AWS VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) is a virtual network environment provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that enables you to construct a logically isolated area of the AWS Cloud from which you may launch AWS services in a virtual network of your choice. It allows you complete control over your virtual networking environment, allowing you to choose your own IP address range, create subnets, and configure route tables and network gateways.
1. What is VPC?
Ans:
- With the utilize of a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) benefit, clients can dispatch AWS assets in a virtual arrange of their choosing inside a coherently separated zone of the AWS cloud.
- Clients possess all control over the components of their virtual organizing environment, such as IP address ranges, subnet arrangement, course table setup, and arranged door setup.
- Assets interior a VPC are secure and kept separated from other systems, much obliged to this isolation.
2. How do Security Bunches and NACLs contrast in a VPC?
Ans:
- In a VPC, security is accomplished through the utilization of both Security Bunches and Arrangements to Control Records (NACLs), but they work unexpectedly.
- To control approaching and active activity at the occurrence level, Security Bunches work as a virtual firewall for instances.
- Notwithstanding outbound controls, they are stateful answers to allowed inbound activity.
- On the other hand, NACLs are stateless, work at the subnet level, and require express rules to allow return activity. They can be connected to allow and forbid permissions.
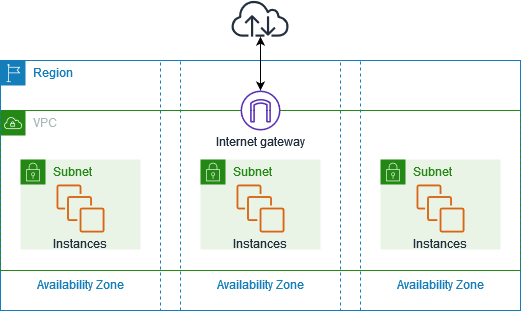
3. What is the reason for an Online Door in a VPC?
Ans:
An Online Door (IGW) serves as the bridge between a VPC and the web. It permits EC2 occasions inside a VPC to communicate with the web, providing a way for Web activity to and from the VPC. The IGW guarantees that the arranged activity can be steered appropriately from the VPC to the web and vice versa, empowering occasions with open IP addresses to be reachable from the Internet.
4. What is VPC peering?
Ans:
VPC peering is an organizing association between two VPCs that empowers you to conduct activity between them utilizing private IPv4 or IPv6 addresses. Occasions in VPC can communicate with each other as in case they were inside a same organize. VPC peering can be set up between VPCs over diverse AWS accounts and, indeed, over diverse districts (Inter-Region VPC Peering). It’s a coordinated course that permits for more secure and proficient information transfer.
5. What may be a Door, and why is it used?
Ans:
- A NAT (Arrange Address Interpretation) Gateway enables occasions in a private subnet to communicate with administrations outside the VPC (like the) but anticipates the web from starting an association with those instances.
- It’s utilized to supply a web network to EC2 instances in private subnets while maintaining their security from inbound web activity.
- NAT Doors are overseen, profoundly accessible, and adaptable, giving a dependable way to get to the web without exposing the occasions to coordinate web access.
6. Depict the work of Course Tables in a VPC?
Ans:
Course Tables in a VPC characterize rules, known as courses, that decide where arranged activity from your VPC is coordinated. Each subnet in a VPC must be related to a course table, which indicates permitted ways for outbound activity. For illustration, a course table can coordinate internet-bound activity to the web portal or activity between subnets. They are vital for characterizing how information is directed inside and outside of a VPC.
7. How does AWS guarantee VPC security?
Ans:
AWS guarantees VPC security through a combination of Security Bunches, NACLs (Organize Get to Control Records), VPC Stream Logs, and the rule of slightest benefit. Security Bunches act as a firewall for EC2 occasions, controlling inbound and outbound activity at the occasion level. NACLs give a layer of security at the subnet level. VPC Stream Logs capture data approximately the IP activity reaching to and from organize interfacing in your VPC, empowering checking and investigating.
8. What are Subnets, and why are they critical in a VPC?
Ans:
- Subnets are subdivisions of a VPC’s IP address that run that portion of the VPC into numerous systems that can be confined from each other.
- This separation is vital for organizing assets, overseeing activity, and improving security inside a VPC.
- Subnets permit a coherent division of administrations by work, reach level, or other criteria, supporting productive utilization of IP addresses and decreasing the risk of network-related issues.
- They are fundamental for creating a coherently organized, secure, and versatile AWS environment.
9. What is the difference between AWS Managed VPN and AWS Direct Connect?
Ans:
| Feature | AWS Managed VPN | AWS Direct Connect |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Encrypted VPN tunnel over the internet | Dedicated private connection to AWS |
| Use Case | Suitable for occasional or low-bandwidth connections | Ideal for high-throughput, low-latency, or consistent connectivity requirements |
| Configuration | Managed service, minimal configuration required | Requires physical or virtual connection, requires configuration of routers and network appliances | Scalability | Limited scalability, throughput depends on VPN configuration | Scalable bandwidth options, up to 100 Gbps |
10. Explain Elastic IP (EIP) and its use cases in AWS VPC?
Ans:
An Elastic IP (EIP) could be an IPv4 address offered by AWS for dynamic cloud computing. Unlike a regular public IP, an EIP can be associated with any instance in your VPC and can be moved from one instance to another. It’s particularly useful for cases where a persistent public IP address is necessary, such as when hosting a website on an EC2 instance or for DNS. EIPs help in avoiding having to DNS records if an instance is stopped and restarted, which normally would change its public IP.
11. What may be an Endpoint, and when would you utilize it?
Ans:
- A web portal, NAT device, VPN association, or AWS Coordinate Interface association is not essential when employing a VPC Endpoint to set up associations between the VPC and endorsed AWS administrations or VPC endpoint administrations.
- Virtual gadgets with tall accessibility, repetition, and level scaling are called endpoints.
- By avoiding activity from clearing out the Amazon arrange between the VPC and the administrations, they are utilized to safely get to AWS administrations without utilizing open IP addresses. This moves forward security and reduces the necessity for open IP addresses.
