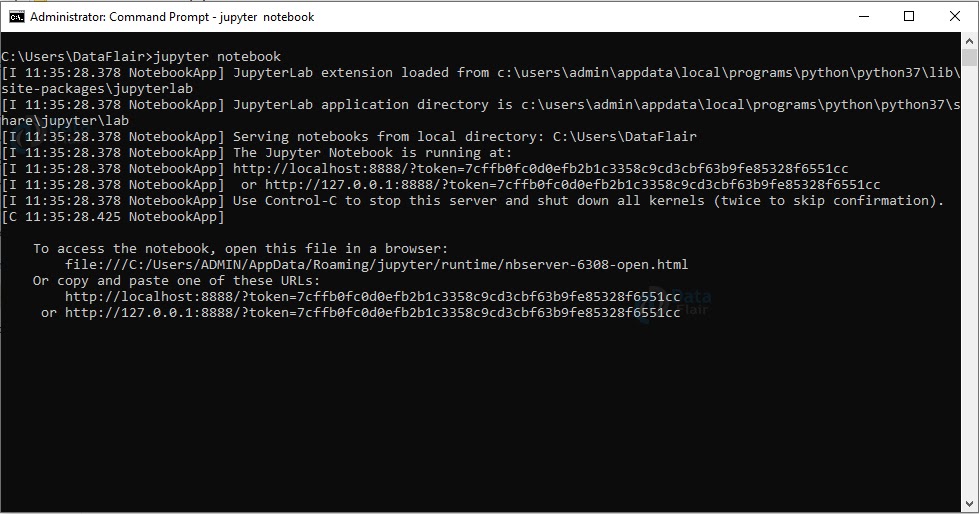
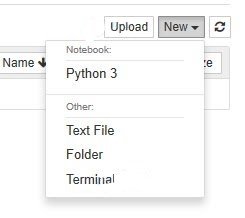
This is your new notebook. You can type in this. To execute a statement or multiple statements at once, press Shift+Enter. Pressing only Enter will only take you to the next line.
Installing Python Anaconda Libraries
You have successfully installed Anaconda. Now, how will you install libraries or packages with it? Let’s see how.
Open the Anaconda Prompt and use the ‘conda install command’ with the package name.
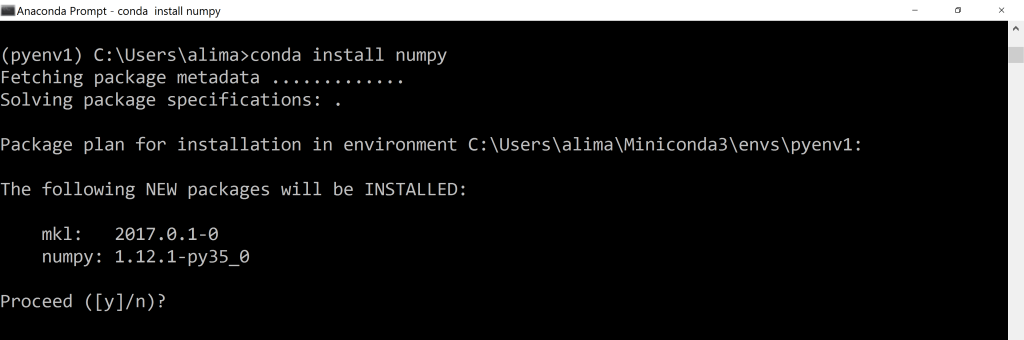
You must check top python libraries
Now, you can install this package.
Anaconda Navigator
- Anaconda Navigator is a desktop GUI that ships with Anaconda and lets you launch applications and manage conda packages, environments, and channels without having to use a command-line interface.
- It can search for packages in a local Anaconda repository or on Anaconda Cloud. With Navigator, you don’t need to type commands in a terminal, it lets you work with packages and environments with just a click.

With Navigator, you can access:
- JupyterLab
- Jupyter Notebook
- QTConsole
- Spyder
- VSCode
- Glueviz
- Orange 3 App
- Rodeo
- RStudio
At the time of writing, the latest version of Anaconda is 1.9.7.
Installing Anaconda on MacOS
- This section details the installation of the Anaconda Distribution of Python on MacOS. Most versions of MacOS come pre-installed with legacy Python (Version 2.7). You can confirm the legacy version of Python is installed on MacOS by opening and running a command at the MacOS terminal. To open the MacOS terminal use [command]+[Space Bar] and type terminal in the Spotlight Search bar.
