NetApp, a prominent data management and storage company, offers a variety of solutions for organizations seeking to efficiently manage and protect their data. With a focus on data storage, data management, and data protection, NetApp’s products include high-performance storage arrays, all-flash and hybrid storage systems, as well as innovative data management tools like data deduplication and compression to optimize storage resources. For companies looking to improve data accessibility, lower storage costs, and guarantee data integrity across a range of environments—from hybrid and multi-cloud deployments to on-premises data centers—these solutions are essential.
1. What is NetApp?
Ans:
NetApp, Inc. is an American multinational company that provides hybrid cloud data services and solutions for managing data and apps in on-premises and cloud environments. Founded in 1992, the company has been at the forefront of storage technology innovation, offering a range of products and services that encompass various forms of data storage, data management, and cloud integration. Their solutions aim to simplify data management and streamline operations for businesses.
2. What is a WAFL in NetApp?
Ans:
WAFL, which stands for Write Anywhere File Layout, is a proprietary file system developed by NetApp. It’s unique in its ability to handle large amounts of data efficiently. One of the main advantages of WAFL is its snapshot capability, which allows for consistent point-in-time copies of the file system. Its design optimizes write and read operations, reduces disk I/O, and integrates seamlessly with NetApp’s RAID-DP (a form of RAID 6) for data protection.
3. What is a Storage Area Network (SAN)?
Ans:
Servers are connected to storage devices (like tapes and arrays) via a specialised high-speed network called a Storage Area Network (SAN). SANs are primarily used to enable shared storage devices’ storage volumes to be accessed by multiple servers. It operates at the block level and is typically used for data-intensive applications, databases, and virtualized environments.
4. Differentiate between SAN and NAS.
Ans:
| Aspect | SAN (Storage Area Network)() | NAS (Network Attached Storage)() | |
| Architecture |
High-speed network connecting storage to servers using Fibre Channel or iSCSI. |
File-level storage connected to the network via Ethernet and TCP/IP. | |
| Access Type | Block-level access, treating storage as raw block devices | File-level access, acting as a file server with shared folders. |
5.What are aggregates in NetApp?
Ans:
In the context of NetApp, aggregates are a fundamental storage unit. They are collections of physical disks, known as RAID groups, that are combined together to function as a single storage pool. These aggregates host one or multiple flexible volumes. An aggregate can be thought of as a container that holds the actual data. The health and performance of an aggregate can directly influence the performance of the volumes and LUNs (Logical Unit Numbers) that reside on it. They play a key role in NetApp’s data management, allowing for functionalities like snapshots, deduplication, and thin provisioning.
6. What is the purpose of a FlexVol in NetApp?
Ans:
FlexVol, short for Flexible Volume, is a feature in NetApp storage systems that offers a dynamic, virtualized data container. This means you can create, resize, or even delete a FlexVol volume without causing any disruption to the system’s operations. This agility facilitates better storage utilization, as administrators can adjust storage resources based on real-time needs, optimizing storage space and efficiency.
7. What is SnapMirror?
Ans:
SnapMirror is NetApp’s primary replication technology designed for data protection, backup, and disaster recovery. It replicates data changes from a source volume on one NetApp storage system to a destination volume on another. This ensures data consistency and availability. Moreover, SnapMirror can operate across different locations, making it ideal for disaster recovery scenarios where data needs to be available in geographically diverse places.
8. How does SnapShot work in NetApp?
Ans:
NetApp’s SnapShot technology takes point-in-time images of a file system, capturing its state. But instead of copying the actual data, SnapShot leverages a technique where only the changes or “deltas” since the last SnapShot are stored. This makes SnapShots extremely space efficient. When a user accesses data from a SnapShot, NetApp uses a combination of the original data and the changes stored in the SnapShot to present the data as it appeared at that specific point in time.
9. What is the significance of NVRAM in NetApp?
Ans:
NVRAM, which stands for Non-Volatile Random Access Memory, plays a critical role in NetApp systems by logging all write operations. Before data is written to the disks, it’s first logged to NVRAM. This ensures that even if there’s a system failure before the data is committed to the disks, there’s a persistent record of those operations. Once the system is restored, the logged operations in NVRAM can be replayed, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
10. What is Deduplication?
Ans:
In data storage, deduplication is the process of locating and removing redundant copies of data in order to maximise storage efficiency. For instance, if multiple users store the same file, deduplication ensures that only one unique instance of that data is stored, with all other references pointing to that single copy. This process can significantly reduce storage needs, especially in environments where redundancy is high, like virtualized systems or backup archives.