12. How can you screen the activity in your VPC?
Ans:
Activity in a VPC can be checked utilizing VPC Stream Logs and AWS CloudWatch. VPC Stream Logs capture data on almost the IP activity aiming to and from organize interfacing in VPC, permitting you to screen and troubleshoot network issues, survey security rules, and guarantee arranged compliance. Stream log information can be distributed to Amazon CloudWatch Logs and Amazon S3 for analysis and chronicling. CloudWatch advance gives measurements for monitoring the execution of the arrange, counting bytes and parcels in/out, which can be utilized to identify inconsistencies or optimize traffic.
13. What is the process for connecting multiple VPCs using VPC Peering?
Ans:
To associate numerous VPCs utilizing VPC Peering, you start a peering association from one VPC (the requester) to another VPC (the accepter). This can be done by indicating the VPC IDs and, in a few cases, the locale (for cross-region peering). Once the peering association asks is sent, the accepter VPC must accept the ask for the peering connection to be built up. After acceptance, course tables in each VPC ought to be overhauled to include courses that point to the CIDR square of the looked VPC, empowering inter-VPC communication. It’s critical to note that VPC Peering associations are a one-to-one relationship and don’t bolster transitive peering.
14. What is the noteworthiness of the Most Course Table in a VPC?
Ans:
In a VPC, the Most Route Table is the default course table that every VPC has. It controls the directing for all subnets that don’t have a particularly related course table. The Most Route Table at first contains, as it were, neighborhood courses for communication inside the VPC. However, it can be adjusted to include courses coordinating activity to a web door, virtual private door, NAT portal, or VPC peering association. Understanding and appropriately arranging the Most Course Table is fundamental for overseeing arrange activity stream inside your VPC effectively.
15. How does AWS Coordinate Connect benefit VPC connectivity?
Ans:
- AWS Coordinate Interface bypasses the Internet and provides a committed, private association from an on-premises organization to AWS.
- For VPCs, it empowers a more reliable arranged involvement with lower inactivity and expanded transmission capacity at a lower toll compared to internet-based connections.
- It is usually especially useful for applications that require customary, high-volume communication between an information center and AWS, such as information relocation, catastrophe recovery, or half-breed cloud models.
- Coordinate Interface makes it simpler to scale and organize networks and advances security by guaranteeing that information does not traverse the open Internet.
16. What are VPC Stream Logs, and what are their limitations?
Ans:
- VPC Flow Logs capture data on almost the IP activity going to and from network interfaces in your VPC, permitting point-by-point assessment of information bundles for security, arranging checking, and investigating purposes.
- They can be empowered for a particular subnet, the whole VPC, or an individual network interface. In any case, they don’t capture real-time information, don’t log activity predetermined for the
- Amazon DNS server, activity produced by instances when they contact the Amazon Windows license activation server, and activity to and from 169.254.169.254 (the occasion metadata benefit).
- Moreover, Stream Logs don’t capture bundle payloads, as they were metadata about the traffic.
17. What is the contrast between an Open and a Private Subnet in a VPC?
Ans:
In a VPC, an open subnet is one that’s related to a course table that features a course to a Web Door (IGW), allowing instances inside this subnet to get to the web specifically. A private subnet, in any case, does not have a course to the IGW and thus, occurrences inside a private subnet cannot straightforwardly access the Internet. Instead, they can access the Internet through services such as NAT Gateways (placed in a public subnet) or through a VPN connection.
18. How do you ensure high availability and fault tolerance in your VPC architecture?
Ans:
- To guarantee tall accessibility and blame resilience in a VPC, you ought to plan your architecture with repetition and failover frameworks in mind.
- This includes deploying occasions over different Accessibility Zones (AZs) within a locale, utilizing Versatile Stack Balancers to distribute traffic among instances, setting up Auto Scaling to powerfully alter the number of instances, and executing Course 53 wellbeing checks for DNS failover.
- Moreover, leveraging administrations like AWS CloudFormation for foundation as code ensures quick recovery and arrangement in other locales or AZs if needed.
19. What is AWS Travel Portal, and how does it disentangle arranged architecture?
Ans:
AWS Travel Door acts as a cloud switch, rearranging organized engineering by permitting you to interface VPCs and on-premises networks through a central center. This decreases the complexity of overseeing numerous VPC peering associations and VPNs by uniting them into a single connection point. Travel Portal underpins transitive steering, which empowers VPCs to communicate with each other without requiring personal peering associations.
20. Depict the steps that emigrate an EC2 occurrence from one VPC to another.
Ans:
Moving an EC2 occasion from one VPC to another includes a few steps: First, create an Amazon Machine Picture (AMI) of the occurrence you would like to relocate. At that point, share this AMI with the target AWS account (on the off chance that the VPCs are totally different accounts). Another is dispatching an unused occurrence in the target VPC utilizing the shared AMI. At long last, in the event that it is essential, reconfigure the organized settings (such as overhauling the security gather, NACLs, and course tables) and the instance’s IP address to match the target VPC’s configuration.
21. What are the benefits of using AWS PrivateLink?
Ans:
- AWS Private Link provides secure private connectivity between VPCs, AWS services, and on-demand operations on the Amazon network.
- Exclude data exposure on the public Internet and reduce the threat of internet-grounded attacks.
- PrivateLink simplifies your network armature by furnishing secure access to services across your VPCs and accounts with minimum firewall rule operation.
- This allows druggies to pierce AWS services as if they were running within their own VPC, perfecting security and connection effectiveness.
22. How can I optimize costs within a VPC?
Ans:
- Consider the following strategies to optimize costs within a VPC.
- To save on EC2 costs, use Reserved Cases or savings plans for predictable workloads.
- Utensil bus Scaling to match capacity to demand and avoid overprovisioning.
- Choose the most cost-effective case type and size for your workload.
- Use Spot Cases for stateless, fault-tolerant, or flexible operations.
- Regularly check and clean up unused coffers, similar to exemplifications of old shots, unused EIPs, or inactive NAT gateways.
- Eventually, use AWS Trusted Advisor to identify and apply cost- saving recommendations.
23. What methods can you use to secure data in transit within your VPC?
Ans:
- To cover data in conveyance within a VPC, apply encryption using Transport Layer Security( TLS) for all dispatches between cases and services.
