These interview questions are tailored to introduce you to the types of queries that may arise in an EMC (EMC Corporation, now part of Dell EMC) interview. Based on my experience, skilled interviewers often initiate discussions with fundamental concepts before progressing to more specific topics. Rather than adhering to a predetermined set of questions, the interview typically unfolds dynamically, evolving based on your responses. Our coverage includes a comprehensive set of top EMC interview questions, encompassing scenario-based inquiries, questions suitable for entry-level candidates, and those designed to assess the expertise of experienced professionals.
1. What is Q-Depth?
Ans:
A higher Q-Depth value often indicates that the storage device or HBA can handle a more significant number of concurrent I/O requests, which may enhance system performance overall by enabling better parallel processing of data. It’s an essential consideration in optimizing storage system efficiency, especially in scenarios with high I/O workloads or demanding applications.
2. How will you discover SAN disks on Hosts?
Ans:
SAN disks can be discovered on hosts using tools like the Storage Management Initiative Specification (SMI-S), storage vendor-specific management software, or command-line utilities like fdisk or parted on Linux.
Utilize SMI-S (Storage Management Initiative Specification): Leverage SMI-S to discover and manage SAN disks in a standardized way, ensuring interoperability between different storage devices.
3. What are Buffer-to-Buffer Credits?
Ans:
Buffer-to-buffer credits are a mechanism in Fibre Channel networks that manages the flow control between two devices. They represent the number of frames a sender can transmit before waiting for an acknowledgment from the receiver. In a Fibre Channel network, when a data frame is transmitted from one device to another, The receiving device confirms that it has received the frame. Buffer-to-buffer credits represent the availability of buffer space in the receiving device for storing incoming frames.
4. What is Drooping?
Ans:
- Drooping in the context of storage or Fibre Channel often refers to a condition where the voltage on the power supply sags, causing a temporary decrease in power. To check for drooping, you may need to monitor voltage levels during system operation.
- Addressing drooping is essential to ensure the stable and dependable electrical and electronic system functioning. Voltage regulators, signal conditioning, and proper transmission line design are some of the measures taken to mitigate drooping effects.
5. What is the difference between Hard and Soft Zoning?
Ans:
| Hard zoning | Soft Zoning | Physically enforces access restrictions at the switch level.. | Relies on logical grouping based on device identifiers; access is not strictly enforced at the switch level. |
|---|---|
| In Fibre Channel (FC) SAN (Storage Area Network) environments, complex zoning is a strict and hardware-based method of access control. | Soft zoning is a more flexible and software-based approach to access control in FC SANs. |
6. What is Port Zoning?
Ans:
Port Zoning is a method of access control in Fibre Channel (FC) Storage Area Networks (SANs). In Port Zoning, devices are grouped based on the physical Fibre Channel ports they are connected to on the Fibre Channel switch. Each port or set of ports is assigned to a specific zone, allowing or restricting communication between devices connected to those ports.
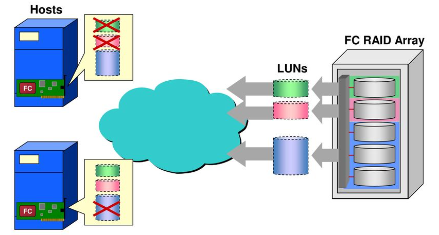
7. Why do we need LUN Masking?
Ans:
- LUN Masking is a security mechanism that controls which hosts can access specific LUNs (Logical Unit Numbers) in a storage array. It helps in preventing unauthorized access to specific storage resources.
- LUN Masking is a critical aspect of storage management in SAN environments, providing security, access control, and data protection to ensure the integrity and availability of stored data.
8. What is Zoning in a SAN?
Ans:
Zoning is a SAN configuration method that controls access to resources by grouping devices into zones. It defines which devices can communicate with each other within the SAN. Zoning in a Storage Area Network (SAN) is a method of controlling access to resources within the SAN by creating logical groups of devices.
9. Explain the Role of Initiators and Targets in SAN.
Ans:
Initiators are devices that initiate I/O requests, typically servers or hosts. Targets are devices that respond to these requests, often storage arrays. In a SAN, initiators connect to targets to perform data transfers.
- Initiators: Devices that initiate data transfer requests in a SAN. Identified by unique worldwide port names (WWPNs).
- Targets: Devices that respond to initiator requests with the requested data. Identified by unique worldwide node names (WWNNs).
10. What is WWN (World Wide Name) in SAN?
Ans:
A WWN is a unique number that is given to each device in a SAN. It is used for addressing and identifying devices in the Fibre Channel or iSCSI networks.
- Role: Unique identifier for devices in a Storage Area Network. Types are followed.
- WWPN (World Wide Port Name): Assigned to each port on a Fibre Channel HBA or storage port.
- WWNN (World Wide Node Name): Assigned to each Fibre Channel node or device.
- Format: Hexadecimal representation (e.g., 20:00:00:25:B5:10:00:00).
- Importance: Ensures global uniqueness, aids in routing, and is crucial for zoning and LUN masking in SAN configurations.
11. Define LUN (Logical Unit Number).
Ans:
- Definition: Unique identifier for a logical storage unit.