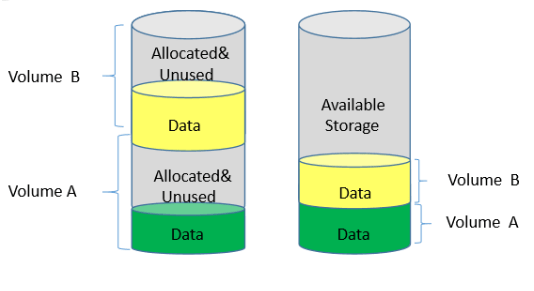
11. What is Thin Provisioning?
Ans:
Thin provisioning in data storage refers to the practice of allocating storage capacity dynamically to applications on an as-needed basis, instead of pre-allocating a fixed amount of storage in advance. This means storage is consumed only when data is written, optimizing utilization. By overcommitting storage in this manner, organizations can achieve better efficiency and flexibility, reducing costs and wastage associated with unused storage space.
12. How does NetApp ensure high availability?
Ans:
NetApp ensures high availability primarily through its Clustered Data ONTAP (cDOT) architecture. This allows multiple storage controllers to function as a single system, providing non-disruptive operations and seamless failover capabilities. If one node or controller fails, its workload can be automatically transferred to another node without causing disruptions. Additionally, features like RAID-DP (double parity RAID) and MetroCluster further enhance data protection and availability.
13. What is SnapVault?
Ans:
SnapVault is NetApp’s backup solution designed for efficient disk-to-disk backup and recovery. It leverages snapshot technology, enabling faster and more space-efficient backups by storing only changed blocks of data. SnapVault creates a read-only copy of the source data on secondary storage, providing a longer retention period for backups and facilitating compliance with data retention policies.
14. What is FPolicy in NetApp?
Ans:
FPolicy is a framework provided by NetApp that allows administrators to monitor, filter, and respond to file operations on a NetApp system. FPolicy can integrate with third-party applications to create file access and screening policies. For instance, it can be used to block certain types of files from being saved or to alert administrators about specific file operations, enhancing security and compliance.
15. What is MetroCluster?
Ans:
NetApp MetroCluster is a solution that combines array-based clustering with synchronous data replication. It provides continuous data availability and zero data loss at the granularity of a storage virtual machine. In the event of a site failure, MetroCluster allows for automatic and transparent switchover to the surviving site, ensuring business continuity. The synchronous replication ensures that data is always up to date on both sites, minimizing the risk of data loss during switchover scenarios.
16. How do you upgrade ONTAP in NetApp?
Ans:
Upgrading ONTAP in a NetApp system typically involves a series of steps. First, the desired ONTAP software image is downloaded from the NetApp support site. Using the “system image” commands, administrators can manage this software image. The process typically involves putting the system in maintenance mode, installing the new image, and then rebooting the system. Before any upgrade, it’s critical to check compatibility, review the upgrade guide for any specific considerations, and ensure backups of configurations and data.
17. What is the maximum volume size in NetApp?
Ans:
The maximum volume size in NetApp does change with different ONTAP versions and configurations. As of the last update, the maximum size for a FlexVol volume was 100TB. However, it’s always good to refer to the latest NetApp documentation or system specifications for the most recent and specific data limits.
18. What is the difference between VSM and QSM in SnapMirror?
Ans:
VSM (Volume SnapMirror): This mode replicates entire volumes. It’s an efficient method to ensure disaster recovery for the whole volume.
QSM (Qtree SnapMirror): In contrast, QSM focuses on replicating individual Qtrees within a volume. This is beneficial if only specific data subsets (represented by the qtree) need to be replicated, offering finer granularity.
19. Explain NDMP.
Ans:
NDMP, which stands for Network Data Management Protocol, is an open-standard protocol used for backup and recovery of network-attached storage (NAS) devices. It allows for a standardized method of backing up data irrespective of the NAS vendor. NDMP separates the data path from the control path, enabling the data to be transferred directly between the storage device and the backup device, minimizing the impact on network performance.
20. What is CIFS?
Ans:
CIFS, or Common Internet File System, now more commonly known as SMB (Server Message Block), is a network protocol mainly used by Windows-based systems for sharing files, printers, and other resources across a network. It allows users to open, read, and write files across the network as if they were on their local machine. CIFS provides various features like file locking, data integrity, and authentication, making it a widely used protocol in corporate environments for sharing resources.