- Use AWS VPN or AWS Direct Connect for secure, translated connectivity between your on-demand network and AWS.
- AWS PrivateLink allows you to securely access AWS services or VPC endpoint services without using the public Internet.
- Also, ensure that all API calls from your VPC to AWS services are made over HTTPS to maintain data confidentiality and integrity.
24. What is a network access control list( NACL), and how is it different from a security group?
Ans:
- A voluntary network access control list in a VPC is a firewall that regulates business to and from one or further subnets.
- Functions as Although can configure NACLs using analogous rules to security groups, there are important differences.
- NACL is stateless.
- That is, it doesn’t track the status of TCP connections or apply rules to incoming and gregarious business independently.
- In discrepancy, security groups are stateful, apply only to cases, and automatically allow return business for initiated connections.
- NACLs provide a broader control position at the subnet level, while security groups provide further grainy control at the case level.
25. How do I set up a VPC for serverless armature with AWS Lambda?
Ans:
- First, set up a VPC with an applicable CIDR block to set up a serverless armature using AWS Lambda.
- You are required to produce a VPC. Next, configure the public and private subnets.
- Internet access is needed if the AWS Lambda function needs to pierce AWS services or public endpoints that are not VPC-enabled.
- Next, configure the routing tables for these subnets meetly
- Eventually, when producing the Lambda function, specify the VPC, subnet, and security group in the VPC settings.
26. What is the process and what are the benefits of using AWS site-to-site VPN?
Ans:
- AWS point-to-point VPN establishes a secure private lair from your network or data center to your AWS VPC.
- This process involves creating a virtual private gateway on the AWS side, connecting it to your VPC, and creating a client gateway on your side that represents a physical device or software operation.
- Next, configure a VPN connection between these gateways.
- The benefits include secure communication between your on-demand network and your AWS VPC.
27. What’s the connection limit for AWS VPC gaping, and how can I increase it?
Ans:
- AWS VPC Peering has a limit on the number of active and outstanding gaping connections per VPC.
- This may vary by region and is subject to AWS service limits.
- You can start with a limit that supports a reasonable number of gaping connections, ranging from 50 to 125, but this is subject to change and may vary depending on your AWS account and specific conditions.
- Still, you can request an increase from the AWS Management Console by going to the Service Quotas section and opting for your VPC service If you need to increase this limit.
- From there, find your VPC gaping connection share and request an increase by specifying the new limit you want and the reason for the increase.
28. What role does subnet CIDR play in a VPC, and how does it affect network design?
Ans:
A subnet cloddish interdomain routing( CIDR) block defines the IP address range of a subnet within a VPC. It Determines the number of IP addresses available to coffers( similar to EC2 cases) in the EC2 case. Choosing the applicable size for your subnet CIDR is important for effective network design because it impacts the scalability, security, and insulation of network coffers. Small CIDR blocks can limit operation growth, and large blocks can affect wasted IP address allocation. Proper planning enables effective subnet design that considers current and unborn requirements while ensuring that network parts are logically organized by function, security position, or operation.
29. How does AWS ensure network security and insulation within a VPC?
Ans:
AWS ensures network security and insulation within a VPC through several mechanisms. First, VPC is logically insulated from other virtual networks in his AWS pall, furnishing a secure and private terrain for your coffers. Security groups and network access control lists( NACLs) give stateful and stateless business control in case and subnet situations. Subnetting allows you to further insulate your coffers and allows you to design public, private, and DMZs. AWS also offers features similar to VPC gaping, which provides secure connectivity between VPCs, and AWS PrivateLink, which provides private connectivity between your VPC and AWS services. Encryption in conveyance(using TLS across AWS services) and at rest( using keys managed by AWS KMS) makes your data indeed more secure.
30. What strategy do you recommend for disaster recovery in an AWS VPC terrain?
Ans:
We recommend a multi-layered approach for disaster recovery in an AWS VPC terrain. First, use AWS Regions and Vacuity Zones to install critical structures in geographically insulated locales so that an outage in one area does not impact your entire business. Apply automated backups and shots of EC2 cases and databases in S3, voluntarily replicated to multiple regions. Use Route 53 health checks and DNS failover to automatically redirect business to healthy endpoints. Consider using AWS CloudFormation or AWS Elastic Beanstalk to snappily automate and replicate structure setup in another region. Test your disaster recovery procedures regularly to ensure they meet your business durability needs.
31. How does AWS VPC Traffic reflecting work, and what benefits does it give?
Ans:
- AWS VPC Business reflecting allows you to use an EC2 case’s Elastic Network Interface( ENI) and route it to a specified destination for analysis.
- This point enables comprehensive packet examination for security and network monitoring, compliance, and troubleshooting without the need to emplace third-party tools in your VPC.
- Benefits include better security with real-time monitoring, the capability to detect network and operation anomalies, and increased visibility of VPC business for forensic analysis and compliance checkups.
- Business reflection is an important tool for maintaining robust security and functional effectiveness.
32. What’s the difference between an Internet gateway and a NAT gateway in an AWS VPC?
Ans:
- An Internet gateway( IGW) enables communication between cases in a VPC and the Internet, making bidirectional Internet access easier.
- It’s stateless, scales horizontally, and provides a path for cases with public IP addresses to pierce the Internet and vice versa.
- On the other hand, a NAT gateway allows cases in private subnets to have Internet access without exposing them to the Internet. This is stateful.
- That is, it remembers gregarious requests and allows return business.
- An IGW allows external businesses to initiate communication with cases, whereas a NAT gateway only allows internal cases to initiate connections, furnishing an advanced position of security for internal coffers.
33. What are the main considerations when designing a VPC with IPv6?
Ans:
- When designing a VPC using IPv6, remember that IPv6 addresses are encyclopedically unique and not natively private, so careful security group and NACL configuration is needed to protect your coffers.
- Corroborate that your VPC and subnet are IPv6-enabled and assign them an IPv6 CIDR block.
- Note that IPv6 doesn’t support broadcast or multicast and relies on other protocols for these features.
- Design with binary mound operations( IPv4 and IPv6) in mind to ensure comity and availability.