- Role: Represents a portion of storage in a SAN.
- Format: Typically numerical (e.g., LUN 0, LUN 1).
- Usage: Addresses and manages storage resources for hosts.
- Importance: Essential for efficient storage organization and access.
12. How does Multipathing enhance SAN reliability?
Ans:
- Redundancy: Offering multiple paths between servers and storage.
- Load Balancing: Distributing I/O to prevent congestion and optimize performance.
- Failover: Automatically redirecting data flow during path failures.
- Increased Availability: Maintaining connectivity despite failures.
- Improved Performance: Utilizing multiple paths concurrently for enhanced SAN performance.
13. Explain the purpose of SAN Fabric Access Control Lists (ACLs) and their use in security.
Ans:
SAN Fabric Access Control Lists define rules that control access to specific resources within the SAN. They enhance security by restricting which devices or users can communicate with designated storage resources.SAN Fabric Access Control Lists are essential for enforcing security measures within a Storage Area Network. They provide:
- A robust mechanism for controlling access at the port level.
- Regulating zoning and LUN masking.
- Preventing unauthorized access.
- Ensuring compliance with security policies and regulations.
14. Explain the Role of a SAN Switch.
Ans:
A SAN switch is a networking device that connects servers and storage devices in a storage area network. It facilitates the transfer of data between different devices and ensures efficient communication within the SAN.SAN switch plays a crucial role in providing connectivity, managing data traffic, ensuring reliability, and facilitating the efficient operation of a Storage Area Network.
15. What is SAN Fabric?
Ans:
SAN Fabric is the network infrastructure in a Storage Area Network (SAN).
- Components: Includes Fibre Channel switches, HBAs, and storage devices.
- Function: Facilitates high-speed data transfer between servers and storage.
- Topology: Often organized in a switched fabric for scalability.
- Role: Enables zoning, controls access, and ensures efficient data flow.
- Importance: Forms the backbone of SANs for resilient and high-performance storage.
16. Explain the Purpose of a Storage Array in SAN.
Ans:
- Data Storage: Centralized storage management for SAN.
- High Capacity: Offers substantial storage space.
- Data Protection: Implements RAID for fault tolerance.
- Performance Optimization: Enhances data access performance.
- Scalability: Allows easy capacity expansion.
- Centralized Management: Simplifies administration.
17. What is the Importance of QoS (Quality of Service) in SAN?
Ans:
- Optimized Performance: Ensures optimal performance for critical applications.
- Prioritized Access: Provides priority access to storage resources.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Allocates bandwidth efficiently based on application needs.
- Congestion Prevention: Manages data flow to prevent network congestion.
- SLA Adherence: Helps meet SLA requirements for different applications.
18. Define SAN Disk Repurposing and its advantages in storage management.
Ans:
SANDisk Repurposing involves reallocating storage resources for different purposes or applications. It helps optimize resource utilization and adapt to changing storage needs without acquiring additional hardware.SANDisk Repurposing offers advantages in terms of cost savings, resource optimization, flexibility, reduced environmental impact, streamlined management, quick implementation, and enhanced return on investment. It enables organizations to adapt to changing storage requirements efficiently while making the most of their existing storage infrastructure.
19. What is LUN Masking, and how does it contribute to SAN Security?
Ans:
LUN Masking is a technique in Storage Area Networks (SANs) that selectively presents or masks Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs) to specific servers or hosts. It controls which servers have access to particular storage resources.LUN Masking is a security measure that restricts access to specific LUNs for certain hosts. It enhances SAN security by ensuring that only authorized hosts can access designated storage resources, preventing unauthorized access.
20. Describe the Function of the Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop (FC-AL) Topology.
Ans:
- Topology: Ring or loop connecting multiple devices.
- Shared Channel: Devices share a single communication channel.
- Arbitration: Determines device access to prevent collisions.
- Initialization: Devices establish the loop and identify each other.
- Single Access: Only one device accesses the loop at a time.
- Simplicity: Simple and cost-effective for smaller SANs.
21. What is SAN Booting, and why is it used?
Ans:
SAN Booting involves booting a server directly from a storage area network instead of using local storage. It is used for centralized management, simplified maintenance, and ensuring consistent system images across multiple servers.SAN Booting is commonly used in enterprise environments to improve manageability, enhance disaster recovery capabilities, and optimize resource utilization across a network of servers.
22. Explain the concept of Storage Virtualization in SAN.
Ans:
Storage virtualization abstracts physical storage resources, presenting them as a single, logical pool. It simplifies storage management, improves flexibility, and enables efficient utilization of storage capacity in a SAN. Storage virtualization in SANs enhances agility, efficiency, and flexibility in managing storage resources, making it a crucial component in modern storage infrastructures.
23. What is the purpose of a SAN Extension?
Ans:
- Data Replication: Supports replication for disaster recovery.
- Business Continuity: Ensures continuous operations with remote data.
- Disaster Recovery: Facilitates rapid recovery in disasters.
- Geographic Separation: Enables SAN connectivity between distant locations.
- Data Migration: Supports non-disruptive migration between storage arrays.