21. Differentiate between FC and iSCSI protocols.
Ans:
FC (Fibre Channel): This is a high-speed network technology designed specifically for storage communication. It typically requires specialized hardware like FC switches and Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) in servers to connect to FC SANs.
iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface): iSCSI, on the other hand, encapsulates SCSI commands into IP packets, allowing them to be transported over standard Ethernet networks. This means you can use existing network infrastructure, and it doesn’t need specialized hardware like Fibre Channel does.
22. What is RAID-DP?
Ans:
RAID-DP (RAID Double Parity) is NetApp’s proprietary RAID technology designed to provide enhanced protection for stored data. While traditional RAID 6 also provides double parity, RAID-DP does so with better performance and efficiency. The two parity disks in RAID-DP can protect against two simultaneous disk failures, ensuring data remains safe and accessible even in such scenarios.
23. Explain the role of Data ONTAP.
Ans:
Data ONTAP is NetApp’s flagship storage operating system. It provides the foundation for a multitude of storage and data management tasks, including deduplication, thin provisioning, data replication (SnapMirror, SnapVault), and more. With its unified architecture, Data ONTAP supports various protocols, allowing for both SAN and NAS operations. Furthermore, its modular and scalable nature enables seamless integration with cloud services, making hybrid cloud setups feasible.
24. What are the different disk types used in NetApp storage?
Ans:
SSDs (Solid State Drives): These are high-performance disks with no moving parts, suitable for high I/O operations.
SAS (Serial Attached SCSI): These are high-performance disks designed for enterprise storage and offer a balance between performance and capacity.
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment): These disks are more economical and offer higher capacity but at the cost of lower performance compared to SSDs and SAS.
25. How do you troubleshoot a failed disk in NetApp?
Ans:
- Use “sysconfig -r” to identify failed disks.
- Check logs in OnCommand System Manager for failure details.
- Replace failed disks, preferably with hot-swap.
- The system will auto-reconstruct the disk.
- Lastly, verify any firmware updates to prevent future issues.
26. What is FlexClone?
Ans:
NetApp’s FlexClone technology allows administrators to create instantaneous, virtual copies of datasets, be it an entire FlexVol volume or just a single file. These clones are writable and do not initially consume any additional storage space, since they reference the same blocks as the parent. However, as changes are made to the clone, it starts consuming storage space for the changed blocks. This capability is crucial for test/dev environments, analytics, and other scenarios where duplicate data is needed without duplicating storage costs.
27. Explain Infinite Volume in NetApp.
Ans:
NetApp’s Infinite Volume is a feature designed to address the challenges of managing extremely large datasets. It offers a scalable solution where you can create a single namespace that can grow up to 20PB, eliminating the need for data migrations as the dataset grows. This scalability, combined with NetApp’s data management capabilities, offers efficient, seamless access to vast datasets without compromising performance.
28. What is the maximum size of an aggregate in NetApp?
Ans:
The maximum aggregate size in NetApp can vary depending on the ONTAP version and the hardware being used. As of ONTAP 9, in certain configurations, the aggregate size can go up to 800TB. However, it’s always crucial to consult the latest documentation or system limitations for the most updated figures.
29. Explain Flash Pool.
Ans:
Flash Pool is a part of NetApp’s Virtual Storage Tiering technology. It allows the combination of Solid State Drives (SSDs) and traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) within the same aggregate. This setup provides automatic data tiering between the SSDs and HDDs. Frequently accessed (hot) data blocks are moved to SSDs for faster access, while less frequently accessed (cold) blocks remain on HDDs. This delivers improved performance without the high cost of an all-flash setup.
30. How do you secure data in NetApp storage?
Ans:
- Encryption for data at-rest (NVE) and in-transit (e.g., HTTPS).
- RBAC for user access control.
- Secure Multi-Tenancy for data separation in shared storage.
- Compliance tools like SnapLock with WORM capabilities.
- Data Masking and Anonymization for data privacy.
31. What is SnapRestore?
Ans:
SnapRestore is a data recovery technology by NetApp. It leverages the system’s SnapShot capabilities, allowing users or administrators to instantly revert a volume or a file back to a previous state as captured in a Snapshot. This can be especially useful for quickly recovering from accidental deletions or system malfunctions.