- Also, modernize your routing tables and security rules to include IPv6 business.
- Take advantage of IPv6’s nearly unlimited address space to plan for scalability and unborn growth.
34. How can an AWS Lambda function access the Internet in a VPC?
Ans:
An AWS Lambda function in a VPC can route business through a NAT gateway or a NAT case in a public subnet. You can pierce the Internet. First, you need to configure your Lambda function in your VPC and specify the private subnet in which it’ll operate. Next, a NAT gateway or NAT case is created on the public subnet with a route to the Internet through the Internet gateway.
35. What is the importance of Elastic IP (EIP) in AWS VPC and what are its best practices?
Ans:
Versatile IP (EIP) addresses are inactive IPv4 addresses advertised by AWS for energetic cloud computing. An EIP can be related to any occurrence in your VPC and is planned to veil the disappointment of an occurrence or computer program by rapidly remapping the address to another occasion in your VPC. Best hones incorporate restricting the utilization of EIPs to scenarios where it is fundamental for an open IP to stay related to a particular occasion for its lifecycle, such as public-facing web servers or NAT portals.
36. What part do Arrangement Bunches play in AWS VPC, and what sorts are available?
Ans:
Situation Bunches in AWS VPC manage how occurrences are physically situated inside the AWS foundation, impacting the organized execution and idleness between occasions. There are three sorts of Arrangement Bunches: Cluster, Spread, and Segment. Cluster Situation Bunches put occurrences near together interior a single Availability Zone to attain moo idleness and high-throughput communication.
37. What are the suggestions for adjusting a VPC’s IPv4 CIDR block?
Ans:
- Adjusting a VPC’s IPv4 CIDR piece permits you to amplify its IP address run by including auxiliary CIDR pieces. This may be fundamental as your environment develops and you require more IP addresses for modern assets.
- However, it’s critical to note that you cannot alter or erase the essential CIDR square once it’s set; you’ll, as it were, include auxiliary pieces.
- Arranging is vital as including auxiliary CIDR pieces may require alterations to course tables, ACLs, and security bunch rules to guarantee appropriate traffic flow and security.
- This highlight improves the adaptability and scalability of your AWS environment without the ought to make a unused VPC.
38. How does AWS VPC bolster VPN associations, and what are the components involved?
Ans:
AWS VPC bolsters VPN associations to safely interface your on-premises arrange to your AWS framework. The key components included in setting up a VPN association incorporate the Client Portal, which is your physical gadget or computer program application on your side; the Virtual Private Door or Travel Door on the AWS side; and the VPN association itself, which encrypts the activity between the two doors.
39. Can you resize a VPC after its creation, and if so, how?
Ans:
You cannot straightforwardly resize the essential CIDR piece of a VPC once it’s made. AWS permits you to include auxiliary CIDR squares to a VPC, successfully expanding its addressable space. This can be done by going to the VPC dashboard, selecting the VPC you would like to expand, and at that point, including extra IPv4 or IPv6 CIDR squares. This approach gives adaptability in an organized plan and allows for growth without the ought to migrate assets to an unused VPC.
40. What is the distinction between AWS VPC peering and AWS Travel Gateway?
Ans:
- AWS VPC Peering permits you to associate two VPCs to empower steering of activity between them utilizing private IP addresses without requiring activity to navigate through the open web or a door.
- It’s a one-to-one relationship and doesn’t scale well for complex systems due to its non-transitive nature. AWS Travel Portal, on the other hand, acts as an organized center that interfaces different VPCs and on-premises systems.
- It rearranges organized administration and scales effectively by permitting transitive steering between all associated systems. Travel Portal is perfect for bigger, more complex arrange models that require centralized administration and connectivity between numerous VPCs and outside networks.
41. How do Security Bunches and Organized Get to Control Records (NACLs) contrast in AWS VPC?
Ans:
Security Bunches and Organize to Control Records (NACLs) both serve as layers of security inside AWS VPC, but they work at distinctive levels and have particular characteristics. Security Groups act as the virtual firewall for EC2 occasions, controlling inbound and outbound activity at the occurrence level. They are stateful, meaning they consequently permit return activity for permitted inbound activity. NACLs, on the other hand, work at the subnet level, giving a layer of defense for all occurrences inside the subnet. Whereas Security Bunches are best for fine-grained control over individual occasions, NACLs are appropriate for broader subnet-level security policies.
42. What is subnetting in AWS VPC, and what are its benefits?
Ans:
- Subnetting in AWS VPC includes partitioning a VPC’s IP address run into smaller systems (subnets), each inside a particular Accessibility Zone. This division permits for effective utilization of IP addresses, moved forward organized organization, and upgraded security and activity control.
- By making subnets, you’ll confine diverse sorts of occasions (e.g., web servers in open subnets and databases in private subnets) to control get to and activity stream more granularly.
- Subnetting, too, empowers you to plan profoundly accessible designs by conveying assets over different Accessibility Zones, lessening the effect of disappointments and guaranteeing that your applications stay accessible.
43. Describe AWS VPC’s Shared Obligation Demonstrate in terms of organizing security.
Ans:
Concurring to the AWS VPC’s Shared Obligation Show, AWS is in charge of shielding the equipment that bolsters the organized network, information center physical security, and organized foundation, all of which control the administrations given by AWS Cloud. Clients are capable of securing their information inside the VPC, which incorporates arranging organizing control records (NACLs), security bunches, and firewall rules, scrambling information in travel and at rest, and overseeing IAM parts and arrangements to control get-to-the-VPC resources.
44. Clarify the part of a NAT Door in a VPC and its benefits over a NAT Instance.
Ans:
A NAT Gateway in a VPC enables instances in a private subnet to initiate outbound internet traffic without receiving inbound traffic from the Internet, which is crucial for updating software, accessing external resources, or using AWS services. Unlike a NAT Instance, which is a managed EC2 instance acting as a NAT device, a NAT Gateway could be managed by AWS service, providing high availability, automatic scaling, and redundancy without the need for manual setup or maintenance. It offers better bandwidth efficiency, lower latency, and higher throughput compared to NAT Instances.