24. What is SAN Booting?
Ans:
SAN Booting involves booting a server directly from a storage area network instead of using local storage. It is used for centralized management, simplified maintenance, and ensuring consistent system images across multiple servers. SAN Booting is the process of booting a computer or server directly from a Storage Area Network (SAN) rather than a local storage device.
25. Explain the concept of Storage Virtualization in SAN.
Ans:
Storage virtualization abstracts physical storage resources, presenting them as a single, logical pool. It simplifies storage management, improves flexibility, and enables efficient utilization of storage capacity in a SAN. Storage Virtualization in SANs enhances agility, efficiency, and flexibility in managing storage resources, making it a crucial component in modern storage infrastructures.
26. What is the purpose of a SAN Extension?
Ans:
- Disaster Recovery: Facilitates data replication over long distances for rapid recovery.
- Business Continuity: Ensures continuous operations with remote data copies.
- Remote Data Access: Enables accessing storage resources over extended distances.
- Non-Disruptive Data Migration: Supports migration between geographically separated SANs.
- High Availability: Enhances availability by providing access to data despite disasters or outages.
27. Define the terms IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) and Throughput in the context of SAN performance.
Ans:
- IOPS represents the number of Input/Output Operations a storage system can perform in one second. It measures the rate of read and write operations on the storage, indicating its performance in handling data requests. Throughput refers to the amount of data transferred per unit of time, measuring the efficiency of data transfer in a SAN.
- Both IOPS and Throughput are crucial metrics in evaluating and optimizing the performance of Storage Area Networks (SANs), providing insights into the speed and efficiency of data operations.
27. How does Thin Provisioning contribute to efficient storage utilization in SAN?
Ans:
- Dynamic Allocation: Allocates storage as needed.
- Optimized Utilization: Reduces over-provisioning and optimizing resources.
- Space Efficiency: Creates larger virtual volumes efficiently.
- Avoids Wasted Space: Minimizes allocation of empty volumes.
- Flexibility: Enables easy expansion without manual intervention.
- Improved Performance: Enhances performance with efficient storage operations.
29. What is a SAN Trunk, and how is it different from a regular SAN connection?
Ans:
A SAN Trunk is a link aggregation technique that combines multiple physical connections into a single logical connection, providing increased bandwidth and redundancy. It differs from a regular connection by enhancing overall performance and reliability.
30. Explain the concept of SAN Boot LUN.
Ans:
A SAN Boot LUN is a dedicated logical unit used for storing the operating system and boot files when booting from SAN. It ensures that the necessary files are accessible to initiate the system boot process over the storage area network. This approach offers benefits such as centralized management, improved flexibility, and simplified maintenance. It enables more effective resource usage, as multiple servers can share the same SAN Boot LUN, reducing the need for individual storage on each server.
31. What is Persistent Binding in the context of SAN configurations?
Ans:
Persistent Binding is a mechanism that ensures a consistent association between a Fibre Channel HBA (Host Bus Adapter) and a specific target or LUN. It helps maintain stable connections and prevents disruptions during system reboots. This approach offers benefits such as centralized management, improved flexibility, and simplified maintenance. It enables more effective resource usage, as multiple servers can share the same SAN Boot LUN, reducing the need for individual storage on each server.
32. Explain the difference between Asymmetric and Symmetric LUN Masking.
Ans:
- Asymmetric LUN : Masking allows different hosts to access the same LUN with different access permissions,
- Symmetric LUN Masking: Symmetric LUN Masking grants identical access permissions to multiple hosts for the same LUN. All hosts have equal access to their assigned LUNs.
33. Define SAN Fabric Zoning and its types.
Ans:
SAN Fabric Zoning is the process of grouping devices within a SAN to control their communication. Two main types are complex zoning (physically enforced) and soft zoning (software-based), which provide different levels of access control.
- Soft Zoning: Configured via software, flexible with WWN identification.
- Complex Zoning: Implemented at the hardware level for stricter isolation and enhanced security.
34. What are FLOGI (Fabric Login) and PLOGI (Port Login) in the Fibre Channel?
Ans:
- FLOGI (Fabric Login): Initiates login between a device and Fibre Channel fabric, establishing device identity.
- PLOGI (Port Login): Occurs after FLOGI and establishes a connection between a device and a specific Fibre Channel port.
35. How does SAN QoS (Quality of Service) impact performance?
Ans:
SAN QoS prioritizes and manages traffic to ensure that critical data receives preferential treatment, optimizing performance and responsiveness within the storage area network.SAN QoS (Quality of Service) impacts performance in a Storage Area Network by prioritizing and managing the flow of data. It ensures that critical applications receive the necessary resources and prioritization over less critical ones.
36. Explain the concept of SAN Snapshot.
Ans:
A SAN Snapshot is a point-in-time copy of data that allows for data recovery, backup, or testing without affecting the primary data. It provides a consistent view of data at a specific moment. A SAN Snapshot is a point-in-time copy or snapshot of a Storage Area Network (SAN) volume. It captures the state of the data at a specific moment without requiring a full backup. SAN snapshots are created rapidly and provide a reference point for data recovery or analysis.
37. What is the purpose of SAN Encryption?
Ans:
The purpose of SAN (Storage Area Network) encryption is to enhance the security of data during transmission within the SAN. SAN Encryption secures data in transit within a storage area network to protect against unauthorized access. It is implemented through encryption technologies applied to the data during transmission.