- In the MacOS Terminal type (note: the dollar sign $ is used to indicate the terminal prompt. The dollar sign $ does not need to be typed): $ python
- You will most likely see Python version 2.7 is installed. An issue for MacOS users is that the installed system version of Python has a set of permissions that may always allow Python to run and may not allow users to install external packages. Therefore, I recommend the Anaconda distribution of Python is installed alongside the system version of Python that comes pre-installed with MacOS.
- You will be able to run Python code using the Anaconda distribution of Python, and you will be able to install external packages using the Anaconda distribution of Python.
Follow the steps below to install the Anaconda distribution of Python on MacOS.
Steps:
- Visit Anaconda.com/downloads
- Select MacOS and Download the .pkg installer
- Open the .pkg installer
- Follow the installation instructions
- Source your .bash-rc file
- Open a terminal and type python and run some code.
1. Visit the Anaconda downloads page
Go to the following link: Anaconda.com/downloads
2. Select MacOS and download the .pkg installer
In the operating systems box, select [MacOS]. Then download the most recent Python 3 distribution (at the time of this writing the most recent version is Python 3.6) graphical installer by clicking the Download link. Python 2.7 is legacy Python. For problem solvers, select the most recent Python 3 version.
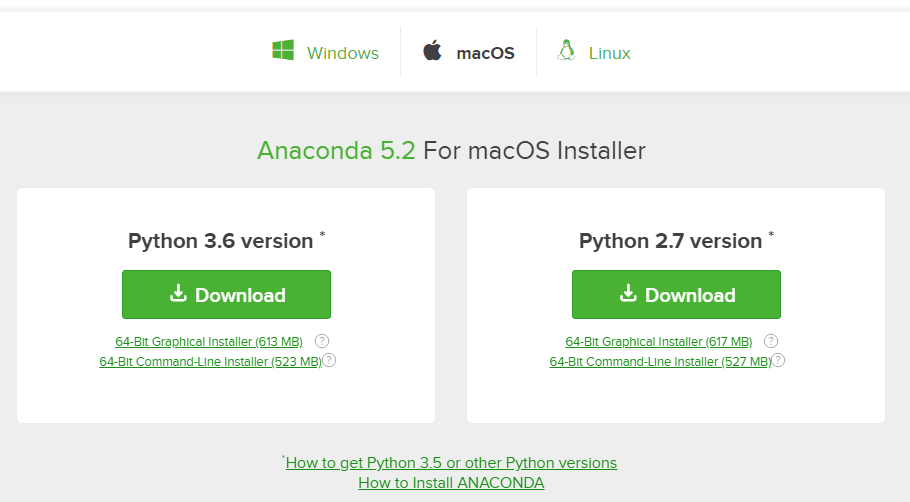
You may be prompted to enter your email. You can still download Anaconda if you click [No Thanks] or [x] and don’t enter your Work Email address.
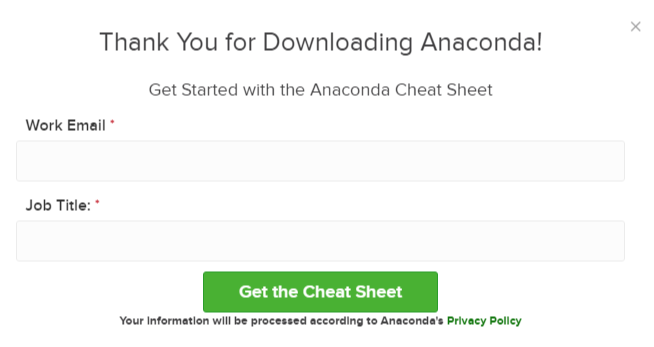
3. Open the .pkg installer
Navigate to the Downloads folder and double-click the .pkg installer file you just downloaded. It may be helpful to order the contents of the Downloads folder by date to find the .pkg file.
4. Follow the installation instructions
Follow the installation instructions. It is advised that you install Anaconda for the current user and that Anaconda is added to your PATH.
5. Source your .bash-rc file
Once Anaconda is installed, you need to load the changes to your PATH environment variable in the current terminal session.
Open the MacOS Terminal and type:
- $ cd ~
- $ source .bashrc
6. Open a terminal and type python and run some code.
Open the MacOS Terminal and type:
- $ python
You should see something like
Python 3.6.3 | Anaconda Inc. |
At the Python REPL (the Python >>> prompt) try:
>>> import this
If you see the Zen of Python, the installation was successful. Exit out of the Python REPL using the command exit(). Make sure to include the double parenthesis () after the exit command.