32. What is Synchronous and Asynchronous replication in NetApp?
Ans:
Synchronous replication: Every time data is written to the primary system, it’s immediately replicated to the secondary system. It ensures that primary and secondary data sets are always identical but might introduce latency due to the wait for confirmation from the secondary system.
Asynchronous replication: Data replication occurs at predetermined intervals or after a specific amount of time, from the primary system to the secondary system. It provides better performance compared to synchronous replication but at the cost of potential data loss during that interval.
33. What is the function of StorageGRID?
Ans:
StorageGRID by NetApp is an object storage solution, primarily designed to manage and store vast amounts of unstructured data. It’s scalable, durable, and provides capabilities like geo-distributed content repository, data lifecycle policies, and multi-site replication. It’s optimal for archiving, backup, and large-scale content repositories.
34. How does Clustered ONTAP differ from 7-Mode?
Ans:
Clustered ONTAP: Offers scalability and flexibility by allowing multiple nodes to operate together as a unified system. It provides seamless data movement between nodes, non-disruptive operations, and continuous data access even during upgrades.
7-Mode: Represents the traditional mode of operation before the introduction of clustering. It operates as a standalone system, and while robust and reliable, it lacks the scalability and flexibility offered by Clustered ONTAP.
35. What are Qtrees in NetApp storage?
Ans:
Qtrees are a hierarchical level between volumes and files/directories in the NetApp storage system. They allow administrators to apply quotas to limit space or file usage and set security styles. Qtrees are beneficial for segregating and managing workloads or user data within a single volume.
36. Explain AutoSupport in NetApp.
Ans:
AutoSupport is a proactive monitoring and reporting feature of NetApp systems. It automatically collects system information, performance data, and potential issues, then sends this information to NetApp’s support for analysis. This helps in early detection and resolution of issues, ensuring optimal system performance and uptime.
37. What is the role of Storage Manager in NetApp?
Ans:
Storage Manager is a tool by NetApp designed to facilitate the provisioning, monitoring, and management of storage resources. It provides administrators with a unified interface to control storage allocations, monitor storage health, and ensure data protection and compliance.
38. How do you configure a new disk shelf in NetApp?
Ans:
- When adding a new disk shelf in a NetApp system:
- Physically connect the shelf to the NetApp controller.
- Use the “disk show” command to verify the system recognizes the new disks.
- Assign disks to a specific controller.
- Initialize the disks to prepare them for use.
39. Explain SVM (Storage Virtual Machine) in NetApp.
Ans:
SVM, or Storage Virtual Machine, in NetApp provides a virtualized, logical view of the storage, abstracting the underlying physical storage infrastructure. It allows administrators to create isolated environments with their own set of resources, policies, and protocols.
- import requests
- api, u, p = ‘https://your-netapp-cluster/api/’, ‘your_username’, ‘your_password’
- c, d = lambda n: requests.post(f”{api}s/{n}”, headers={‘content-type’:’application/json’}, auth=(u, p), json={“name”: n, “aggregates”: [“aggr1”, “aggr2”], “rootVolume”: {“name”: “rootvol”, “aggregates”: [“aggr1″]}}), lambda n: requests.delete(f”{api}s/{n}”, headers={‘content-type’:’application/json’}, auth=(u, p))
- c(‘new_svm_name’)
- d(‘svm_to_delete’)
40. What are the data protection features in NetApp?
Ans:
Snapshots: Point-in-time copies of data.
SnapMirror: Data replication technology for backup and recovery.
SnapVault: Disk-based backup solution.
MetroCluster: Ensures continuous data availability and zero data loss.
41. What is the purpose of FlexGroup in NetApp?
Ans:
FlexGroup is a large container that balances performance across member FlexVols, offering massive capacity without compromising on performance. It’s optimized for modern workloads like artificial intelligence, high-tech manufacturing, media rendering, and design collaborations.
42. Can you explain Storage Efficiency features in NetApp?
Ans:
NetApp offers several storage efficiency features like Deduplication (eliminating duplicate blocks of data), Compression (reducing the size of data before writing to disk), and Compaction (combining multiple small writes into a single block to save space).
43. What is a Vserver in NetApp terminology?
Ans:
A Vserver (or Storage Virtual Machine, SVM) is a logical storage unit in Clustered Data ONTAP. It has its own set of administrative domains, can own data volumes and LIFs, and present data to clients using various protocols.
44. What is the difference between a VIF and LIF?
Ans:
VIF (Virtual Interface) is a term used in 7-Mode for combining multiple network ports for redundancy or performance. LIF (Logical Interface) is used in Clustered ONTAP to represent a network address that can move between physical ports and nodes.