38. Explain the concept of SAN Port Types (E, F, and FL Ports).
Ans:
- E Port (Expansion Port): Connects Fibre Channel switches to expand the SAN fabric.
- F Port (Fabric Port): Connects end devices (servers, storage) to the Fibre Channel fabric.
- FL Port (Fibre Channel Loop Port): Used in Fibre Channel Arbitrated
- Loop (FC-AL): topologies, connecting devices in a loop.
39. What is NPIV (N_Port ID Virtualization) in SAN?
Ans:
NPIV is a feature in Storage Area Networks that allows multiple virtual N_Port identifiers (NPIVs) to share a single physical Fiber Channel port on a switch or host adapter. It enables virtualization at the N_Port level, allowing multiple virtual servers or virtual machines to share the same physical SAN connection while maintaining independent Fibre Channel identities.
40. Explain the concept of SAN Fabric Merge.
Ans:
SAN Fabric Merge is the process of combining or integrating two separate Storage Area Networks (SANs) into a single unified SAN fabric. This integration is typically done to consolidate resources, improve manageability, and facilitate communication between devices previously on separate SANs. For a successful project, careful planning and execution are essential. Merge without disruptions to data access and storage connectivity.
41. Define SAN Routing and its role in larger SAN architectures.
Ans:
SAN Routing involves the use of routing devices within a Storage Area Network (SAN) to enable communication between different SAN fabrics. These devices, often called SAN routers, facilitate data transfer and connectivity across geographically dispersed or segmented SANs.
42. What is SAN Health Check?
Ans:
A SAN Health Check is a systematic evaluation and analysis of the overall functionality and state of a storage area network (SAN). This proactive assessment involves reviewing various aspects of the SAN infrastructure, including hardware, software, configuration, and performance metrics. The goal is to identify potential issues, ensure optimal functionality, and prevent problems that could impact data availability or performance
43. Explain the concept of SAN Fabric Resilience.
Ans:
SAN Fabric Resilience refers to the ability of a Storage Area Network (SAN) fabric to maintain consistent and reliable data access even in the face of disruptions, failures, or changes within the network. Resilience measures are implemented to ensure that the SAN can recover quickly from events that might otherwise lead to downtime or data loss.SAN Fabric Resiliency involves designing a fabric to withstand failures and disruptions. Key components include redundant paths, switches, and power supplies, as well as techniques like trunking and zoning for fault tolerance.
44. What is the purpose of SAN Cache, and how does it impact performance?
Ans:
A cache is a high-speed storage buffer used to temporarily store frequently accessed data. It enhances performance by reducing latency and improving response times in data retrieval operations.
- SAN Cache Purpose: High-speed, temporary storage for frequently accessed data in a storage system
- Impact on Performance: Reduces latency, improves I/O performance, enhances throughput, and optimizes storage resources.
45. Explain the role of ALUA (Asymmetric Logical Unit Access) in SAN.
Ans:
ALUA (Asymmetric Logical Unit Access) in SAN: ALUA is a feature in Storage Area Networks that defines different paths to a storage device based on their preferred or optimized access paths. It enables devices to access a storage unit through multiple paths but designates one path as the primary, optimizing performance and reducing latency. ALUA is particularly beneficial in configurations where storage devices are accessible through multiple controllers or ports, ensuring efficient and asymmetric access to logical units based on the preferences set by the storage system.
46. What is SAN Q-Flow, and how does it impact storage traffic management?
Ans:
SAN Q-Flow is a technology that prioritizes and allocates bandwidth for different types of storage traffic within a storage area network. It optimizes the flow of data and enhances overall performance.”SAN Q-Flow” doesn’t appear to be a recognized term in the context of Storage Area Networks (SANs). It’s advisable to check the latest documentation, vendor materials, or industry updates for specific information on SAN Q-Flow and its impact on storage traffic management.
47. Explain the concept of SAN Boot from iSCSI.
Ans:
SAN Boot from iSCSI involves booting a server directly from a storage area network using the iSCSI protocol. It allows for centralized management of boot images and configurations.SAN Boot from iSCSI involves configuring a server to boot its operating system directly from a storage device located on an iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface) network. Instead of using a local disk for the operating system, the server connects to an iSCSI target, treating it as a remote disk, and loads the OS from there. This approach allows for centralized management of boot images, simplified provisioning, and flexibility in managing server configurations in a Storage Area Network (SAN) environment.
48. Define SAN Compression and its benefits in storage environments.
Ans:
- SAN Compression involves reducing the size of data before it is stored in the SAN. It conserves storage space, minimizes bandwidth requirements, and enhances overall storage efficiency. Reduces data size in a Storage Area Network (SAN) for efficient storage and transmission.
- Benefits: Optimizes bandwidth, improves storage efficiency, speeds up data transfer, and potentially leads to cost savings.
49. What is the purpose of SAN Latency?
Ans:
SAN Latency is the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the destination in a storage area network. It is measured in milliseconds and impacts overall system responsiveness and performance.SAN Latency refers to the time delay in data transmission within a Storage Area Network. The purpose of monitoring and managing SAN latency is to ensure optimal performance and responsiveness in accessing and transferring data. Low latency is crucial in maintaining efficient communication between storage devices and servers, contributing to a responsive and reliable storage infrastructure.