>>> exit()
Installing Anaconda on Linux
This section details the installation of the Anaconda distribution of Python on Linux, specifically Ubuntu 18.04, but the instructions should work for other Debian-based Linux distributions as well.
Ubuntu 18.04 comes pre-installed with Python (Version 3.6) and legacy Python (Version 2.7). You can confirm the legacy version of Python is installed by opening up a terminal.
In the terminal type:
$ python
You will most likely see Python Version 2.7 is installed. If you enter:
$ python3
You will most likely see Python Version 3.6 is also installed. You can use the 3.6 Version of Python, but each time a new package needs to be downloaded, the $ pip3 install command must be used.
Install the Anaconda distribution of Python to follow the examples in the book without the need to install additional third-party packages.
Steps:
- Visit Anaconda.com/downloads
- Select Linux
- Copy the bash (.sh file) installer link
- Use wget to download the bash installer
- Run the bash script to install Anaconda3
- source the .bash-rc file to add Anaconda to your PATH
- Start the Python REPL
1. Visit the Anaconda downloads page
Go to the following link: Anaconda.com/downloads
2. Select Linux
On the downloads page, select the Linux operating system

3. Copy the bash (.sh file) installer link
In the Python 3.6 Version* box, right-click on the [64-Bit(x86) Installer] link. Select [copy link address].
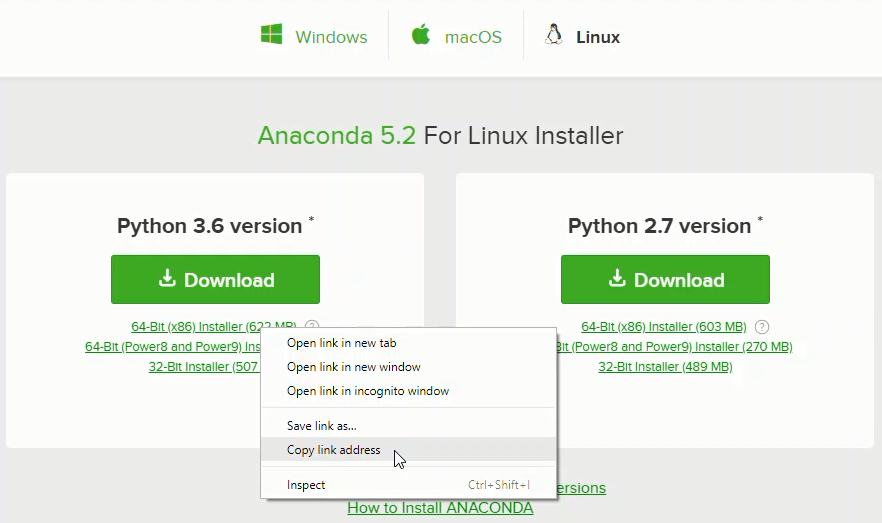
4. Use wget to download the bash installer
- Now that the bash installer (.sh file) link is stored on the clipboard, use wget to download the installer script. In a terminal, cd into the home directory and make a new directory called tmp. cd into tmp and use wget to download the installer.
- Although the installer is a bash script, it is still quite large and the download will not be immediate (Note the link below includes <release>. the specific release depends on when you download the installer).
- $ cd ~
- $ mkdir tmp
- $ cd tmp
- $ https://repo.continuum.io/archive/Anaconda3<release>.sh
5. Run the bash script to install Anaconda3
With the bash installer script downloaded, run the .sh script to install Anaconda3. Ensure you are in the directory where the installer script downloaded:
$ ls
Anaconda3-5.2.0-Linux-x86_64.sh
Run the installer script with bash.
$ bash Anaconda3-5.2.0-Linux-x86_64.sh
Accept the Licence Agreement and allow Anaconda to be added to your PATH. By adding Anaconda to your PATH, the Anaconda distribution of Python will be called when you type $ python in a terminal.
6. source the .bash-rc file to add Anaconda to your PATH
Now that Anaconda3 is installed and Anaconda3 is added to our PATH, source the .bashrc file to load the new PATH environment variable into the current terminal session. Note the .bashrc file is in the home directory. You can see it with $ ls -a.
- $ cd ~
- $ source .bashrc
7. Start the Python REPL
To verify the installation is complete, open Python from the command line:
- $ python
- Python 3.6.5 |Anaconda, Inc.| (default, Mar 29 2018, 18:21:58)
- [GCC 7.2.0] on linux
Type “help”, “copyright”, “credits” or “license” for more information.
>>>
If you see Python 3.6 from Anaconda listed, your installation is complete. To exit the Python REPL, type:
>>> exit()
Installing Python from Python.org
- Below is the recommended way to install a new version of Python from Python.org on each of the three major operating systems: Windows, MacOS and Linux.