45. What does a VPC default to?
Ans:
- A default VPC in AWS is automatically created for your AWS account, the primary you provision Amazon EC2 resources. It is configured with a default set of resources that includes an online route table and default subnets in each Availability Zone.
- The default VPC is designed to allow you to deploy resources immediately without having to configure a new VPC.
- Every instance launched in this VPC can have public IP addresses and can access the Internet, assuming its security group and network ACL allow the necessary traffic.
46. What makes up Amazon VPC?
Ans:
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is made up of a few key components: subnets, course tables, web portals (IGW), NAT doors, arrange get-to-control records (NACLs), security bunches, VPC endpoints, and alternatively, VPN associations and Coordinate Interface for on-premises network.
- These components work together to form a virtual organization inside AWS that’s coherently separated from the other virtual systems, permitting to control of IP address ranges, subnets, course tables, and organized gateways.
47. How do you use a route table in a VPC?
Ans:
A course table in AWS VPC contains the set of rules, known as courses, that decide where arranged activity from your VPC is coordinated. Each subnet in a VPC must be related to the course table, which indicates the permitted ways for the outbound activity. To utilize a course table, you make it, characterize courses that indicate the goal CIDR and the other jump (e.g., internet door, virtual private portal, NAT portal), and after that course table with one or more subnets. This setup controls the stream of activity out of the subnets.
48. What is the work of an Amazon VPC router?
Ans:
The Amazon VPC switch serves as a virtual switch for your VPC, empowering communication between your VPC subnets and overseeing activity directing between distinctive components of the VPC, such as subnets, web doors, and VPN associations. It is mindful of upholding course tables related to each subnet, deciding how the activity is coordinated inside the VPC and to outside systems. The VPC switch is profoundly accessible and overseen by AWS, requiring no client configuration.
49. What are Internet Gateways in a VPC?
Ans:
A VPC’s Web Door (IGW) could be a profoundly accessible, evenly scaled VPC component that encourages communication between occurrences inside the VPC and the Internet. It makes it conceivable for occasions to connect to the web and bad habit versa that have open IP addresses. Any VPC that needs a coordinated web connection must have an IGW since it could be a component for empowering the web network for EC2 occasions in open subnets.
50. How can I determine the Availability Zone associated with my subnets in AWS VPC?
Ans:
Each subnet in an AWS VPC is linked to a specific Availability Zone (AZ). To find out which AZ your subnets are in, you can use the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or SDKs. In the AWS Management Console, navigate to the VPC dashboard, select “Subnets,” and you will see a list of subnets along with their associated Availability Zones. Understanding this information is crucial for planning high availability and fault tolerance by distributing your resources across multiple AZs.
51. In a VPC, how numerous Amazon EC2 occurrences is the greatest number that can be used?
Ans:
The most extreme number of Amazon EC2 occasions you’ll be able to in a VPC isn’t settled; the EC2 occurrence limits of your AWS account represent it. These limits are per locale and can be expanded by asking for a constraint increment from AWS Support. AWS accounts initially have default limits, but these can be balanced based on your prerequisites. It’s vital to oversee your asset utilization and ask for constant increments in the progress toward these limits.
52. How does ClassicLink work?
Ans:
Through the utilization of ClassicLink, occasions running on the EC2-Classic stage can be connected to a VPC and communicate with one another by means of private IP addresses. You must, begin with empowering ClassicLink for the VPC sometime recently, connecting each EC2-Classic occasion to the VPC independently in arrange to utilize it. Applications that must run in both situations or move from EC2-Classic to VPC will discover this capability. A bridge called ClassicLink makes it simpler to go continuously to VPC.
53. What highlights does the AWS VPC offer?
Ans:
Total control over the virtual organizing environment, counting the asset situation, association, and security, is one of the capabilities that AWS VPC offers. In expansion to designing course tables, subnets, arranging doors, and your possess IP address run, you’ll be able to do these things. A public-facing subnet for web get-to, private subnets for backend frameworks, and the utilization of Security Bunches and Organized ACLs for granular get-to control are assisted highlights.
54. Where are VPCs residing?
Ans:
- VPCs reside inside the AWS Cloud infrastructure, logically confined from other virtual systems in the AWS Cloud.
- They can span numerous Accessibility Zones inside a single AWS Locale, giving the adaptability to plan and design your organized engineering inside the AWS ecosystem.
- Accessibility Zones are the unmistakable areas inside an AWS Locale that are built to be protected from the disappointments in other Accessibility Zones, advertising the capacity to function flexible, profoundly accessible, and fault-tolerant applications.
55. What employments does an Amazon VPC switch serve?
Ans:
The Amazon VPC switch serves as a virtual switch inside your VPC, empowering the stream of traffic between distinctive subnets, to and from the web through a Web Portal, and to other administrations inside AWS through benefit portals like VPC Endpoints. It’s responsible for upholding course tables related to each subnet, deciding how the activity is coordinated inside the VPC, and guaranteeing the network between occasions, AWS administrations, and outside systems.
56. What is the cost for you to share Amazon’s cloud space with them?
Ans:
The cost to utilize Amazon’s cloud space shifts depending on the administrations utilized, such as Amazon EC2 for computing, Amazon S3 for capacity, and Amazon RDS for databases. Estimating is pay-as-you-go based on assets expended like compute hours, capacity space, information exchange, and particular benefit highlights. AWS offers a free tier for unused clients, which incorporates limited access to numerous administrations for 12 months. After surpassing free level limits or for administrations not secured, you’re charged month to month for the assets utilized.
57. What is AWS PrivateLink?
Ans:
- Without requiring the data to go over the open Internet, AWS PrivateLink offers a private, secure link between your virtual private cloud (VPC), AWS services, and on-premises applications. It gives you the ability to securely and scalable expose your VPC services to other AWS accounts or services.
- By ensuring that traffic does not pass through the public Internet, PrivateLink dramatically improves security and privacy by lowering the danger of being vulnerable to threats.
- Eliminating the requirement for NAT devices or public IP addresses to enable service communication streamlines network design. Applications needing strict security and privacy controls for data in transit are best suited for AWS PrivateLink.