50. Explain the concept of SAN Copy.
Ans:
SAN Copy is a feature that allows the efficient copying of data between storage devices within a SAN. It is commonly used for data migration, replication, and backup purposes.SAN Copy is a feature in Storage Area Networks (SANs) that facilitates the efficient and reliable replication of data between storage devices.
51. Define SAN Fabric Scalability and discuss considerations for scaling SAN.
Ans:
SAN Fabric Scalability refers to the ability of a storage area network to grow and accommodate additional devices.
- Switch Capacity: Ensure switches can accommodate more ports.
- Bandwidth: Evaluate and upgrade for increased data traffic.
- Topology: Adjust SAN topology for scalability.
- Zoning and Services: Update configurations to include new devices.
- Firmware Compatibility: Confirm compatibility for all components.
52. What is the role of SAN Management Software?
Ans:
SAN Management Software is used to configure, monitor, and optimize the components of a storage area network. It provides features such as zoning management, performance monitoring, and firmware upgrades. The use of SAN management software is essential in overseeing and controlling the components within a Storage Area Network (SAN).
53. Explain the concept of SAN End-of-Life (EOL) and considerations for upgrading or replacing components.
Ans:
SAN End-of-Life refers to the stage in a component’s lifecycle where it is no longer supported. Considerations include evaluating compatibility, planning for migration, and ensuring continued support for critical functionalities.SAN End-of-Life (EOL) refers to the stage in the life cycle of components within a Storage Area Network (SAN) where the manufacturer or vendor discontinues support, maintenance, and further development for those components.
54. What are SAN Endpoints, and how are they addressed in a Fibre Channel network?
Ans:
- SAN Endpoints: Devices in a Storage Area Network (SAN), including servers and storage arrays.
- Addressing in Fibre Channel Network: Identified by World Wide Names (WWNs) – N_Port WWN for individual ports and F_Port WWN for Fibre Channel switches
55. Define SAN Quality of Service (QoS) Classes.
Ans:
SAN QoS Classes are categories that prioritize different types of traffic within a storage area network. Classes help ensure that critical data, such as database transactions, receives higher priority over less time-sensitive traffic.SAN Quality of Service (QoS) Classes are predefined sets of service levels in a Storage Area Network. These classes prioritize and manage the performance, reliability, and availability of data traffic within the SAN based on specific requirements.
56. Explain the concept of SAN Cache Mirroring.
Ans:
SAN Cache Mirroring involves duplicating the cache contents between multiple controllers or storage devices. It enhances data protection by maintaining redundancy and lowering the chance that data may be lost in the case of a controller failure.SAN Cache Mirroring involves duplicating the contents of cache memory between two storage controllers in a Storage Area Network (SAN).
57. What is the role of SAN Encryption Zones?
Ans:
- SAN Encryption Zones define specific areas within the storage network where encryption is applied to protect data in transit.
- Configuration involves setting up policies to enable encryption for designated zones.SAN Encryption Zones define specific areas within a Storage Area Network (SAN) where data encryption is applied.
- By creating encryption zones, administrators can selectively encrypt sensitive data, enhancing security and compliance.
- This targeted approach allows organizations to apply encryption to specific subsets of data rather than the entire SAN, providing flexibility in meeting security requirements while managing performance considerations.
58. Define SAN Fabric Partitioning and its benefits.
Ans:
Logically dividing a SAN into isolated sections for access control. Enhances security, optimizes performance, isolates faults, and simplifies management
59. Explain the purpose of SAN Load Balancing.
Ans:
SAN Load Balancing optimizes the distribution of traffic across multiple paths, ensuring efficient utilization of available bandwidth. It is achieved through techniques like path selection algorithms and dynamic load balancing policies.SAN Load Balancing ensures optimal distribution of data traffic across multiple paths, devices, or switches within a Storage Area Network (SAN).
60. What is the significance of SAN Virtualization?
Ans:
SAN Virtualization abstracts underlying storage resources, presenting them as a virtualized pool. It simplifies storage management, enhances flexibility, and allows for efficient utilization of storage capacity. Simplified management enhances flexibility, optimizes resource utilization, and enables seamless data migration in Storage Area Networks.
61. Define SAN Monitoring and discuss key metrics monitored in a storage environment.
Ans:
SAN Monitoring involves observing and analyzing various metrics to guarantee peak performance and spot possible problems. Key metrics include throughput, latency, error rates, and utilization of storage components.
Key Monitored Metrics:
- Throughput: Measures data transfer rates.
- Latency: Monitors time for data travel.
- Error Rates: Tracks transmission issues.
- Utilization: Measures resource usage.
- IOPS: Quantifies input/output operations.
- Queue Depth: Monitors command backlog.
62. Explain the role of SAN Zone Merging and the considerations for its implementation.
Ans:
SAN Zone Merging involves combining or reconfiguring zones within a Fibre Channel fabric. Considerations include minimizing disruptions, validating consistency, and ensuring that merged zones align with the intended access requirements.