45. What is the purpose of the partner command in NetApp?
Ans:
The partner command is used in 7-Mode systems to manage and check the status of the HA (High Availability) partner node in an active-active configuration.
46. Can you explain the FAS and AFF series in NetApp’s portfolio?
Ans:
FAS (Fabric-Attached Storage) systems are versatile storage platforms supporting a mixture of HDD and SSD, optimized for a balance of performance and capacity. AFF (All Flash FAS) are high-performance systems exclusively using SSDs, designed for low-latency, high-IOPS workloads.
47. How do you create a volume in NetApp ONTAP?
Ans:
To create a volume in NetApp ONTAP, first access the ONTAP command-line interface. Decide the aggregate for the volume. Then, use the “volume create” command specifying the Vserver, volume name, aggregate, and size. After creation, verify with the “volume show” command. If necessary, mount the volume for accessibility. Always refer to official NetApp guidelines when making changes.
48. What are Storage Classes in NetApp’s StorageGRID?
Ans:
Storage Classes in StorageGRID allow data to be stored redundantly across multiple locations or storage tiers based on policy, ensuring availability, durability, and cost optimization.
49. Explain the function of SIS (Secondary Storage Efficiency) in NetApp?
Ans:
SIS (now commonly referred to as Deduplication) in NetApp identifies duplicate blocks in a volume and removes them, replacing with references to a single copy, thus saving space.
50. What are the best practices for performing a SnapMirror update?
Ans:
- Ensure source and destination systems are reachable.
- Schedule updates during off-peak hours for minimal impact.
- Keep track of the progress and look for any errors or warnings.Validate data integrity post update.
- Keep track of Snapshot dependencies, so necessary Snapshots are not accidentally deleted.
51. How does Clustered ONTAP provide non-disruptive operations?
Ans:
Clustered ONTAP provides the ability to move data, network connections, and workloads non-disruptively across nodes in a cluster. This enables maintenance, technology refreshes, or workload balancing without application interruptions.
52. What are the key components of a NetApp cluster?
Ans:
A NetApp cluster consists of multiple nodes (storage systems), a cluster interconnect (networking component), aggregates (physical storage pools), SVMs (virtual storage servers), and LIFs (logical network interfaces).
53. Explain ONTAP Select.
Ans:
ONTAP Select is a software-defined storage (SDS) solution that brings the ONTAP storage and data management features to commodity servers running in virtualized environments.
54. What are the protocols supported by NetApp storage systems?
Ans:
NFS: File access for UNIX/Linux.
CIFS/SMB: File access for Windows.
iSCSI: Block access over IP.
FC: High-speed block access.
FCoE: Block access over Ethernet.
55. What is NetApp’s unified architecture?
Ans:
- NetApp’s unified architecture refers to its ability to support multiple storage protocols on a single platform, allowing flexibility in accessing data as file or block storage.
- If you need more in-depth explanations or further questions, let me know!
56. What is Hybrid Cloud in the context of NetApp?
Ans:
Hybrid Cloud, in the NetApp context, refers to the integration of on-premises NetApp storage systems with public cloud resources. This approach allows enterprises to leverage the scalability and flexibility of public clouds while retaining the performance and control of their on-premises data.
57. Can you explain NetApp’s Cloud Volumes ONTAP?
Ans:
Cloud Volumes ONTAP (CVO) is NetApp’s data management solution for cloud environments. It extends ONTAP’s rich data services to public cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. With CVO, enterprises can manage, protect, and optimize their data in the cloud, benefiting from features like deduplication, compression, and data tiering. Additionally, CVO aids in hybrid cloud workflows, disaster recovery, and backup strategies.
58. What is NetApp’s Data Fabric?
Ans:
Data Fabric is NetApp’s vision and suite of data services and solutions that provide consistent capabilities across a choice of endpoints spanning on-premises and multiple cloud environments. It’s designed to manage data seamlessly across different cloud environments, making data migration, backup, and hybrid cloud operations simpler and more integrated.
59. How does NetApp handle ransomware and security threats?
Ans:
Snapshot Technology: Provides point-in-time copies of data, allowing quick recovery from ransomware attacks without paying the ransom.
ONTAP Security: Incorporates features like multifactor authentication, role-based access control, and data encryption, both at-rest and in-transit.
NetApp Volume Encryption: Enables granular, volume-level encryption for data without needing application modification.
