
- C# Operators Introduction
- Math Operators
- Social Operators
- Sensible Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Task Operators
- Various Operators
- Administrator Precedence in C#
- C# Assignment Operators
- C# Comparison Operators
- C# Logical Operators
- Conclusion
- Math Operators
- Social Operators
- Coherent Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Task Operators
- Misc Operators
- A = 0011 1100
- B = 0000 1101
- A&B = 0000 1100
- A|B = 0011 1101
- A^B = 0011 0001
- ~A = 1100 001
- int x = 10;
- The option task administrator (+=) enhances a variable:
- int x = 10;
- x += 5;
- A rundown of all task administrators:
- Operator Example Same As
- = x = 5 x = 5
- += x += 3 x = x + 3
- -= x – = 3 x = x – 3
- *= x *= 3 x = x * 3
- /= x/= 3 x = x/3
- %= x %= 3 x = x % 3
- &= x &= 3 x = x and 3
- |= x |= 3 x = x | 3
- ^= x ^= 3 x = x ^ 3
- >>= x >>= 3 x = x >> 3
C# Operators Introduction :-
Administrators in C# are Special Symbols to Denote the Operation That the Program Needs to Perform. This Tutorial Explains C# Operators exhaustively With Examples:
In our past instructional exercise, we found out with regards to Conditional Statements in C#. We additionally figured out how to utilize if, if-else and if-else if explanations to characterize various conditions.
A contingent assertion, for example, “if” is otherwise called a dynamic assertion as they give the client a component to characterize a result in view of a choice characterized by administrators.The administrators offer a method for characterizing choices in view of Logic, Arithmetic Operations, Comparison, and so forth
An administrator is an image that advises the compiler to perform explicit numerical or legitimate controls. C# has rich arrangement of underlying administrators and gives the accompanying sort of administrators −
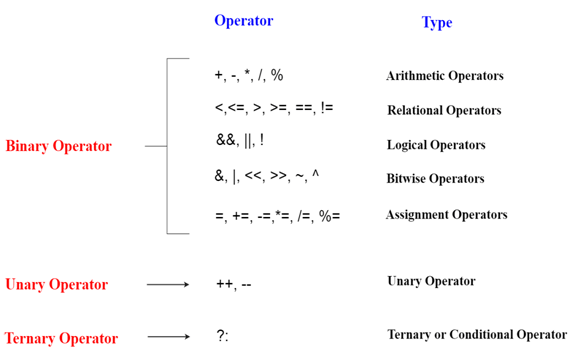
Math Operators :-
Following table shows every one of the math administrators upheld by C#. Expect variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 20 then, at that point, −
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| + | Adds two operands | A + B = 30 |
| – | Subtracts second operand from the first | A – B = -10 |
| * | Multiplies both operands | A * B = 200 |
| / | Divides numerator by de-numerator | B / A = 2 |
| % | Modulus Operator and remainder of after an integer division | B % A = 0 |
| ++ | Increment operator increases integer value by one | A++ = 11 |
| — | Decrement operator decreases integer value by one | A– = 9 |
Social Operators :-
Following table shows every one of the social administrators upheld by C#. Accept variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 20, then, at that point, −
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| == | Checks if the values of two operands are equal or not, if yes then condition becomes true. | (A == B) is not true. |
| != | Checks if the values of two operands are equal or not, if values are not equal then condition becomes true. | (A != B) is true. |
| > | Checks if the value of left operand is greater than the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. | (A > B) is not true. |
| < | Checks if the value of left operand is less than the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. | (A < B) is true. |
| >= | Checks if the value of left operand is greater than or equal to the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. | (A >= B) is not true. |
| <= | Checks if the value of left operand is less than or equal to the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. | (A <= B) is true. |
Sensible Operators :-
Following table shows every one of the sensible administrators upheld by C#. Accept variable A holds Boolean worth valid and variable B holds Boolean worth bogus, then, at that point,
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| && | Called Logical AND operator. If both the operands are non zero then condition becomes true. | (A && B) is false. |
| || | Called Logical OR Operator. If any of the two operands is non zero then condition becomes true. | (A || B) is true. |
| ! | Called Logical NOT Operator. Use to reverses the logical state of its operand. If a condition is true then Logical NOT operator will make false. | !(A && B) is true. |
Bitwise Operators :-
Bitwise administrator chips away at bits and perform little by little activity. Reality tables for and, |, and ^ are as per the following −
|
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Expect in the event that A = 60; and B = 13; in the paired organization they are as per the following −
The Bitwise administrators upheld by C# are recorded in the accompanying table. Expect variable A holds 60 and variable B holds 13, then, at that point, −
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| & | Binary AND Operator copies a bit to the result if it exists in both operands. | (A & B) = 12, which is 0000 1100 |
| | | Binary OR Operator copies a bit if it exists in either operand. | (A | B) = 61, which is 0011 1101 |
| ^ | Binary XOR Operator copies the bit if it is set in one operand but not both. | (A ^ B) = 49, which is 0011 0001 |
| ~ | Binary Ones Complement Operator is unary and has the effect of ‘flipping’ bits. | (~A ) = -61, which is 1100 0011 in 2’s complement due to a signed binary number. |
| << | Binary Left Shift Operator. The left operands value is moved left by the number of bits specified by the right operand. | A << 2 = 240, which is 1111 0000 |