- Compatibility: Ensure device compatibility to prevent connectivity issues.
- Impact Analysis: Evaluate potential effects on SAN traffic and performance.
- Documentation: Update and maintain comprehensive documentation.
- Testing: Thoroughly test merged zones for proper operation.
- Communication: Inform stakeholders to maintain transparency.
- Rollback Plan: Develop a plan to revert in case of issues quickly.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor SAN performance post-merge for optimal operation.
63. What is SAN Top Talkers Analysis, and how does it aid in performance optimization?
Ans:
SAN Top Talkers Analysis involves identifying devices or applications that generate the most traffic within the SAN. It helps optimize performance by addressing potential bottlenecks or congestion points.SAN Top Talkers Analysis is a proactive approach to optimizing performance within a Storage Area Network. It provides insights into data traffic patterns, aids in identifying and addressing bottlenecks, and supports resource optimization. This improves the overall dependability and efficiency of the SAN.
64. Define SAN Logins (LOGO/LOGI) and their significance in the initialization process.
Ans:
SAN Logins include LOGO (Logout) and LOGI (Login) procedures, which are part of the initialization process in Fibre Channel. LOGO terminates a connection, while LOGI establishes a new connection or re-establishes an existing one.
Significance in Initialization:
- LOGI (Login): Initiates the connection between a device (like a host or storage) and the Fibre Channel fabric during the initialization process.
- LOGO (Logout): Terminates the connection, releasing resources and signaling the end of the device’s participation in the SAN.
65. Explain the role of SAN Performance Tuning in optimizing storage system efficiency.
Ans:
SAN Performance Tuning involves adjusting configurations and parameters to maximize a storage area network’s performance. It includes adjustments to settings such as buffer size, queue depth, and device parameters to achieve better throughput and response times. Optimizes SAN efficiency by maximizing bandwidth, reducing latency, optimizing I/O, balancing resources, reviewing zoning, and proactively monitoring and analyzing performance metrics.
66. Define SAN Boot Parameters and discuss considerations when configuring them.
Ans:
SAN Boot Parameters include settings that define how a server boots from a storage area network. Considerations involve ensuring compatibility with the SAN infrastructure, specifying the boot LUN, and configuring timeout values.
Considerations:
- Boot LUN Selection: Specify the boot LUN on the SAN.
- WWN Configuration: Ensure correct HBA WWN configuration.
- Firmware Compatibility: Verify compatible HBA and storage firmware.
- Boot Order: Set the appropriate boot order.
- Path Redundancy: Configure redundant paths for reliability.
- Zoning Configuration: Permit server access in zoning configurations.
- Network Configuration: Confirm correct network settings for SAN communication.
67. What is SAN Fabric Trunking, and how does it improve bandwidth utilization?
Ans:
Aggregates multiple links into a logical group in a SAN.
- Improvement in Bandwidth Utilization:
- Increased Aggregate Bandwidth: Combines bandwidth for higher throughput.
- Load Balancing: Distributes traffic evenly across links.
- Redundancy: Enhances fault tolerance with multiple paths.
68. Explain the concept of SAN Fibre Channel Forward Error Correction (FEC).
Ans:
SAN Fibre Channel Forward Error Correction is a method for identifying and fixing data mistakes transmission. It enhances reliability by ensuring data integrity during communication within the Fibre Channel fabric.FEC in SAN Fibre Channel involves the implementation of error correction techniques to detect and correct data transmission errors in real time.
69. Define SAN Persistent Ports and their role in maintaining consistent configurations.
Ans:
Fibre Channel port configurations persisting across reboots.
Role in Maintaining Consistent Configurations:
- Stability: Ensures stable configurations after reboots.
- Prevention of Loss: Prevents loss of critical settings.
- Simplified Management: Contributes to simplified SAN management.
70. What is the purpose of SAN Extended Fabric?
Ans:
SAN Extended Fabrics enable Fibre Channel communication over long-distance connections. It is achieved through technologies like Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP) or dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM). SAN Extended Fabric refers to the extension of a Storage Area Network (SAN) across geographically dispersed locations. The primary purpose is to facilitate data replication, disaster recovery, and business continuity by allowing SAN connectivity between remote sites.
71. Explain the significance of SAN Edge Switches in storage network architecture.
Ans:
- Device Connectivity: Connect servers, storage, and devices at the edge to the SAN.
- Zoning Control: Facilitate zoning configurations for security and data isolation.
- Aggregation: Aggregate connections, simplifying cabling and improving manageability.
- Expansion Support: Accommodate additional ports to support SAN growth.
- Traffic Localization: Localize SAN traffic, reducing load on core switches for optimized data transfer.
72. Define SAN Affinity Rules and their use in optimizing data placement.
Ans:
Directives in a SAN defining relationships between devices.Use in Optimizing Data Placement.
- Data Locality: Enhances access speed by promoting data locality.
- Performance Optimization: Minimizes data transfer times for improved performance.
- Resource Utilization: Strategically places data to align with application requirements.
- Avoidance of Interference: Prevents conflicts or bottlenecks, optimizing data access.
73. What is SAN Storage Tiering, and how does it enhance performance and cost efficiency?
Ans:
- SAN Storage Tiering: Categorizes data into performance and cost tiers.