60. What is NetApp StorageGRID?
Ans:
StorageGRID is NetApp’s object-based storage solution designed for rich content repositories, archives, and data lakes. It supports the S3 protocol and is engineered for hybrid cloud integrations, offering capabilities like policy-based data placement, multi-site replication, and tiering to external clouds.
61. How does NetApp integrate with Kubernetes?
Ans:
NetApp has introduced Trident, a dynamic storage provisioner, for Kubernetes and OpenShift environments. Trident integrates ONTAP, Element, and SANtricity software with Kubernetes, allowing containerized applications to dynamically provision persistent storage volumes. It ensures that stateful applications in Kubernetes can retain their data even after a restart.
62. What is NetApp’s HCI (Hyper-Converged Infrastructure) solution?
Ans:
NetApp’s HCI is an enterprise-scale hyper-converged infrastructure solution that combines storage, compute, and networking into a single scalable, on-premises platform. It integrates Element software with compute and storage to offer predictable performance, flexibility, and automation. It’s particularly designed for hybrid multicloud environments.
63. How does ONTAP AI leverage AI and ML workloads?
Ans:
ONTAP AI is NetApp’s solution to streamline and accelerate AI and ML workflows. By integrating NVIDIA DGX servers and NetApp AFF systems, ONTAP AI provides a high-performance platform for data analytics and artificial intelligence. The combination ensures rapid data processing and efficient data management, allowing data scientists and engineers to train models faster and glean insights more quickly.
64. Can you explain the SaaS Backup service of NetApp?
Ans:
NetApp SaaS Backup is a cloud-based service offering backup and restore functionalities for SaaS applications. It provides data protection capabilities for applications like Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and Google Workspace. With this service, businesses can recover data swiftly in case of data loss, accidental deletions, or malicious attacks.
65. How does NetApp manage IoT and edge data?
Ans:
NetApp provides solutions for IoT and edge computing through its ONTAP data management software and StorageGRID. These tools help in capturing, storing, and processing data at the edge, close to where it’s generated, ensuring real-time insights. NetApp’s solutions also enable seamless data movement from edge to core data centers to cloud, optimizing storage, processing, and analytics across the data lifecycle.
66. How does NetApp ensure data mobility across hybrid clouds?
Ans:
NetApp’s Data Fabric solution enables seamless data mobility across hybrid environments. With tools like Cloud Volumes ONTAP and SnapMirror, users can easily move data between on-premises systems and multiple cloud providers. This ensures that data can be placed where it’s needed most, based on performance, cost, or regulatory requirements, without any data gravity concerns.
67. What is NetApp’s stance on sustainability and green IT?
Ans:
NetApp is committed to sustainability, evident in their eco-efficient products, operational excellence, and green initiatives. Their storage solutions are designed to reduce the data center footprint, thereby conserving energy. NetApp’s modular design philosophy allows components to be replaced without needing an entire system overhaul, leading to reduced electronic waste.
68. How does NetApp support DevOps and CI/CD pipelines?
Ans:
NetApp provides storage solutions that cater to the dynamic needs of DevOps and CI/CD workflows. Trident, for instance, automates persistent storage provisioning in Kubernetes environments, while FlexClone technology enables instant, space-efficient clones of datasets, aiding in rapid testing and development cycles.
69. What are the analytics and monitoring tools provided by NetApp for its storage solutions?
Ans:
NetApp offers Active IQ, a cloud-based analytics tool that uses AI and community wisdom to provide insights, risk assessments, and actionable intelligence. It helps in proactive fault resolution, optimization recommendations, and upgrade planning. Additionally, ONTAP System Manager provides a GUI for real-time system monitoring and management.
70. Can you explain the multi-tenancy features in NetApp storage systems?
Ans:
NetApp storage systems support secure multi-tenancy, enabling different departments or clients to share the same infrastructure without compromising security. SVM (Storage Virtual Machine) is a cornerstone of this, encapsulating data access, network configurations, and policies. Each SVM operates independently, ensuring data isolation and individualized management.
71. What is the role of NetApp in digital transformation initiatives?
Ans:
Digital transformation often requires agile data infrastructure, and NetApp’s portfolio supports this by accelerating applications, simplifying data services, and ensuring data availability everywhere, from the edge to the core to the cloud. With its hybrid and multi-cloud capabilities, NetApp ensures that businesses can modernize their IT without disruption, driving innovation and competitive differentiation.