- This book is based on Python version 3.6. Some of the examples in the book may not work properly on legacy Python (version 2.7). I recommend installing the Anaconda Distribution of Python on Windows and MacOSX. The installation of Anaconda on these operating systems was detailed in previous sections.
Installing Python on Windows
Go to https://www.python.org/downloads/ and download the latest release. Make sure to select the box [add Python to my path] during the installation.
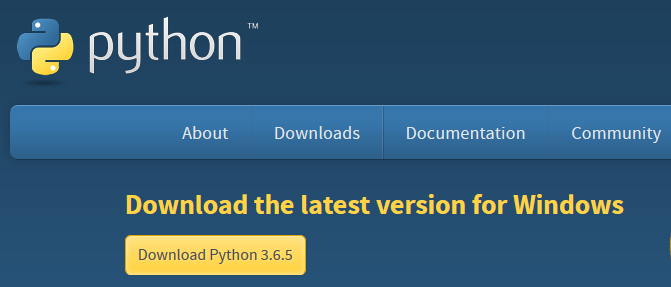
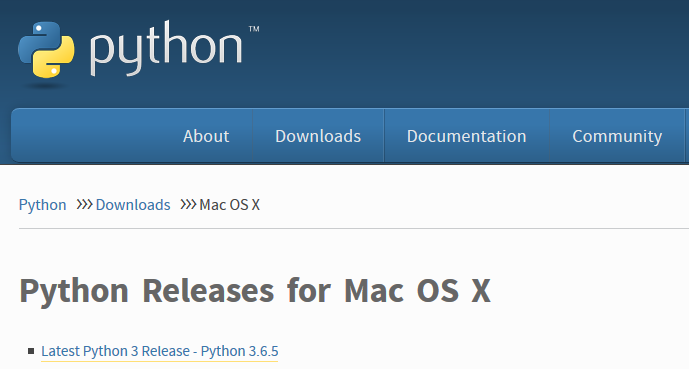
Installing Python on MacOS
Go to https://www.python.org/downloads/mac-osx/ and download the latest release.
Installing Python on Linux
Open a terminal and enter $ python to see if a version of Python is already installed on the system.
- $ python
- Python 2.7.12 (default, Dec 4 2017, 14:50:18)
- [GCC 5.4.0 20160609] on linux2
Type “help”, “copyright”, “credits” or “license” for more information.
>>> exit()
In the code block above, the version of Python is Python 2.7.12. If the Python version is 2.7 or below, try the command $ python3.
- $ python3
- Python 3.6.7 (default, Oct 22 2018, 11:32:17)
- [GCC 8.2.0] on linux
Type “help”, “copyright”, “credits” or “license” for more information.
>>> exit()
If no version of Python is shown, you can download a release of Python 3.6 from the deadsnakes package repository.
- $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa : deadsnakes/ppa
- [Enter]
- $ sudo apt-get update
- $ sudo apt-get install python3.6
After installation, you may need to append your PATH environment variable to ensure the newly installed Python 3.6 version is the version of Python called when using the terminal. The commands below will add /usr/bin to your PATH, and add an alias in .bashrc so that the command $ python3.6 produces the Python 3.6 REPL. Take care to ensure the double chevron >> is used, as a single chevron > will overwrite the .bashrc file.
- $ cd ~
- $ echo “PATH=/usr/bin:$PATH” >> ~/.bashrc
- $ echo “alias python3.6=’/usr/bin/python3.6′” >> ~/.bashrc
- $ source .bashrc
- $ python3.6
- Python 3.6.6 (default, Jun 28 2018, 04:42:43)
- [GCC 5.4.0 20160609] on linux
Type “help”, “copyright”, “credits” or “license” for more information.
>>> exit()
What Companies are Using Anaconda?
Anaconda is trusted by these leading companies around the world:
- BMW
- Cisco
- Citi Bank
- HSBC
- GlaxoSmithKline
- GE Power
- Samsung
- Zurich
- Brookhaven
- City of Boston
- Columbia University
- CloudQuant
- IQT
- Lloyds Banking Group
- Otto Group
- Machinalis
- Marshall Wace
- Mayo Clinic
- Micron
- Molex
- National Grid
- PIMCO
- US Army Corps of Engineers
- West Health
- US Securities and Exchange Commission
- SunTrust
- Banco Pichincha
- ComEd
- RENNER
- elo
- But even other than these, Anaconda has more than 15 million users worldwide.