- Enhancement of Performance and Cost-Efficiency:
- Optimized Performance: Places high-priority data on high-performance tiers.
- Cost Efficiency: Stores less critical data on lower-cost tiers.
- Resource Utilization: Allocates resources efficiently based on data characteristics.
- Adaptability: Allows dynamic adjustments to match changing data access patterns.
74. Explain the concept of SAN Synchronization.
Ans:
SAN Synchronization involves ensuring that data copies across different locations are consistent and up-to-date. It is crucial in data replication scenarios to maintain integrity and reliability.SAN Synchronization refers to the process of ensuring consistency and alignment of data, configurations, or states across different components within a Storage Area Network (SAN).
75. Define SAN Boot Fabric Login and its role in the boot process.
Ans:
- SAN Boot Fabric Login (FLOGI): Initial Fibre Channel step during boot.
- Fabric Entry: Initiates device communication with Fibre Channel fabric.
- WWN Assignment: Assign a unique worldwide name (WWN) to the device.
- Configuration Exchange: Exchanges configuration info for proper initialization.
- Access to SAN Services: Grants access to SAN services, crucial for boot and data operations.
76. What is SAN Extension Gateway, and how does it enable SAN connectivity over distance?
Ans:
- SAN Extension Gateway: Facilitates SAN connectivity over extended distances.
- Fibre Channel Extension: Extends Fibre Channel connections for longer distances.
- Protocol Conversion: Enables communication between SANs with different protocols.
- Fiber optic or IP networks: Fiber optic or IP networks are used to transmit SAN data.
- Data Replication: Supports data replication between geographically dispersed SANs.
77. Explain the purpose of SAN Convergence.
Ans:
SAN Convergence involves combining storage and data networking traffic onto a single network infrastructure. It simplifies network architecture, reduces complexity, and enhances resource utilization.SAN convergence also enables the use of standard network equipment and protocols, making it easier to manage, scale, and maintain the network infrastructure. This approach enhances flexibility and efficiency in allocating resources while supporting the increasing demands of data storage and communication in modern IT environments.
78. Define SAN Disk Pooling and discuss its benefits in storage management.
Ans:
- SANDisk Polling involves grouping storage devices into pools, allowing for dynamic allocation of resources. It enhances storage management by optimizing capacity utilization and improving flexibility in resource allocation.
- SAN disk pooling is a storage management strategy that offers improved resource utilization, simplified administration, flexibility, scalability, dynamic provisioning, enhanced performance, and efficient load balancing in a Storage Area Network environment.
79. What is SAN Isolation, and why is it important in a storage environment?
Ans:
SAN Isolation involves separating or containing specific components within the SAN to prevent disruptions or unauthorized access. It is necessary to keep everything stable, secure, and functional in the storage network.SAN isolation is essential in a storage environment to enhance security, optimize performance, contain faults, meet compliance requirements, and facilitate effective resource management within the Storage Area Network.
80. Explain the concept of SAN Fabric Delegation and its role in administration.
Ans:
SAN Fabric Delegation allows administrators to delegate specific management tasks within the storage fabric to different users or groups. It streamlines administrative responsibilities and enhances collaboration.SAN Fabric Delegation involves assigning specific administrative responsibilities to different individuals or roles within a Storage Area Network (SAN).
81. Define SAN Tape Library and its role in backup and archiving.
Ans:
- A SAN Tape Library is a type of storage that stores and retrieves data using magnetic tape. It is essential for backup and
- archiving strategies, providing a cost-effective and scalable solution for long-term data retention.
- A SAN Tape Library is a storage device that uses tape cartridges to provide high-capacity, cost-effective storage for backup and archiving purposes in a Storage Area Network (SAN).
- It facilitates efficient data backup, long-term data retention, and archiving by storing data on tape cartridges, which are sequentially accessed for retrieval and archival purposes.
82. What is SAN Disk Virtualization, and how does it contribute to storage efficiency?
Ans:
SAN Disk Virtualization abstracts physical storage devices, presenting them as a virtualized pool. It contributes to storage efficiency by enabling centralized management, improved utilization, and simplified provisioning of storage resources.SAN Disk Virtualization is the abstraction of physical storage devices into a virtualized layer, allowing centralized management and allocation of storage resources in a Storage Area Network (SAN).
83. Explain the concept of SAN Trunking Algorithms and their impact on load balancing.
Ans:
- SAN Trunking Algorithms determine how traffic is distributed across multiple links in a trunk. Examples include Round Robin, Least Recently Used (LRU), or Source/Destination IP-based algorithms. They impact load balancing efficiency within the SAN.
- Different trunking algorithms, such as round-robin or least recently used (LRU), aim to use the data across evenly available links. This load balancing ensures that the SAN network is utilized efficiently, preventing bottlenecks and optimizing overall performance by distributing traffic across multiple paths in a balanced manner.
84. Define SAN Port Mirroring and its role in troubleshooting and analysis.
Ans:
SAN Port Mirroring involves copying traffic from one port to another for analysis or troubleshooting purposes. It allows administrators to monitor and diagnose issues within the SAN. This capability aids in diagnosing issues, analyzing performance, and monitoring the behavior of the SAN without disrupting its operations. Administrators can use the mirrored traffic to identify anomalies, diagnose errors, and gain insights into the network’s performance for effective troubleshooting and optimization.