| >> | Binary Right Shift Operator. The left operands value is moved right by the number of bits specified by the right operand. | A >> 2 = 15, which is 0000 1111 |
Task Operators :-
There are following task administrators upheld by C# −
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| = | Simple assignment operator, Assigns values from right side operands to left side operand | C = A + B assigns value of A + B into C |
| += | Add AND assignment operator, It adds right operand to the left operand and assign the result to left operand | C += A is equivalent to C = C + A |
| -= | Subtract AND assignment operator, It subtracts right operand from the left operand and assign the result to left operand | C -= A is equivalent to C = C – A |
| *= | Multiply AND assignment operator, It multiplies right operand with the left operand and assign the result to left operand | C *= A is equivalent to C = C * A |
| /= | Divide AND assignment operator, It divides left operand with the right operand and assign the result to left operand | C /= A is equivalent to C = C / A |
| %= | Modulus AND assignment operator, It takes modulus using two operands and assign the result to left operand | C %= A is equivalent to C = C % A |
| <<= | Left shift AND assignment operator | C <<= 2 is same as C = C << 2 |
| >>= | Right shift AND assignment operator | C >>= 2 is same as C = C >> 2 |
| &= | Bitwise AND assignment operator | C &= 2 is same as C = C & 2 |
| ^= | bitwise exclusive OR and assignment operator | C ^= 2 is same as C = C ^ 2 |
| |= | bitwise inclusive OR and assignment operator | C |= 2 is same as C = C | 2 |
Various Operators :-
There are not many other significant administrators including sizeof, typeof and ? : upheld by C#.
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| sizeof() | Returns the size of a data type. | sizeof(int), returns 4. |
| typeof() | Returns the type of a class. | typeof(StreamReader); |
| & | Returns the address of an variable. | &a; returns actual address of the variable. |
| * | Pointer to a variable. | *a; creates pointer named ‘a’ to a variable. |
Administrator Precedence in C# :-
Administrator priority decides the gathering of terms in an articulation. This influences assessment of an articulation. Certain administrators have higher priority than others; for instance, the increase administrator has higher priority than the expansion administrator.
For instance x = 7 + 3 * 2; here, x is allocated 13, not 20 since administrator * has higher priority than +, so the primary assessment happens for 3*2 and afterward 7 is added into it.
Here, administrators with the most noteworthy priority show up at the highest point of the table, those with the least show up at the base. Inside an articulation, higher priority administrators are assessed first. Show Examples
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| Postfix | () [] -> . ++ – – | Left to right |
| Unary | + – ! ~ ++ – – (type)* & sizeof | Right to left |
| Multiplicative | * / % | Left to right |
| Additive | + – | Left to right |
| Shift | << >> | Left to right |
| Relational | < <= > >= | Left to right |
| Equality | == != | Left to right |
| Bitwise AND | & | Left to right |
| Bitwise XOR | ^ | Left to right |
| Bitwise OR | | | Left to right |
| Logical AND | && | Left to right |
| Logical OR | || | Left to right |
| Conditional | ?: | Right to left |
| Assignment | = += -= *= /= %=>>= <<= &= ^= |= | Right to left |
| Comma | , | Left to right |
C# Assignment Operators :-
Task administrators are utilized to relegate qualities to factors. In the model underneath, we utilize the task administrator (=) to appoint the worth 10 to a variable called x:
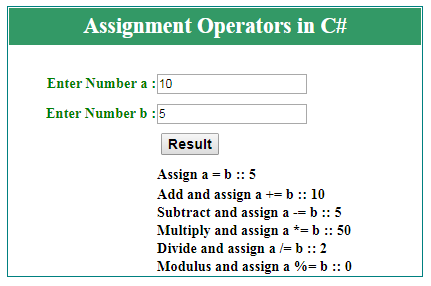
Model :
C# Comparison Operators :
Examination administrators are utilized to analyze two qualities:
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| == | Equivalent to | x == y |
| != | Not equal | x != y |
| > | More noteworthy than | x > y |
| < | Less than | x < y |
| >= | More prominent than or equivalent to | x >= y |
C# Logical Operators :
Legitimate administrators are utilized to decide the rationale between factors or qualities:
|
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| && Intelligent | Returns valid assuming the two assertions are true | x < 5 && x < 10 | |
| || Intelligent | Returns valid on the off chance that one of the assertions is true | x < 5 || x < 4 | |
| ! Sensible not | Reverse the outcome, returns bogus in the event that the outcome is true | !(x < 5 && x < 10) |
Conclusion :-
In this instructional exercise, we found out with regards to the various kinds of administrators in the C# programming language. We found out with regards to the utilization and images of these administrators.The number-crunching administrator is utilized by the program to perform basic arithmetical tasks like expansion, deduction, duplication, division, and so on
Social administrators are the ones that are utilized to approve a connection between the two operands as though they are equivalent, more prominent than, not exactly, and so on Task administrators are utilized for relegating esteems to a variable.
A most basic illustration of the task administrator is “equivalent to”. Coherent administrators are utilized for performing sensible activities like AND, OR, NOT, and so onAdministrators are widely utilized for announcing conditions in dynamic proclamations, while utilizing circles or while performing mathematical tasks.