58. In the VPC, what is ClassicLink?
Ans:
- Through the use of private IP addresses, ClassicLink enables communication between instances in a VPC and an Amazon EC2-Classic platform.
- Customers wishing to switch to a VPC or operate in a hybrid environment can use ClassicLink as a bridge. EC2-Classic was the initial deployment architecture that did not make use of VPCs.
- It enables you to link your EC2-Classic instance to a VPC within the region, allowing instances within the to communicate with the linked EC2-Classic instances as if they were within the same network. ClassicLink simplifies migration to VPC while supporting the phased transition of applications, workloads, and services.
59. What distinguishes VPC from other private clouds that produce so unique?
Ans:
Amazon VPC offers unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and security, distinguishing it from other private clouds. It allows to provision of a logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud that can launch AWS resources in a virtual network that is defined. This includes the ability to choose your own IP address range, create subnets, and configure route tables and network gateways. VPC integrates deeply with other AWS services, providing a seamless environment for deploying applications. The scale of AWS’s infrastructure ensures high availability and durability for your VPC.
60. What may be a private server?
Ans:
A virtual machine offered for sale as a service by an online provider is called a virtual private server (VPS). Customers can install practically any software that runs on an operating system (OS) by giving them superuser access to the operating system instance that it runs on its own. Being able to share the server with other users gives you more privacy than shared hosting. VPSs are frequently used for small to medium-sized apps, websites that have outgrown shared hosting, or as a testing sandbox since they are dynamically scalable to meet users’ needs.
61. Stateful and stateless filtering what are they?
Ans:
- Stateful and stateless filtering relates to how network business is covered and filtered. Stateless filtering operates without regard to the state of network connections; it simply examines packets in insulation, applying a set of rules to each packet to determine whether it should be allowed or blocked without considering once-or-unborn packets.
- In discrepancies, stateful filtering tracks the state of active connections and forms opinions grounded on the packet’s environment within a discussion.
- It allows or blocks business grounded on the connection state, ensuring that only packets matching a known active connection are allowed through. This enhances security by feting and maintaining the environment of ongoing business.
62. What distinguishes a class A, B, and C subnet mask from one another?
Ans:
Class A, B, and C subnet masks are part of the traditional IP addressing system that was used to classify networks into different sizes. A Class A subnet mask is 255.0.0.0, allowing for 16 million hosts on a single network, and is used for veritably large networks. A Class B subnet mask is 255.255.0.0, suitable for medium-sized networks, allowing for 65,536 hosts. A Class C subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, designed for small networks, accommodating up to 256 hosts. The distinction between these classes lies in the dereliction subnet mask, which directly affects the number of possible hosts and the number of available networks.
63. Where in the firewall rule table is the target IP?
Ans:
In a firewall rule table, the target IP address specifies the destination for the rule being applied. It’s a critical element of the rule set that determines how business is handled. The target IP can be set up in the destination field of a rule within the firewall rule table. This specifies which incoming or gregarious packets to match grounded on their destination IP address. Firewall rules are reused in order, and the position of a rule with a specific target IP can affect how business is handled, with the first match in the table generally determining the action( allow or block) for that business.
64. What are the uses for private IP address ranges, and what are they?
Ans:
- Private IP address ranges are reserved by the Internet Assigned Figures Authority( IANA) for use within private networks and aren’t routable on the public Internet. These ranges include10.0.0.0 to10.255.255.255( Class A),172.16.0.0 to172.31.255.255( Class B), and192.168.0.0 to192.168.255.255( Class C). They’re used for internal network bias, allowing for internal communication without using public IP addresses
- This conserves global IP address space and enhances network security by segregating internal business from external business.
- Private IPs are essential for creating secure, scalable, and manageable internal networks similar to those within homes, services, and all surroundings.
65. Explain the meaning and operation of cloddish inter-domain routing( CIDR).
Ans:
Without class, The process of assigning IP addresses and directing Internet Protocol packets is known as inter-domain routing. In discrepancy to conventional class-grounded addressing, CIDR allows for a more flexible allocation of IP addresses by using a memorandum that includes an IP address followed by a rent(/) and a number(e.g.,192.168.1.0/ 24), indicating the subnet mask length. This system allows for variable-length subnet masking, enabling the creation of subnets of colorful sizes. CIDR optimizes the allocation of IP addresses, reduces the size of routing tables, and improves the effectiveness of IP address operation, addressing the limitations of the class-grounded system by furnishing further grainy control over IP address allocation.
66. What distinguishes an internet gateway from an exit-only gateway?
Ans:
An Internet Gateway( IGW) is the VPC element that allows communication between the cases in VPC and the Internet. It supports bidirectional business, enabling coffers within a VPC to initiate outbound connections to the Internet and allow inbound access if configured(e.g., with applicable security group rules). An Exit-Only Internet Gateway, on the other hand, is used specifically with IPv6-enabled VPCs to allow outbound Internet business from the VPC while precluding unasked inbound business. It’s effectively a stateful gateway for IPv6 business, serving an analogous purpose to a NAT gateway but for IPv6.
67. Why would someone use the VPC wizard?
Ans:
- The VPC Wizard in AWS simplifies the process of creating a VPC by furnishing a guided experience for setting up a VPC with colorful networking factors according to stylish practices.
- It’s particularly useful for snappily planting VPCs without having to manually configure each element, similar to subnets, route tables, and internet gateways.
- The wizard offers configured offers configured options for common scripts, including VPCs with a single public or private subnet, VPCs with public and private subnets( including NAT gateways for private coffers to pierce the Internet), and VPCs configured for VPN access.
- Using the VPC Wizard is recommended for those new to AWS or those looking to implement standardized VPC configurations efficiently, reducing the eventuality of configuration crimes and saving time.
68. Which pre-configured options are available through the VPC wizard?
Ans:
The AWS VPC wizard offers several pre-configured options to simplify the setup of a VPC terrain, feeding to different use cases and conditions. These options include setting up a VPC with a single public subnet, a VPC with public and private subnets( NAT), a VPC with public and private subnets and a tackle VPN access( for secure connections to a commercial data center), and a VPC with a private subnet only and a tackle VPN access. Each option automatically configures the VPC’s subnets, route tables, and internet gateways or VPN configurations, as applicable, reducing the complexity and time needed for setup.