85. What is SAN Fabric Virtualization, and how does it improve resource utilization?
Ans:
- SAN Fabric Virtualization abstracts physical fabric resources, creating virtualized representations. It enhances resource utilization by allowing logical segmentation and dynamic allocation of fabric resources.
- SAN Fabric Virtualization involves creating an abstraction layer over the physical components of a Storage Area Network (SAN), enabling centralized control and management of the network.
- This virtualization improves resource utilization by allowing administrators to allocate, configure, and optimize network resources dynamically based on the needs of different applications and workloads.
86. Explain the concept of SAN Health Check Tools and their significance.
Ans:
SAN Health Check Tools are software or utilities that assess the overall health and performance of a storage area network. They identify potential issues, ensure optimal configurations, and support proactive maintenance.SAN Health Check Tools are crucial for proactively monitoring, diagnosing, and optimizing Storage Area Networks.
87. Define SAN Disk Striping and its role in enhancing storage performance.
Ans:
SAN Disk Striping involves distributing data across multiple disks in a systematic manner. It enhances storage performance by parallelizing read and write operations, reducing latency, and improving throughput.SAN Disk Striping is a storage technique that involves breaking down data into small, contiguous blocks and distributing these blocks across multiple disks in a Storage Area Network (SAN).
88. What is SAN Fabric deprovisioning, and why is it essential in SAN management?
Ans:
- SAN Fabric Deprovisioning involves removing or decommissioning specific components or zones within the Fibre Channel fabric.
- It is crucial for maintaining an organized and efficient SAN environment.SAN Fabric Deprovisioning is the process of systematically and securely decommissioning or removing components from a Storage Area Network (SAN).
- This can involve retiring storage devices, switches, or other SAN elements that are no longer needed or are being replaced.
89. Explain the purpose of SAN Performance Metrics and standard metrics used for evaluation.
Ans:
SAN Performance Metrics measure various aspects of storage performance, including throughput, latency, IOPS, and error rates. They provide insights into the efficiency and health of the storage infrastructure.SAN Performance Metrics are measurements used to evaluate and monitor the performance of a Storage Area Network (SAN). These metrics provide insights into various aspects of the SAN’s operation, helping administrators identify bottlenecks, optimize resource utilization, and ensure efficient data transfer.
90. Define SAN Disk Cloning and its use in data replication and backup.
Ans:
SANDisk Cloning involves creating identical copies of a disk or volume. It is used in data replication and backup scenarios to ensure data availability and provide recovery options.SAN Disk Cloning is a versatile tool within a Storage Area Network, providing a reliable method for creating duplicates of disks. This capability supports data replication, backup strategies, disaster recovery planning, testing, and development efforts, contributing to an organization’s overall data management and protection strategies.
91. What is SAN Fabric Trunking Failover, and how does it contribute to high availability?
Ans:
- SAN Fabric Trunking Failover is the ability of a trunked connection to automatically switch to an alternative path in case of a link failure. It enhances high availability by providing redundancy and minimizing downtime.
- SAN Fabric Trunking Failover contributes to high availability in a Storage Area Network by offering redundancy, load balancing, continuous connectivity, improved reliability, automatic recovery, and enhanced fault tolerance.
92. Explain the concept of SAN Traffic Isolation and its importance in optimizing performance.
Ans:
SAN Traffic Isolation involves segregating specific types of traffic within the SAN. It is essential for optimizing performance by preventing interference between different classes of traffic.SAN Traffic Isolation is essential in optimizing performance within a Storage Area Network. It offers an organized method for handling various types of traffic, prevents congestion, enhances security, facilitates troubleshooting, and ensures that critical workloads receive the necessary resources for optimal performance.
93. Define the SAN Fabric Merge Policy and considerations for implementing it.
Ans:
SAN Fabric Merge Policy dictates the rules for combining or merging separate Fibre Channel fabrics. Considerations include maintaining consistent configurations, validating compatibility, and minimizing disruptions during the merge.SAN Fabric Merge Policy refers to the rules and procedures governing the merging of two or more independent SAN fabrics.
94. Explain the role of SAN Virtual LAN (VLAN) Tagging in network segmentation.
Ans:
- SAN VLAN Tagging involves adding VLAN information to Fibre Channel frames, enabling network segmentation within the SAN.
- It helps optimize traffic flow and improves security by isolating devices based on VLAN membership. SAN VLAN Tagging is a powerful tool for network segmentation within a Storage Area Network.
- It enhances security, improves resource utilization, simplifies network management, provides flexibility, and contributes to optimized performance by isolating and logically grouping traffic based on specific criteria.
95. What is SAN Caching, and how does it impact storage performance?
Ans:
SAN Caching involves using high-speed memory to store frequently accessed data, reducing access times and improving storage performance by serving read and write requests more efficiently.SAN Caching, in the context of a Storage Area Network (SAN), involves the use of cache memory within storage controllers or SAN devices to temporarily store frequently accessed data. This cache memory can be utilized for both read and write operations.