72. How does NetApp handle data compliance and governance?
Ans:
NetApp provides several tools and integrations to help with data compliance and governance. SnapLock, for instance, offers WORM (Write Once Read Many) capabilities, ensuring data immutability for regulatory purposes. Additionally, FPolicy and third-party integrations allow for real-time monitoring and audit of data access, ensuring that data usage aligns with compliance standards.
73. What is NetApp Element Software?
Ans:
Element Software is the OS behind NetApp’s HCI and SolidFire all-flash storage. It offers features like scale-out architecture, guaranteed performance, automated data lifecycle management, and robust data protection. Its API-first approach ensures easy automation and integration with third-party systems.
74. What is ONTAP Select’s role in disaster recovery?
Ans:
ONTAP Select, being a software-defined version of ONTAP, can be deployed on commodity servers in secondary or tertiary locations, acting as a DR target. With SnapMirror replication, data can be efficiently replicated from primary ONTAP systems to ONTAP Select instances, ensuring data availability even if the primary site is compromised.
75. How does NetApp integrate with major public cloud providers?
Ans:
NetApp has partnerships and integrations with major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Solutions like Cloud Volumes ONTAP are available natively in these cloud marketplaces. These integrations allow businesses to run their applications seamlessly across hybrid environments, taking advantage of NetApp’s data services irrespective of where the data resides.
76. How does NetApp address the challenge of data silos in modern organizations?
Ans:
NetApp addresses data silos through its Data Fabric architecture. By providing a unified data management solution across different environments – on-premises, edge, and various clouds – Data Fabric allows data to flow seamlessly where it’s needed. This helps businesses break down data silos, enabling integrated analytics, better decision-making, and streamlined operations.
77. What is the role of NetApp Astra in the context of Kubernetes?
Ans:
NetApp Astra is a managed application data service designed for Kubernetes workloads. It offers capabilities like data protection, disaster recovery, and migration for applications running in Kubernetes. With Astra, organizations can manage, protect, and move their application data across on-premises and cloud environments, ensuring that Kubernetes-based applications remain resilient and portable.
78. What is the significance of the AFF (All Flash FAS) in NetApp’s portfolio?
Ans:
The AFF series represents NetApp’s all-flash storage systems, optimized for low latency, high IOPS, and responsiveness. These systems are designed for workloads that require high performance like AI, ML, real-time analytics, and critical databases. With ONTAP’s data management capabilities, AFF systems not only deliver speed but also efficiency, security, and integration with hybrid multi-cloud architectures.
79. How does NetApp assist businesses in achieving a zero RPO (Recovery Point Objective)?
Ans:
NetApp’s MetroCluster provides synchronous replication between two data storage systems, ensuring real-time mirroring of data. In the event of a system or site failure, MetroCluster allows for immediate failover with no data loss, effectively offering a zero RPO. This ensures business continuity and protection against unplanned outages.
80. What is the concept of FabricPool in NetApp systems?
Ans:
FabricPool is a NetApp technology that automates the tiering of data between high-performance SSDs and lower-cost object storage, whether on-premises (like StorageGRID) or in the cloud. Inactive (cold) data is transparently moved to the object storage tier, while hot data remains on the performance tier. This automated tiering optimizes storage costs without compromising data availability.
81. How does NetApp’s “Unified Manager” aid in storage management?
Ans:
NetApp’s Unified Manager is a centralized management tool for ONTAP systems, providing insights, alerts, and automation capabilities. It offers a single-pane view of health, capacity, and performance metrics across clusters. With Unified Manager, administrators can monitor trends, receive proactive alerts, and automate common tasks, thus simplifying storage management.
82. What are the key features of NetApp’s SANtricity software?
Ans:
Performance Efficiency: Optimized for high IOPS and bandwidth.
Data Protection: Supports various RAID levels, including Dynamic Disk Pools.
Synchronous and Asynchronous Replication: Ensures data availability and disaster recovery.
Real-time Analytics: Provides insights into performance and system health.
83. How does NetApp’s SnapCenter Software streamline data protection?
Ans:
apCenter provides a centralized platform for application-consistent data protection and clone management. It integrates with major databases, virtualized environments, and applications. With SnapCenter, businesses can automate backup, restore, and cloning operations, ensuring that applications are protected, recoverable, and easily replicable for test/dev purposes.