69. According to the firewall rule table, what’s the source IP?
Ans:
In the environment of AWS security group rules, the source IP refers to the designated IP address or range specified in a rule from which inbound business is allowed or to which outbound business is directed. It’s defined using CIDR memorandum to allow or circumscribe access to coffers grounded on the forming( for inbound rules) or destination( for outbound rules) IP address. This specification enables fine-granulated access control, ensuring that only businesses from trusted IP ranges can reach your coffers or that your coffers can only communicate with specified IP addresses, enhancing the security posture of your VPC.
70. What do network ACLs’ allow and deny rules mean?
Ans:
- Network Access Control Lists( NACLs) in AWS VPC are used to control business to and from subnets within a VPC. NACLs contain a list of numbered rules that are estimated in order, starting from the smallest number.
- Each rule can either allow or deny business grounded on criteria similar to source IP, destination IP, harborage number, and protocol.
- An’ allow’ rule permits business that matches the rule’s criteria to pass through the NACL, while a’ deny’ rule blocks businesses matching its criteria. NACLs are stateless, meaning they independently estimate inbound and outbound business, taking rules to explicitly allow response business in addition to original requests.
71. What does the AWS CLI run cases command use the stoner data train for?
Ans:
The AWS ec2 run-cases command in the AWS Command Line Interface( CLI) can use a stoner data train to automatically configure cases upon launch. This stoner data can include scripts, commands, or configuration lines. When a case starts, the content of the stoner data train is executed automatically, allowing for the robotization of bootstrapping tasks similar to installing software, applying updates, or configuring settings. This point is necessary for automating the deployment and configuration of cases in a scalable and unremarkable manner, reducing the need for homemade intervention and icing thickness across your EC2 cases.
72. What is a security group rule set?
Ans:
- A security group rule set in AWS defines the inbound and outbound business rules that govern access to EC2 cases or other coffers associated with the security group. Each rule specifies allowed business grounded on protocol, harborage range, and source or destination IP address( CIDR).
- Security groups act as a virtual firewall at the case position, furnishing stateful filtering of business. This means responses to allowed inbound business are automatically allowed regardless of outbound rules. Security groups are pivotal for defining a security border around coffers in a VPC, enabling secure access control and minimizing implicit attack vectors.
73. Which rules in the network ACLs are outbound and incoming?
Ans:
- In Network Access Control Lists( NACLs) within AWS VPC, rules are distributed as either inbound( doorway) or outbound( exit). Inbound rules control the business coming into the subnet from other networks or the Internet, specifying which types of business are allowed or denied entry.
- Outbound rules control the business leaving the subnet to other networks or the Internet, determining what business is permitted to exit. The VPC director defines both sets of rules, which are reused in numerical order, from the smallest to the loftiest rule number, to decide whether a business is allowed to pass.
74. What does Direct Connect end to achieve?
Ans:
The thing of AWS Direct Connect is to give businesses access to a private, devoted network link between their on- demesne network and Amazon’s pall computing coffers. In order to give further reliable, secure, and rapid-fire data transmission rates — essential for high-outturn workloads, real-time data feeds, and cold-blooded pall surroundings this service circumvents the public Internet.
75. Describe the process of connecting a commercial data center to a VPC.
Ans:
Connecting a commercial data center to a VPC can be achieved using AWS Direct Connect or a VPN connection. AWS Direct Connect provides a private, devoted network connection between your data center and AWS, offering further harmonious network performance and potentially lower network costs. Alternatively, a VPN connection over the Internet can secure your data transfer between the data center and VPC using encryption. Both styles enable cold-blooded pall infrastructures, allowing flawless integration and operation of workloads between on-demand surroundings and AWS, easing disaster recovery and data migration, and extending data center capabilities into the pall.
76. What’s Ingress Routing for Amazon VPC?
Ans:
- Doorway Routing in Amazon VPC allows network directors to define routing rules at the VPC position to direct inbound business to and from internet gateways( IGWs) or virtual private gateways( VGWs) to specific EC2 cases, network appliances, or services.
- This point enhances network security and effectiveness by enabling precise control over the inflow of business entering a VPC, allowing for the examination, filtering, and logging of packets before they reach their final destination.
- Use cases include directing business through firewalls or intrusion discovery/ forestallment systems for security purposes or through custom network appliances for tasks like content filtering or business operation, furnishing an important tool for enforcing advanced network infrastructures and security postures within AWS surroundings.
77. What Is an Amazon VPC Internet Gateway Used Only for Egress?
Ans:
An Amazon VPC Internet Gateway( IGW) configured only for exit is used when cases within a VPC need to initiate outbound internet business without allowing unasked inbound internet business. This configuration helps maintain a secure terrain by confining incoming connections while still allowing the cases to pierce external coffers, update software, or use AWS services that bear internet access. By setting up the security group and network access control list( NACL) rules to deny inbound business or not configuring an Elastic IP( EIP) for cases, the IGW generally serves as a route for outbound communication, furnishing a controlled and secure way to manage internet access from within a VPC.
78. What’s business insulation in Amazon VPC?
Ans:
Business insulation in Amazon VPC is a security and design principle that separates colorful types of network businesses to enhance security and functional effectiveness. This can be achieved through the use of multiple subnets, security groups, network access control lists( NACLs), and VPC gaping connections. By separating businesses grounded on type, source, or destination, associations can apply strict access controls, minimize the threat of unauthorized access, and ensure sensitive or critical workloads aren’t exposed to gratuitous pitfalls.
79. What’s IPsec?
Ans:
- IPsec( Internet Protocol Security) is a suite of protocols designed to secure Internet communication by authenticating and cracking every IP packet of a communication session.
- IPsec operates at the network subcaste, allowing it to secure operations without variations and provide end-to-end security across different types of networks.
- It’s generally used in virtual private networks( VPNs) to secure internet business between association’s network and remote druggies or spots.
- IPsec supports two modes: Transport mode, which encrypts the cargo of each packet, and Lair mode, which encrypts the entire packet and adds a new IP title.
- It’s extensively used to create a secure connection over untrusted networks, such as the Internet confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data dispatches.
80. How are cases connected to the Internet a VPC?
Ans:
Cases within a VPC can connect to the Internet ways, but primarily through the use of an Internet Gateway( IGW) or a NAT Gateway/ Instance. Public cases, those with a public IP or Elastic IP( EIP), can directly pierce the Internet IGW, which serves as a scalable, largely available gateway connecting the VPC to the Internet cases without direct internet access, a NAT( Network Address restatement) Gateway or NAT Instance can be used. These NAT biases allow cases in a private subnet to initiate outbound internet business(e.g., for software updates) while precluding unasked inbound business from the internInternettaining the security of the private cases while enabling necessary external dispatches.
81. How do you design a largely available armature in AWS VPC?
Ans:
To design a largely available armature in AWS VPC, you start by planting your structure across multiple vacancy zones ( AZs) within a region to ensure redundancy and failover capabilities. Use Elastic Cargo Balancers( ELB) to distribute business unevenly across cases in different AZs. Apply Auto Scaling to automatically acclimate the number of cases according to demand, ensuring that the operation remains available indeed during business harpoons or case failures.
82. How do you set up a NAT Gateway in a VPC, and what are its advantages?
Ans:
- To set up a NAT Gateway in a VPC, create it in a public subnet and configure private subnet route tables to direct outbound traffic to it. This allows private instances to access the internet while blocking unsolicited inbound traffic.
- Benefits include ease of management, automatic scaling up to 45 Gbps, high availability, and eliminating the need for a dedicated NAT instance, which simplifies infrastructure and reduces administrative tasks.
83. How do you troubleshoot connectivity issues in AWS VPC?
Ans:
Troubleshooting connectivity issues in AWS VPC involves several methodical steps. Begin by verifying the configuration of your VPC, including route tables, to ensure correct routes are established for the intended business inflow. Check the security groups and network ACLs associated with the affected coffers to confirm that the inbound and outbound rules allow the business. Use VPC Flow Logs to dissect the business and identify if packets are being accepted or rejected at colorful points in your network.
84. How do you ensure secure communication between different VPCs?
Ans:
To ensure secure communication between different VPCs, you can work with VPC gaping or AWS Transit Gateway, depending on the complexity and scale of your network. VPC gaping allows two VPCs to communicate with each other as if they’re in the same network. When setting up VPC gaping, ensure that there’s no CIDR block imbrication between the VPCs and configure route tables in each VPC to route business to the gazed VPC.
85. What strategies would you use to resettle an operation to a VPC with minimum time-out?
Ans:
- Migrating an operation to a VPC with minimum time-out requires careful planning and prosecution. Start by completely mapping the being armature, dependencies, and data flows.
- Produce a replica of your operation’s armature within the VPC, using services like Amazon EC2, RDS, and ELB to ensure the new terrain is ready to handle the operation and its cargo.
- Use AWS Database Migration Service( DMS) for flawless database replication with minimum time-out. Apply a blue-green deployment strategy, where the new( green) terrain is tested while the old( blue) terrain remains functional.
86. Bandy the part and benefits of AWS Transit Gateway in a large-scale VPC armature.
Ans:
- AWS Transit Gateway plays a vital part in large-scale VPC infrastructures by simplifying network operation and connectivity across multiple VPCs, VPNs, and on-demand networks.
- It acts as a central mecca that allows for the connection of thousands of VPCs and networks, barring the need for complex and multitudinous gaping connections.
- With Transit Gateway, you can apply a mecca-and-spoke model, polarizing and streamlining network routing and operation.
- This setup enhances network effectiveness, reduces the functions above, and simplifies the network armature.
- Transit Gateway supports multicast, and you can also join your network into different disciplines for advanced security and functional effectiveness
87. How can you optimize costs while maintaining performance in your AWS VPC setup?
Ans:
- Optimizing costs in AWS VPC while maintaining performance involves several strategies. First, influence AWS Reserved Cases and Savings Plans for predictable workloads to profit from significant abatements over standard on-demand pricing.
- Use Auto Scaling to stoutly acclimate the number of cases according to demand, ensuring you are not paying for idle coffers.
- Apply Amazon CloudWatch to cover and dissect operation patterns, allowing for further informed opinions about scaling and resource allocation.
- Use lower case sizes or burstable case types( similar as T- series cases) for non-critical or variable workloads, taking advantage of the birth performance and the capability to burst above the birth as demanded
88. How do you secure sensitive data within a VPC?
Ans:
Securing sensitive data within an AWS VPC requires a multi-layered approach. Start by icing that all data at rest is translated using AWS services like EBS, S3, and RDS, which support encryption with AWS-managed keys or client-managed keys in AWS Key Management Service( KMS). For data in conveyance, use TLS/ SSL encryption across all services and ensure that your security groups and network ACLs are duly configured to allow only authorized access. Apply PrivateLink to expose services within your VPC securely to other VPCs without covering the public Internet.
89.How do you handle VPC gaping in a multi-account AWS terrain?
Ans:
- Handling VPC gaping in a multi-account AWS terrain involves careful planning and operation to ensure secure and effective connectivity. Use AWS Associations to centrally manage and govern your terrain across multiple AWS accounts.
- Influence AWS Resource Access Manager( RAM) to partake in coffers like Subnets, Transits Gateways, and Route tables fluently and securely across accounts within your association.
- When setting up VPC gaping connections, ensure there’s no lapping CIDR block between the VPCs to avoid routing conflicts.
90. Describe how you would set up a secure and scalable web operation armature in AWS VPC.
Ans:
Setting up a secure and scalable web operation architecture in an AWS VPC involves multiple AWS services and stylish practices. Start by structuring your VPC with public and private subnets. To enhance security, place your web servers in the public subnet and database servers in the private subnet.
Use Elastic Cargo Balancing( ELB) in front of web servers to distribute incoming business unevenly across multiple cases and ensure high vacuity. Apply auto Scaling to automatically acclimate the number of cases in response to business oscillations, ensuring that your operation scales up or down seamlessly to meet demand while controlling costs.