84. Can you elaborate on NetApp’s approach to NVMe technology?
Ans:
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory express) is a protocol optimized for NAND flash and next-gen solid-state storage technologies. NetApp has incorporated NVMe in its AFF systems to deliver ultra-low latency and high throughput. Additionally, with ONTAP’s NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) support, users can extend the benefits of NVMe across the data center network, ensuring end-to-end performance optimization.
85. How does NetApp Insight help in monitoring and optimization?
Ans:
Real-time Monitoring: Provides real-time insights into data storage performance and health.
Predictive Analytics: Forecasts potential storage issues and capacity needs using analytics and machine learning.
Performance Optimization: Offers suggestions and best practices to optimize system performance.
86. What is NetApp’s approach to AI-driven data management?
Ans:
Automated Infrastructure Optimisation: The use of artificial intelligence to optimise data storage and resource allocation. AI identifies and prevents possible storage difficulties with predictive maintenance. AI tools for real-time threat detection provide enhanced security.
Automated Data Handling and Insights: Data management tasks that are automated and important insights extracted from data.
87. Can you elaborate on NetApp’s IoT solutions and how they facilitate edge computing?
Ans:
NetApp’s approach to IoT focuses on data’s lifecycle – from the edge, where it’s generated, to the core data centers and clouds, where it’s analyzed and stored. They provide solutions for rapid data ingestion from IoT devices, efficient data transport to the core or cloud, and robust analytics capabilities. ONTAP data management capabilities guarantee that data can be processed and analysed wherever it’s most appropriate, and NetApp’s StorageGRID enables distributed data storage, which is crucial for edge deployments.
88. What is the significance of NetApp’s acquisition of Spot.io?
Ans:
With the acquisition of Spot.io, NetApp bolstered its cloud optimization capabilities. Spot.io provides AI-driven cloud infrastructure optimization, allowing businesses to optimize their cloud costs by automating the selection of the most cost-effective compute and storage resources. This complements NetApp’s data fabric strategy, ensuring that data not only moves seamlessly across the hybrid cloud but also resides in the most cost-effective location.
89. How does NetApp support containerized workloads?
Ans:
NetApp recognizes the increasing adoption of containers in modern IT deployments. With the Trident integration, NetApp facilitates persistent storage provisioning for containerized workloads running in Kubernetes and OpenShift environments. This ensures that stateful applications running in containers have reliable and efficient data storage. Additionally, the Astra platform manages, protects, and migrates data within Kubernetes applications, further enhancing container support.
90. What data migration tools does NetApp offer for transitioning from other storage solutions?
Ans:
Data Fabric: Seamlessly moves data across diverse environments.
Cloud Sync: Safely transfers data between on-premises and cloud.
SnapMirror: Facilitates rapid data replication and migration.
OnCommand Tools: Includes System Manager and Unified Manager for centralized storage configuration and management.
91. How does NetApp address storage for video surveillance data?
Ans:
Video data requires high bandwidth and large storage capacities. NetApp’s E-Series, tailored for big data and high content repositories, is ideal for video surveillance storage. Its high throughput and dense capacity, combined with SANtricity software, ensure reliable and efficient video data storage and retrieval.
92. How does NetApp facilitate digital learning and education sectors?
Ans:
For the education sector, data accessibility, security, and scalability are paramount. NetApp provides solutions tailored for educational institutions, supporting virtual learning environments, research data storage, and administrative data needs. Features like data deduplication, efficient snapshots, and hybrid-cloud integrations ensure that educational data is both secure and readily accessible.
93. What role does NetApp play in healthcare data management?
Ans:
In healthcare, data integrity and availability are crucial. NetApp’s solutions cater to Electronic Health Records (EHR) storage, medical imaging data, and research datasets. With capabilities like MetroCluster for high availability, SnapLock for data immutability, and robust encryption, NetApp ensures that healthcare data is both compliant with regulations and always available.
94. How does NetApp’s Storage as a Service (STaaS) model work?
Ans:
NetApp’s STaaS model offers storage infrastructure on a subscription basis. Instead of significant capital expenditure on storage hardware, organizations can scale their storage needs flexibly, paying only for what they use. This model, combined with NetApp’s data management capabilities, ensures that businesses get top-tier storage solutions without the associated upfront costs.
95. How does NetApp’s “Data Visionary” concept align with its product and service offerings?
Ans:
NetApp’s “Data Visionary” concept encapsulates the idea that in today’s digital era, leveraging data effectively is crucial for innovation and transformation. This vision goes beyond just storage; it’s about harnessing the power of data to make informed decisions, drive efficiencies, and innovate.